Content .. 1247 1248 1249 1250 ..
Nissan Juke F15. Manual - part 1249
TM-186
< SYSTEM DESCRIPTION >
[CVT: RE0F10B]
SYSTEM
FAIL-SAFE
If CAN communication malfunction occurs between TCM and the multi display unit, the mode when the mal-
function occurs is maintained for approximately 30 seconds and the mode is changed to NORMAL mode
when the accelerator pedal is released.
SHIFT LOCK SYSTEM
SHIFT LOCK SYSTEM : System Description
INFOID:0000000012200895
• The shift lock is the mechanism provided to prevent quick start of a vehicle by incorrect operation of a drive
when the selector lever is in P position.
• Selector lever can be shifted from the P position to another position when the following conditions are satis-
fied.
- Ignition switch is ON.
- Stop lamp switch ON (brake pedal is depressed)
- Press the selector button.
SHIFT LOCK OPERATION AT P POSITION
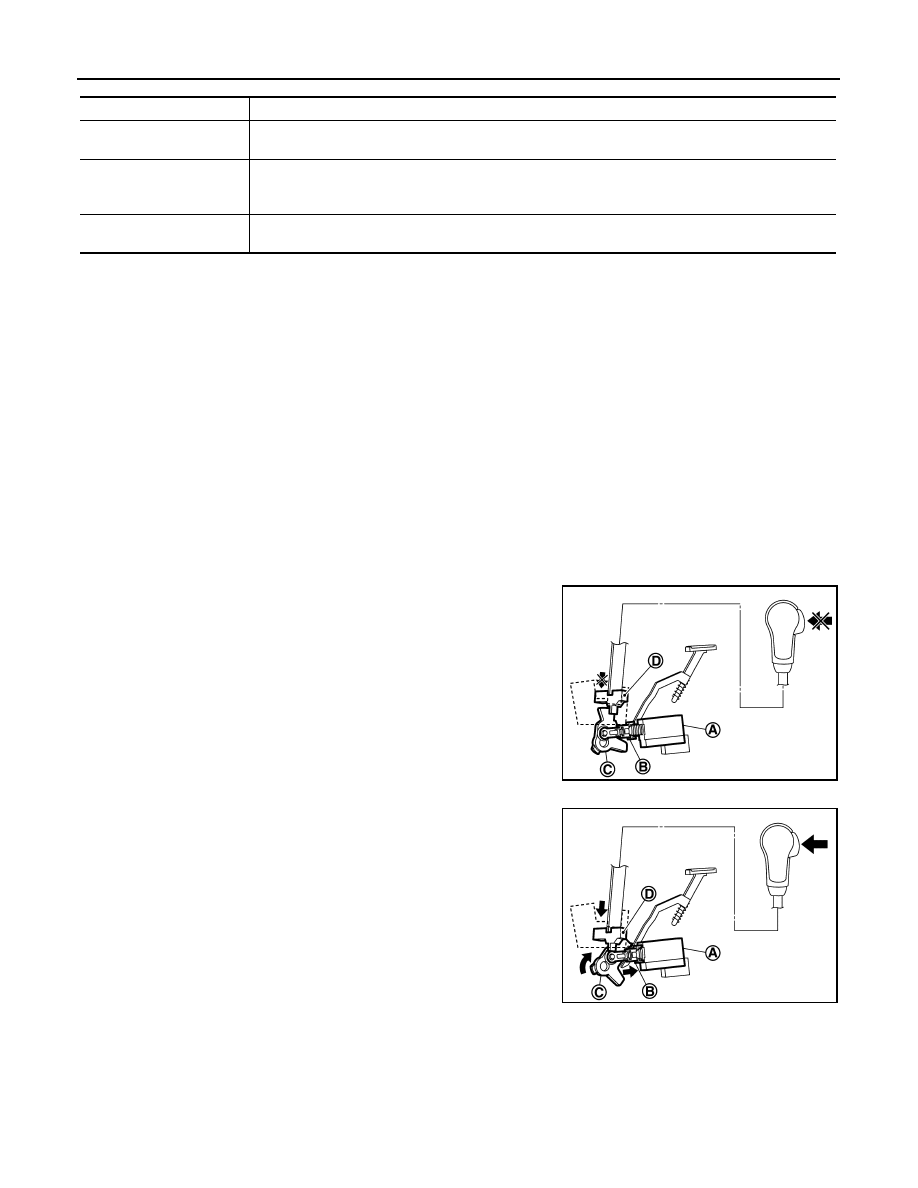
When brake pedal is not depressed (no selector operation allowed)
When the brake pedal is not depressed with the ignition switch ON,
the shift lock solenoid (A) is OFF (not energized) and the solenoid
rod (B) is extended with spring.
The connecting lock lever (C) is located at the position shown in the
figure when the solenoid rod is extended. It prevents the movement
of the detent rod (D). The selector lever cannot be shifted from the P
position for this reason.
When brake pedal is depressed (selector lever operation allowed)
The shift lock solenoid (A) is turned ON (energized) when the brake
pedal is depressed with the ignition switch ON. The solenoid rod (B)
is compressed with the electromagnetic force. The connecting lock
lever (C) rotates when the solenoid rod is compressed. Therefore,
the detent rod (D) can be moved. The selector lever can be shifted to
other positions for this reason.
P POSITION HOLD MECHANISM (IGNITION SWITCH LOCK)
Control mode
Control
NORMAL mode
Driving mode that automatically selects the shift schedule considering the balance of fuel economy and
driving performance based on the driving condition and driving trend.
SPORT mode
Keeps high engine speed and provides direct feel and acceleration performance suitable for driving on
winding road. This driving mode also provides a rhythmical feel obtained by A/T like shifting, and pro-
duces sporty driving.
ECO mode
Driving mode that selects the shift schedule with priority on fuel economy which gives low engine revo-
lution.
JSDIA2338ZZ
JSDIA2339ZZ