Dodge Dakota (R1). Manual - part 209
PINION DEPTH MEASUREMENT
Measurements are taken with pinion bearing cups
and pinion bearings installed in the housing. Take
measurements with Pinion Gauge Set and Dial Indi-
cator C-3339 (Fig. 7).
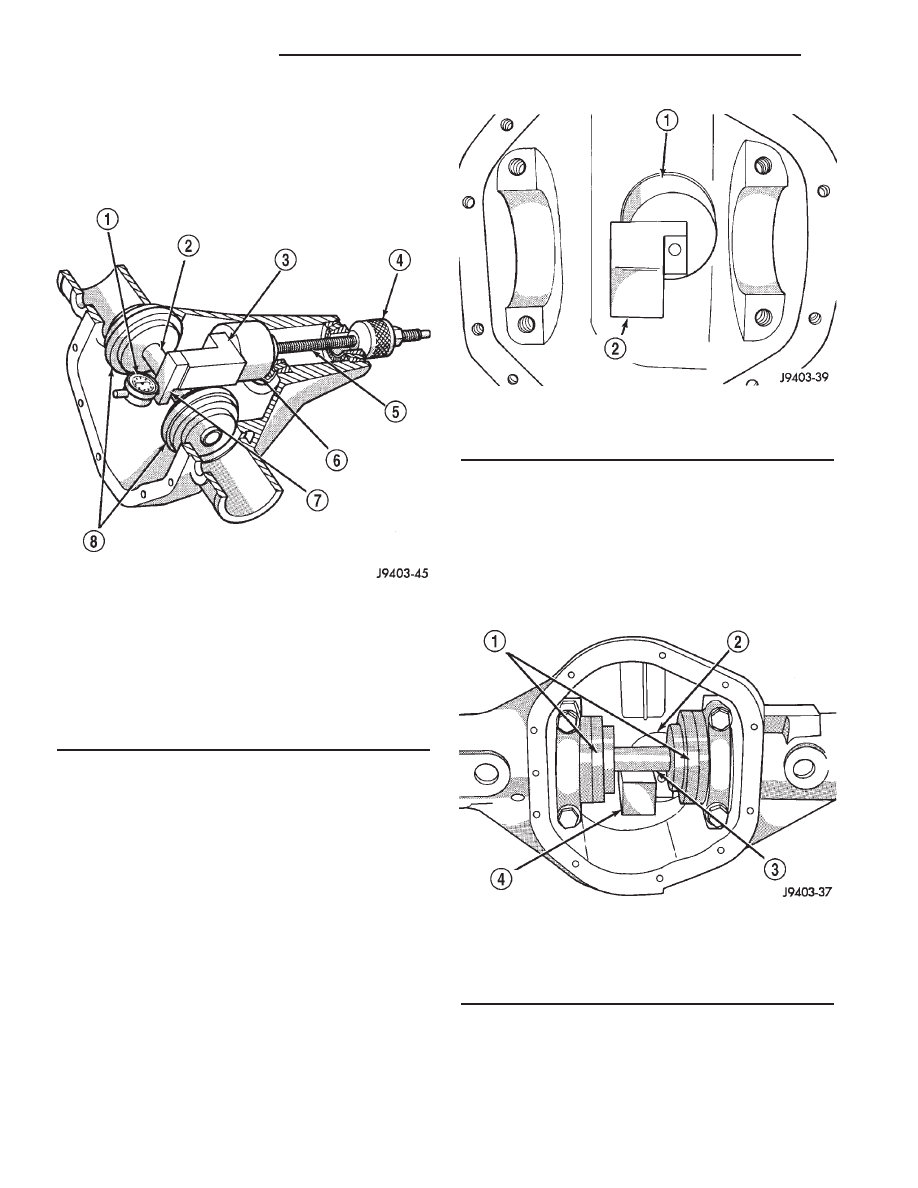
(1) Assemble Pinion Height Block 6739, Pinion
Block 8540 and rear pinion bearing onto Screw 6741
(Fig. 7).
(2) Insert assembled height gauge components,
rear bearing and screw into housing through pinion
bearing cups (Fig. 8).
(3) Install front pinion bearing and Cone-Nut 6740
hand tight (Fig. 7).
(4) Place Arbor Disc 8541 on Arbor D-115-3 in posi-
tion in the housing side bearing cradles (Fig. 9).
Install differential bearing caps on arbor discs and
tighten cap bolts to 41 N·m (30 ft. lbs.).
NOTE: Arbor Discs 8541 has different step diame-
ters to fit other axles. Choose proper step for axle
being serviced.
Fig. 7 Pinion Depth Gauge Tools
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - ARBOR
3 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
4 - CONE
5 - SCREW
6 - PINION BLOCK
7 - SCOOTER BLOCK
8 - ARBOR DISC
Fig. 8 Pinion Height Block
1 - PINION BLOCK
2 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
Fig. 9 Gauge Tools In Housing
1 - ARBOR DISC
2 - PINION BLOCK
3 - ARBOR
4 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
3 - 54
REAR AXLE - 8 1/4
AN
REAR AXLE - 8 1/4 (Continued)