Mitsubishi Outlander (2013+). Manual - part 64
CONSTRUCTION DIAGRAM
ACTIVE STABILITY CONTROL SYSTEM (ASC)
35C-9
ASC OPERATION DISPLAY AND LAMP,
ASC WARNING DISPLAY AND LAMP, ASC
OFF lamp
The ASC system illuminates or flashes the ASC
operation display and lamp, ASC warning display
and lamp or ASC OFF lamp in the following opera-
tion patterns, and informs the driver of the ASC sys-
tem status.
ASC operation display and lamp
• Flashes in 2 Hz (display)/4 Hz (lamp) during the
ASC control.
ASC warning display and lamp
• Turns ON when the system malfunction occurs.
ASC OFF lamp
• ASC-ECU detects the overheat of the brake
pads. When the brake TCL control is prohibited,
the ASC OFF lamp flashes in approximately 2
Hz.
ASC operation display and lamp, ASC warning display and lamp, ASC OFF lamp illumination and
flashing patterns
NOTE:
*
Illuminates if the TCL function or stability control function is defective when the HSA function is
defective. (HSA control prohibited)
ASC-ECU
M2357000100515
This ECU incorporates the ABS function, EBD func-
tion, HSA function, stability control function and TCL
function, brake assist control.
The hydraulic units of the ASC and TCL systems
employ the automatic pressurisation function. These
systems also incorporates G and yaw rate sensor
(integrated with ASC-ECU), steering wheel sensor,
and master cylinder pressure sensor (integrated with
hydraulic unit).
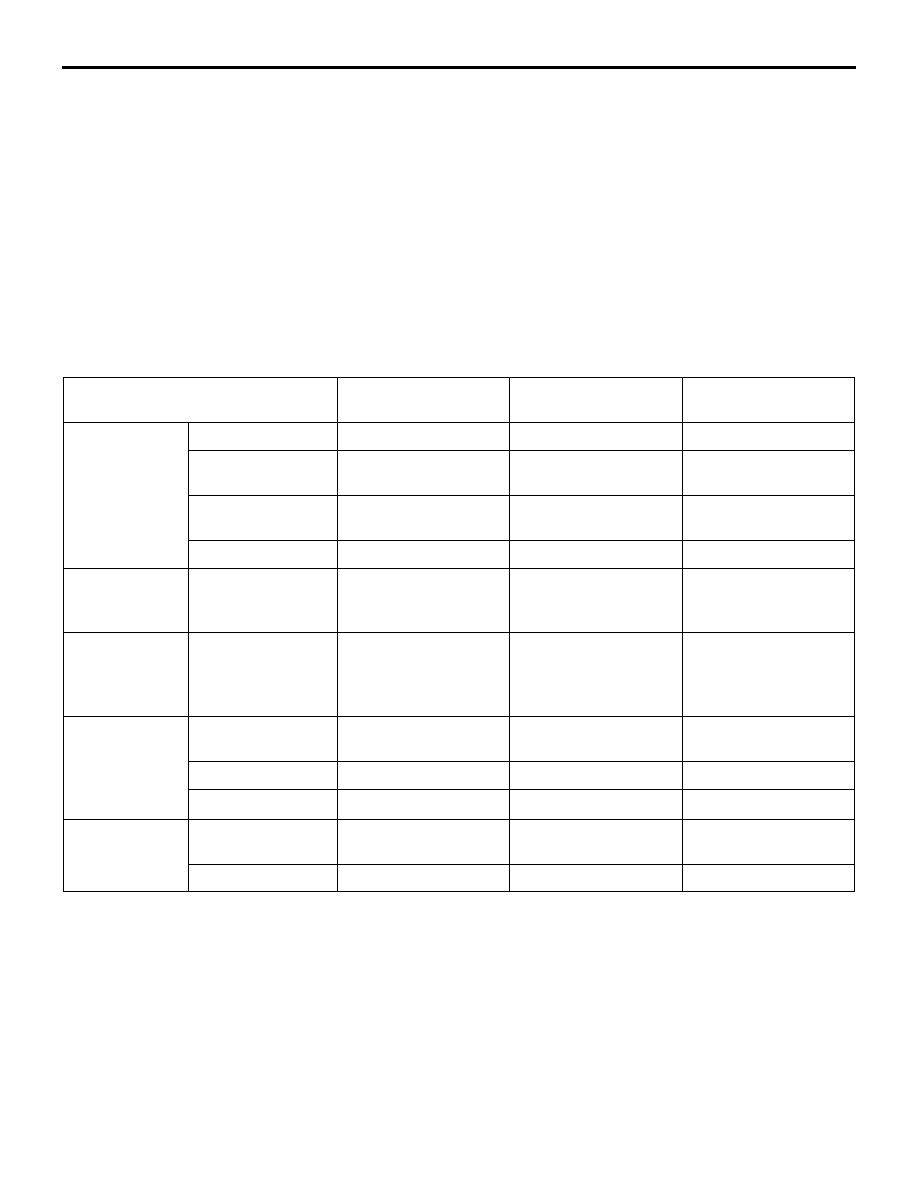
State
ASC operation
display and lamp
ASC warning display
and lamp
ASC OFF lamp
Normal
Normal
−
−
−
Stability control
operated
Flashing (display: 2
Hz, lamp: 4 Hz)
−
−
TCL operated
Flashing (display: 2
Hz, lamp: 4 Hz)
−
−
HSA operated
−
−
−
ASC is disabled
by ASC OFF
switch
ASC disabled
−
−
Illuminates
When the brake
pad
temperature is
high
ASC-ECU informs
the driver that the
brake TCL does
not function.
−
−
Flashing (2 Hz)
Abnormal
Stability control
malfunction
−
Illuminates
Illuminates
TCL malfunction
−
Illuminates
Illuminates
HSA malfunction
−
Illuminates
−
*
M.U.T.-III
connection
Actuator not
operated
−
−
−
Actuator operated
−
Illuminates
Illuminates