Mitsubishi Lancer Evolution 7. Manual - part 238
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -
Emission Control System
17-13
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) SYSTEM
GENERAL INFORMATION
The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system lowers
the nitrogen oxide (NOx) emission level. When the
air/fuel mixture combustion temperature is high,
a large quantity of nitrogen oxides (NOx) is
generated in the combustion chamber. Therefore,
this system recirculates part of emission gas from
the exhaust port of the cylinder head to the
combustion chamber through the intake manifold
to decrease the air/fuel mixture combustion
temperature, resulting in reduction of NOx.
The EGR flow rate is controlled by the EGR valve
so as not to decrease the driveability.
OPERATION
The EGR valve is being closed and does not
recirculate exhaust gases under one of the following
conditions. Otherwise, the EGR valve is opened
and recirculates exhaust gases.
D
The engine coolant temperature is low.
D
The engine is at idle.
D
The throttle valve is widely opened.
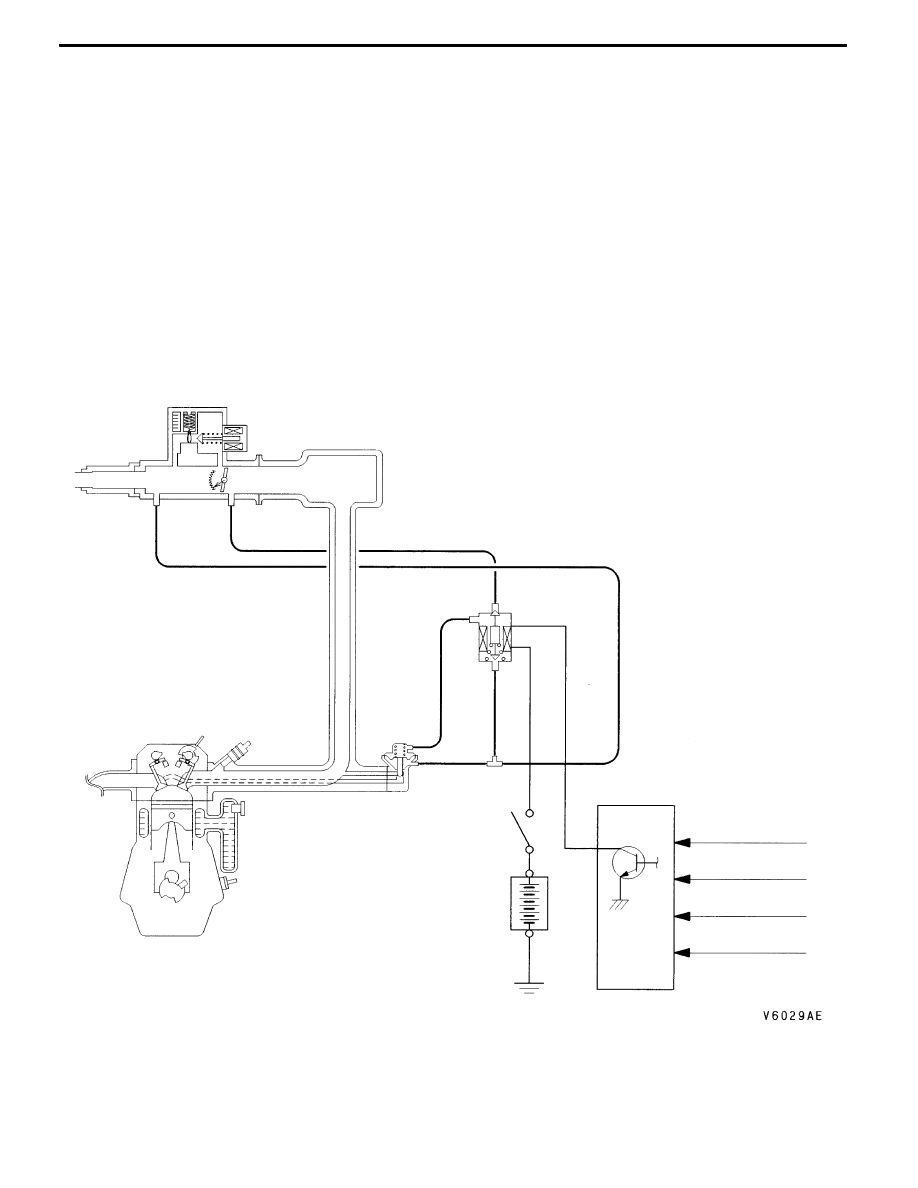
SYSTEM DIAGRAM
ON
Throttle body
EGR control
solenoid valve
Engine
control
relay
Battery
EGR valve
Crank angle sensor
Throttle position sensor
Engine-ECU
Engine coolant
temperature sensor
Air flow sensor