Jeep Wrangler TJ. Manual - part 282
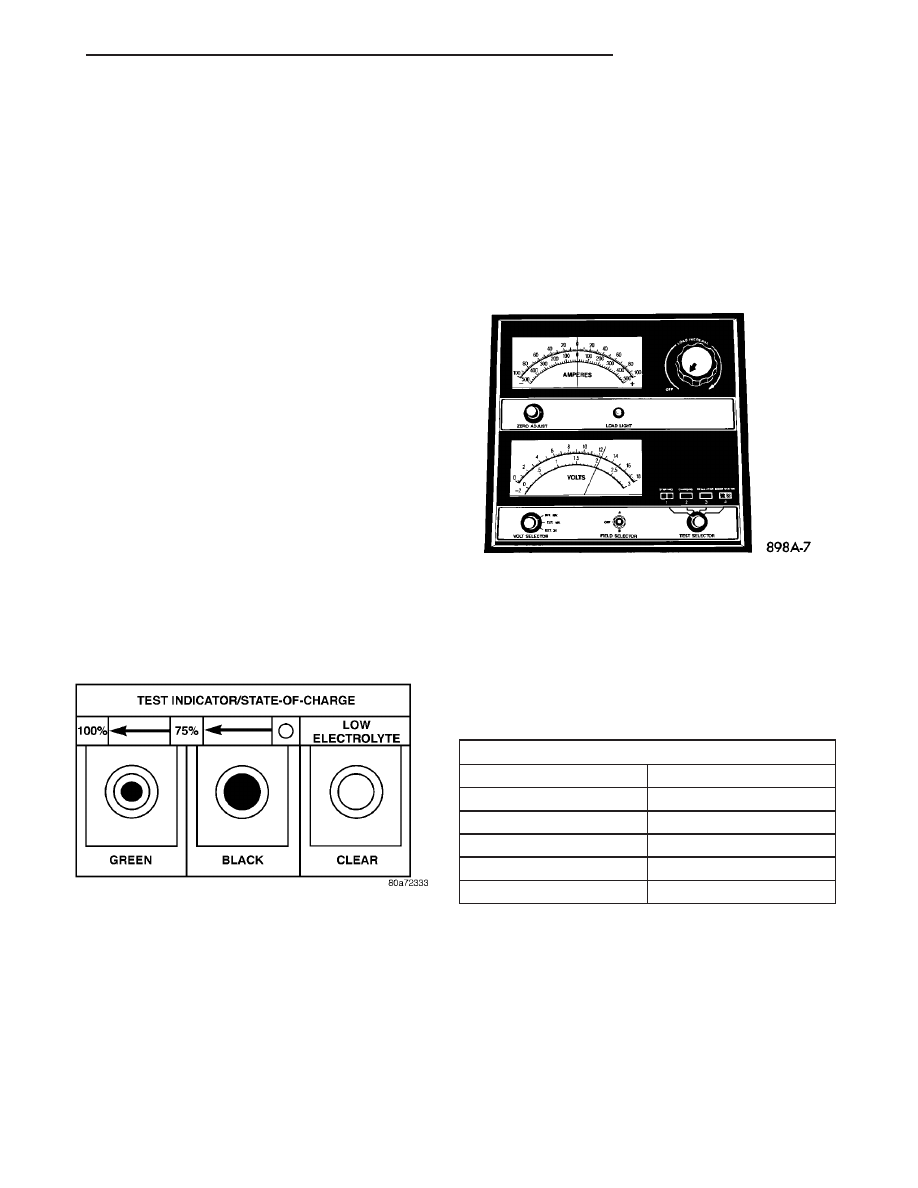
To read the built-in indicator, look into the sight
glass and note the color of the indication (Fig. 7). The
battery
condition
that
each
color
indicates
is
described in the following list:
• Green - Indicates 75% to 100% battery state-of-
charge. The battery is adequately charged for further
testing or return to service. If the starter will not
crank for a minimum of fifteen seconds with a fully-
charged battery, the battery must be load tested.
Refer to Standard Procedures for the proper battery
load test procedures.
• Black or Dark - Indicates 0% to 75% battery
state-of-charge. The battery is inadequately charged
and must be charged until a green indication is visi-
ble in the sight glass (12.4 volts or more), before the
battery is tested further or returned to service. Refer
to Standard Procedures for the proper battery charg-
ing procedures. Also refer to Diagnosis and Testing
for more information on the possible causes of the
discharged battery condition.
• Clear or Bright - Indicates a low battery elec-
trolyte level. The electrolyte level in the battery is
below the built-in indicator. A maintenance-free bat-
tery with non-removable cell caps must be replaced if
the electrolyte level is low. Water must be added to a
low-maintenance battery with removable cell caps
before it is charged. Refer to Standard Procedures for
the proper battery filling procedures. A low electro-
lyte level may be caused by an overcharging condi-
tion. Refer to Charging System for the proper
charging system diagnosis and testing procedures.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - OPEN-CIRCUIT
VOLTAGE TEST
A battery open-circuit voltage (no load) test will
show the approximate state-of-charge of a battery.
This test can be used in place of the hydrometer test
when a hydrometer is not available, or for mainte-
nance-free batteries with non-removable cell caps.
Before proceeding with this test, completely charge
the battery (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY
SYSTEM/BATTERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(1) Before measuring the open-circuit voltage, the
surface charge must be removed from the battery.
Turn on the headlamps for fifteen seconds, then
allow up to five minutes for the battery voltage to
stabilize.
(2) Disconnect and isolate both battery cables, neg-
ative cable first.
(3) Using a voltmeter connected to the battery
posts (see the instructions provided by the manufac-
turer of the voltmeter), measure the open-circuit volt-
age (Fig. 8).
See the Open-Circuit Voltage Table. This voltage
reading will indicate the battery state-of-charge, but
will not reveal its cranking capacity. If a battery has
an open-circuit voltage reading of 12.4 volts or
greater, it may be load tested to reveal its cranking
capacity (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYS-
TEM/BATTERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
OPEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE TABLE
Open Circuit Voltage
Charge Percentage
11.7 volts or less
0%
12.0 volts
25%
12.2 volts
50%
12.4 volts
75%
12.6 volts or more
100%
STANDARD PROCEDURE - IGNITION-OFF
DRAW TEST
The term Ignition-Off Draw (IOD) identifies a nor-
mal condition where power is being drained from the
battery with the ignition switch in the Off position. A
normal vehicle electrical system will draw from five
to thirty-five milliamperes (0.005 to 0.035 ampere)
with the ignition switch in the Off position, and all
non-ignition controlled circuits in proper working
order. Up to thirty-five milliamperes are needed to
enable the memory functions for the Powertrain Con-
Fig. 7 Built-In Indicator Sight Glass Chart
Fig. 8 Testing Open-Circuit Voltage - Typical
TJ
BATTERY SYSTEM
8F - 11
BATTERY (Continued)