Dodge Caliber. Manual - part 22
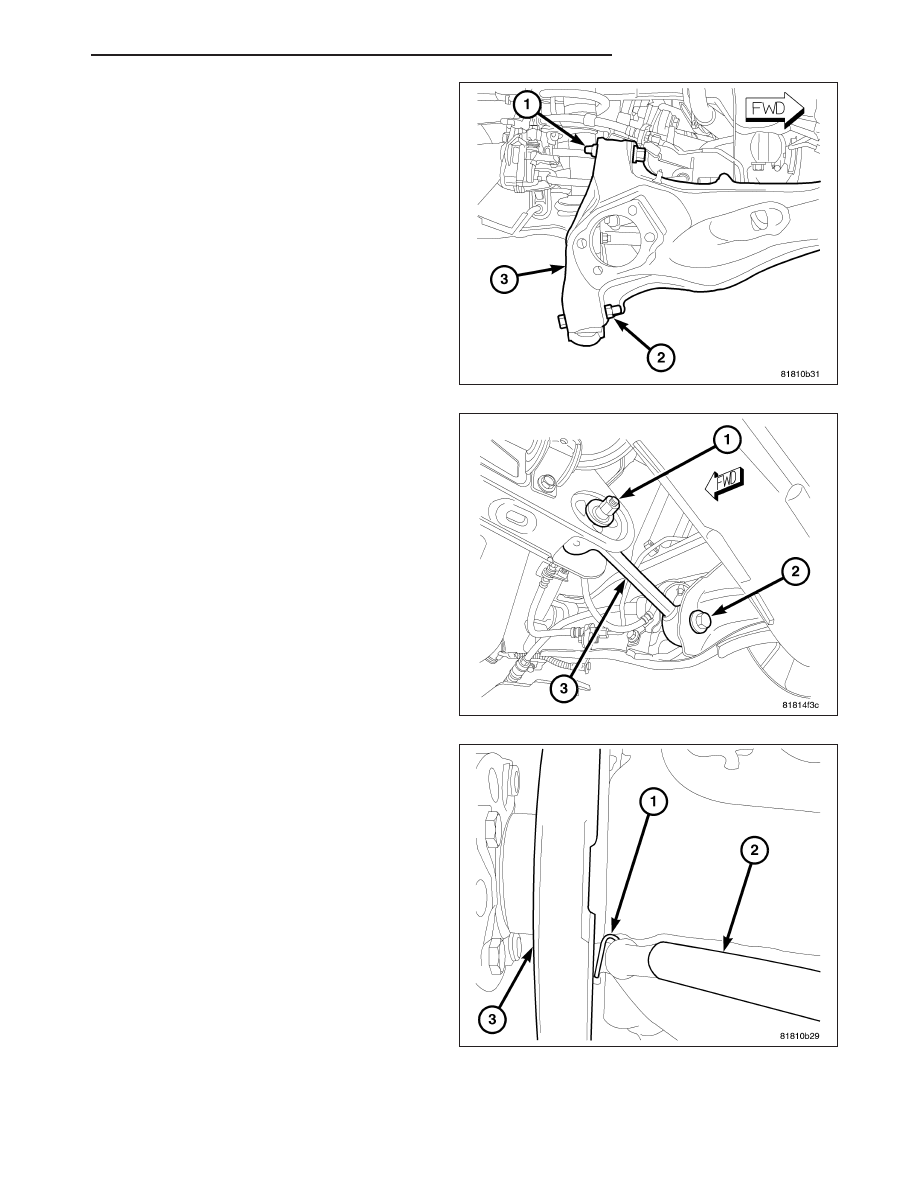
2. Position the upper control arm on the trailing link
(3) and install the bolt and nut (1) securing the arm
to the link. Tighten the mounting bolt nut to 95 N·m
(70 ft. lbs.).
3. Position the lower control arm on the trailing link
(3) and install the bolt and nut (2) securing the arm
to the link. Tighten the mounting bolt nut to 95 N·m
(70 ft. lbs.).
4. Install the bolt (2) securing the toe link to the trail-
ing link. To install the bolt it may be necessary to
flex the trailing link body mount bushing inward or
outward using an appropriate prying tool. Tighten
the mounting bolt to 95 N·m (70 ft. lbs.).
5. Insert the parking brake cable through the trailing
link from the inboard side.
6. Slide the parking brake cable (2) into the brake
support plate (3) with parking brake shoes.
7. Install the hair pin (1) securing the parking brake
cable (2) to the brake support plate (3).
PM
REAR SUSPENSION
2 - 53