DAF XF105. Manual - part 88
1
©
200528
2-1
Description of components
DMCI ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
XF105 series
2. DESCRIPTION OF COMPONENTS
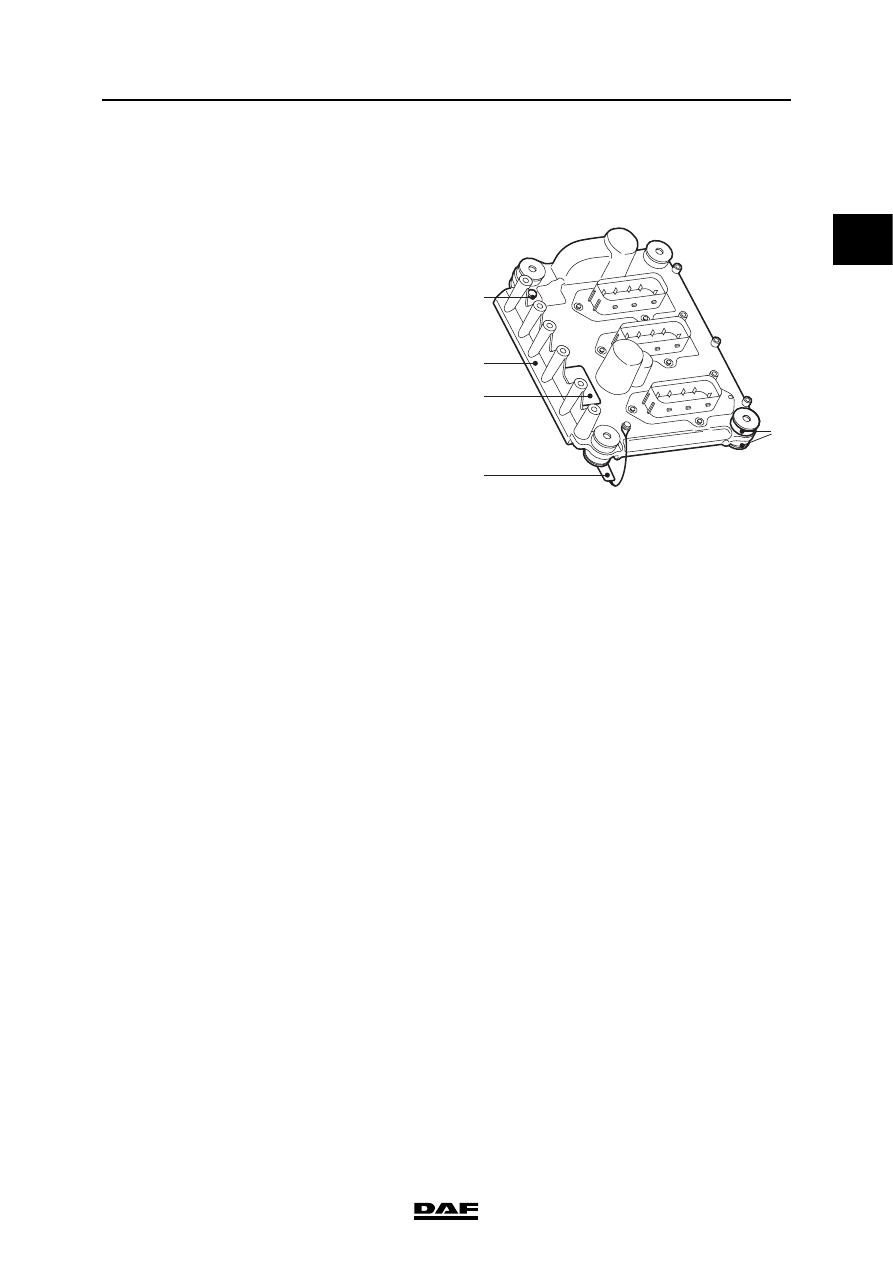
2.1 DMCI ELECTRONIC UNIT
The electronic unit is mounted on the cylinder
block using rubber insulating bushes (3). The
electronic unit has three 62-pin connectors. Input
signals from various sensors are continuously
processed and compared with data stored in
various maps (tables) in the electronic unit.
Actuators are energised on the basis of the
signals received and the maps.
The housing (1) of the electronic unit is directly
connected to the engine block by an earth cable
(2). This earth connection is required because of
internal components which protect against radio
waves from outside.
The electronic unit incorporates an atmospheric
pressure sensor and a temperature sensor.
There is an air vent (4) for the atmospheric
pressure sensor in the housing of the electronic
unit.
An identification sticker (5) is attached to the
electronic unit.
The effect of atmospheric pressure on the
system:
-
the quantity of fuel injected when driving at
high altitudes (low air pressure).
If atmospheric pressure is low (in mountainous
areas), the air is thinner. When the air is thinner it
has a low density. The electronic unit uses this
information to control the turbocharger pressure
and adjust the quantity of fuel to be injected.
The effect of the internal temperature sensor
on the system:
-
none.
The internal temperature sensor measures the
temperature of the electronic unit. If the
temperature becomes too high, a fault code is
stored. The system does not take any further
action on the basis of this information.
Calibration
The performance of pump units and injectors may
differ slightly from one another as a result of small
production tolerances. These small production
differences are compensated for during
production by means of calibration in order to
optimise the engine output, exhaust gas
emissions and handling characteristics. A
calibration code is used to program the pump
units and injectors into the electronic unit
individually. The electronic unit modifies the
control of the pump units and injectors on the
basis of these calibration codes.
i400785
1
5
2
3
4