Dodge Dakota (R1). Manual - part 716
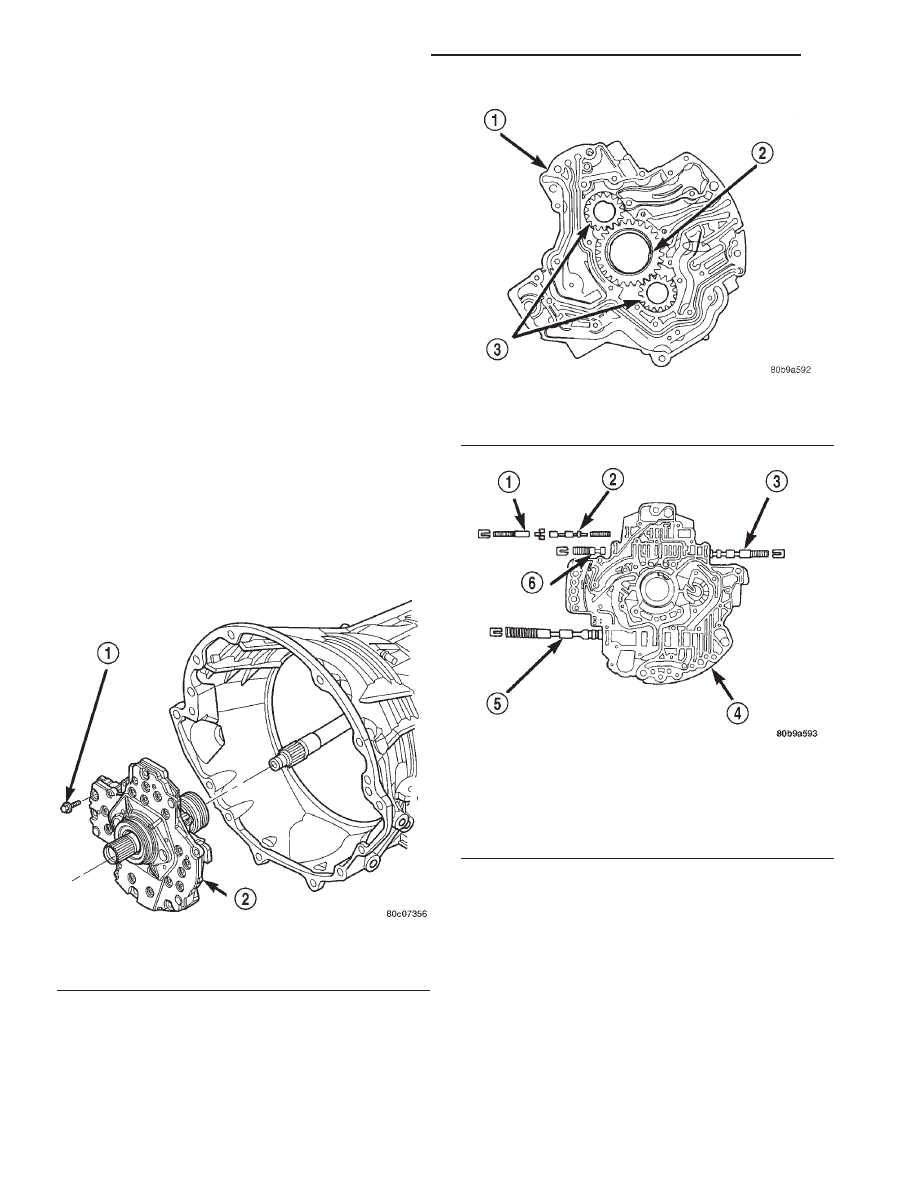
plate is directional and must be installed with the
flat side down.
(12) Install the low/reverse clutch pack snap-ring
(Fig. 82). The snap-ring is selectable and should be
chosen to give the correct clutch pack clearance.
(13) Measure the low/reverse clutch pack clearance
and adjust as necessary. The correct clutch clearance
is 1.14-1.91 mm (0.045-0.075 in.).
(14) Install the overrunning clutch into the low/re-
verse clutch retainer making sure that the index
splines are aligned with the retainer.
(15) Install the overrunning clutch inner snap-
ring.
OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The oil pump (Fig. 85) is located at the front of the
transmission inside the bell housing and behind the
transmission front cover. The oil pump consists of
two independent pumps (Fig. 86), a number of valves
(Fig. 87), a front seal (Fig. 88), and a bolt on reaction
shaft. The converter clutch switch and regulator
valves, pressure regulator valve, and converter pres-
sure limit valve are all located in the oil pump hous-
ing.
OPERATION
As the torque converter rotates, the converter hub
rotates the oil pump drive gear. As the drive gear
rotates both driven gears, the clearance between the
gear teeth increases in the crescent area, and creates
a suction at the inlet side of the pump. This suction
draws fluid through the pump inlet from the oil pan.
As the clearance between the gear teeth in the cres-
cent area decreases, it forces pressurized fluid into
the pump outlet and to the oil pump valves.
At low speeds, both pumps supply fluid to the
transmission. As the speed of the torque converter
increases,
the
pressure
output
of
both
pumps
increases until the primary pump pressure reaches
the point where it can close off the check valve
located between the two pumps. When the check
valve is closed, the secondary pump is shut down and
the primary pump supplies all the fluid to the trans-
mission.
Fig. 85 Oil Pump
1 - OIL PUMP TO CASE BOLT (6)
2 - OIL PUMP
Fig. 86 Oil Pump Gears
1 - PUMP BODY
2 - DRIVE GEAR
3 - DRIVEN GEARS
Fig. 87 Oil Pump Valves
1 - TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR VALVE
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH CONTROL VALVE
3 - TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH SWITCH VALVE
4 - PUMP COVER
5 - PRESSURE REGULATOR VALVE
6 - TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH LIMIT VALVE
21 - 508
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE
AN
LOW/REVERSE CLUTCH (Continued)