DAF XF105. Manual - part 90
1
©
200528
2-9
Description of components
DMCI ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
XF105 series
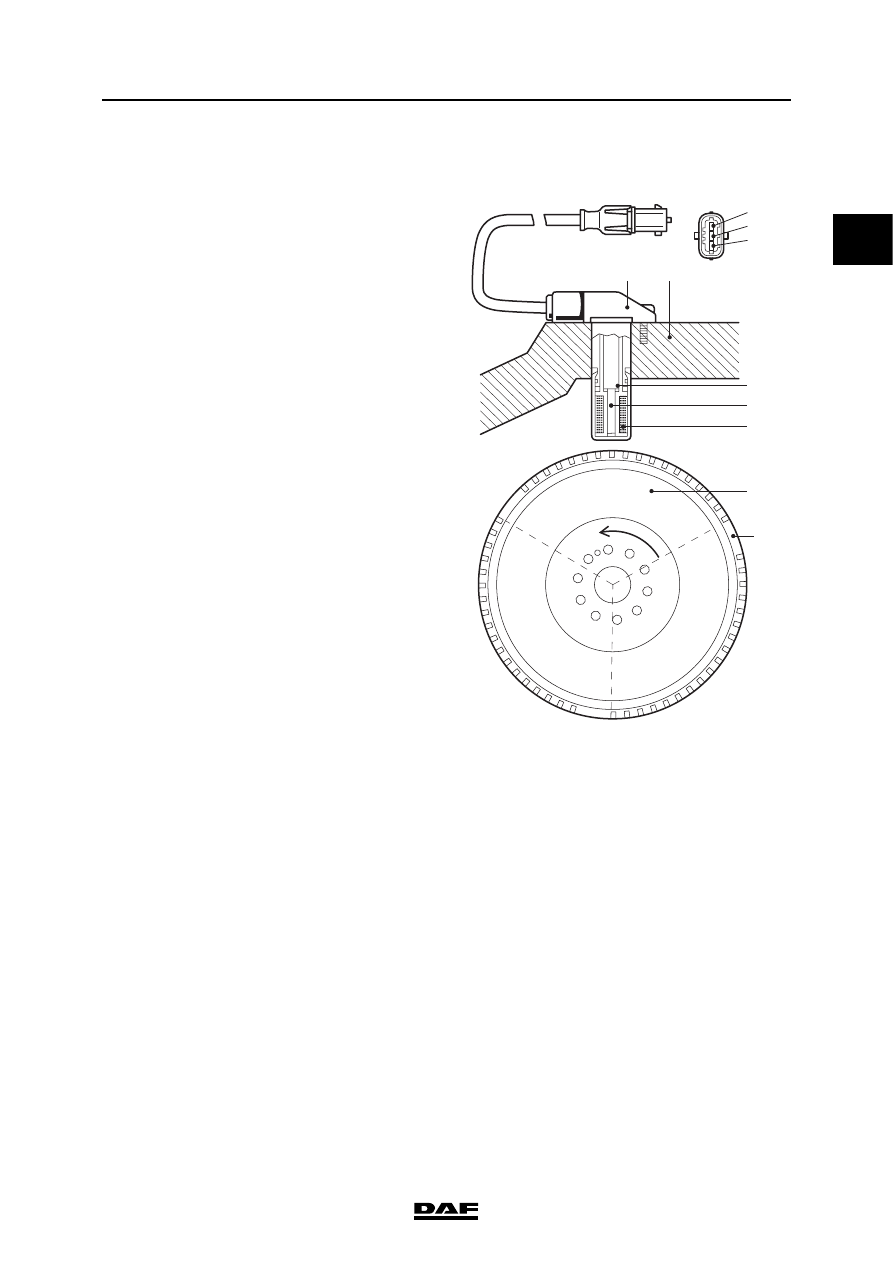
2.8 CRANKSHAFT SENSOR
The crankshaft sensor (F552) registers engine
speed and is used to determine the injection
timing. The crankshaft sensor is responsible,
together with the camshaft sensor, for
synchronisation when starting the engine. If there
is no camshaft signal, the crankshaft signal is
used for cylinder detection.
The crankshaft sensor (A) is mounted on the
flywheel housing (B). It is an inductive sensor and
consists of a magnet (C), a metal core (D) and a
coil (E). Inductive means that the sensor can
generate an alternating voltage signal
independently by means of a changing magnetic
field. The pattern of holes in the flywheel (F)
means that the sensor can generate a specific
alternating signal. The pattern consists of 3
segments each with 18 holes and an area with
2 holes missing (G). Each segment is used for
calculations on two specific cylinders (1/6, 2/5
and 3/4).
The sensor has 3 connections. Pins 1 and 2 are
responsible for the signal. Pin 2 is the signal
connection and pin 1 is the earth connection. Pin
3 is connected to the shield around the signal
wires and to the earth connection (pin 1). This
prevents the engine speed signal being affected
by signals from outside.
1
18
I400731
1
2
3
A
B
N
S
D
C
E
F
G
1
Electrical connection, earth
2
Electrical connection, signal
3
Electrical connection, shield
A
Crankshaft sensor
B
Flywheel housing
C
Magnet
D
Metal core
E
Coil
F
Flywheel
G
Hole pattern