Jeep XJ. Manual - part 302
VALVE SEAT REFACING
(1) Install a pilot of the correct size in the valve
guide bore. Reface the valve seat to the specified
angle with a good dressing stone. Remove only
enough metal to provide a smooth finish.
(2) Use tapered stones to obtain the specified seat
width when required.
(3) Control valve seat runout to a maximum of
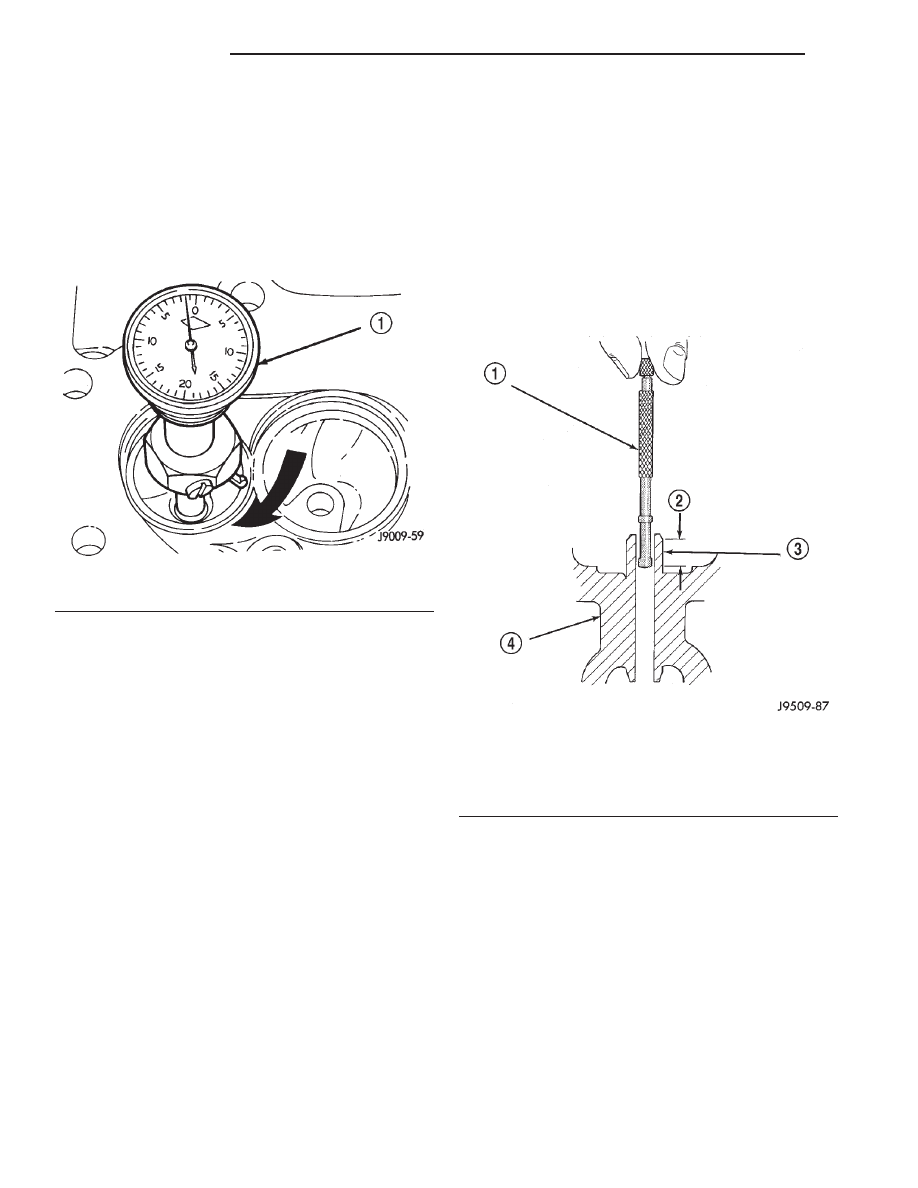
0.0635 mm (0.0025 in.) (Fig. 15).
VALVE STEM OIL SEAL REPLACEMENT
Valve stem oil seals are installed on each valve
stem to prevent rocker arm lubricating oil from
entering the combustion chamber through the valve
guide bores. One seal is marked INT (intake valve)
and the other is marked EXH (exhaust valve).
Replace the oil seals whenever valve service is per-
formed or if the seals have deteriorated.
VALVE GUIDES
The valve guides are an integral part of the engine
cylinder head and are not replaceable.
When the valve stem guide clearance is excessive,
the valve guide bores must be reamed oversize. Ser-
vice valves with oversize stems are available in 0.076
mm (0.003 inch) and 0.381 mm (0.015 inch) incre-
ments.
Corresponding oversize valve stem seals are also
available and must be used with valves having 0.381
mm (0.015 inch) oversize stems.
NOTE: If the valve guides are reamed oversize, the
valve seats must be ground to ensure that the valve
seat is concentric to the valve guide.
VALVE STEM-TO-GUIDE CLEARANCE
MEASUREMENT
Valve stem-to-guide clearance may be measured by
either of the following two methods.
PREFERRED METHOD
(1) Remove the valve from the head.
(2) Clean the valve stem guide bore with solvent
and a bristle brush.
(3) Insert a telescoping gauge into the valve stem
guide bore approximately 9.525 mm (.375 inch) from
the valve spring side of the head (Fig. 16).
(4) Remove and measure telescoping gauge with a
micrometer.
(5) Repeat the measurement with contacts length-
wise to engine cylinder head.
(6) Compare the crosswise to lengthwise measure-
ments to determine out-of-roundness. If the measure-
ments differ by more than 0.0635 mm (0.0025 in.),
ream the guide bore to accommodate an oversize
valve stem.
(7) Compare the measured valve guide bore diam-
eter with specifications (7.95-7.97 mm or 0.313-0.314
inch). If the measurement differs from specification
by more than 0.076 mm (0.003 inch), ream the guide
bore to accommodate an oversize valve stem.
Fig. 15 Measurement of Valve Seat Runout
1 – DIAL INDICATOR
Fig. 16 Measurement of Valve Guide Bore Diameter
1 – GAUGE
2 – 9.525 MM (3/8 INCH)
3 – VALVE STEM GUIDE
4 – CYLINDER HEAD
9 - 76
4.0L ENGINE
XJ
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)