Jeep Grand Cherokee WJ. Manual - part 312
CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
TEST
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
• Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing).
• Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket.
• Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss.
(1) Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the radiator cap.
(2) Start and operate the engine until it attains
normal operating temperature, then turn the engine
OFF.
(3) Remove the spark plugs.
(4) Remove the oil filler cap.
(5) Remove the air cleaner.
(6) Calibrate the tester according to the manufac-
turer’s instructions. The shop air source for testing
should maintain 483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1,379
kPa (200 psi) maximum and 552 kPa (80 psi) recom-
mended.
(7) Perform the test procedures on each cylinder
according to the tester manufacturer’s instructions.
While testing, listen for pressurized air escaping
through the throttle body, tailpipe and oil filler cap
opening. Check for bubbles in the radiator coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal,
with no more than 25% leakage.
FOR EXAMPLE: At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pres-
sure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be main-
tained in the cylinder.
Refer to the Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leak-
age Test Diagnosis chart.
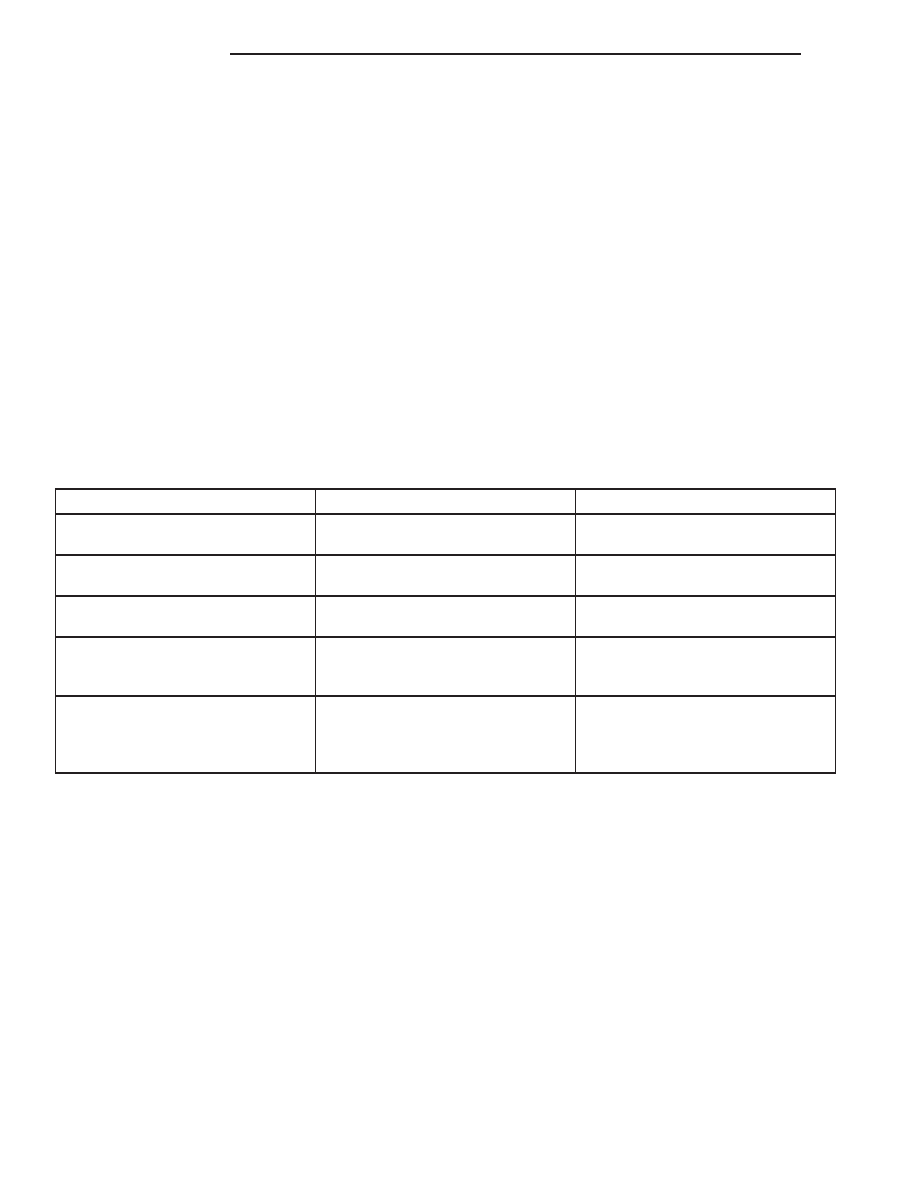
CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION
POSSIBLE CAUSE
CORRECTION
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
THROTTLE BODY
Intake valve bent, burnt, or not
seated properly
Inspect valve and valve seat.
Reface or replace, as necessary
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
TAILPIPE
Exhaust valve bent, burnt, or not
seated properly
Inspect valve and valve seat.
Reface or replace, as necessary
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
RADIATOR
Head gasket leaking or cracked
cylinder head or block
Remove cylinder head and inspect.
Replace defective part
MORE THAN 50% LEAKAGE
FROM ADJACENT CYLINDERS
Head gasket leaking or crack in
cylinder head or block between
adjacent cylinders
Remove cylinder head and inspect.
Replace gasket, head, or block as
necessary
MORE THAN 25% LEAKAGE AND
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH OIL
FILLER CAP OPENING ONLY
Stuck or broken piston rings;
cracked piston; worn rings and/or
cylinder wall
Inspect for broken rings or piston.
Measure ring gap and cylinder
diameter, taper and out-of-round.
Replace defective part as necessary
ENGINE OIL LEAK INSPECTION
Begin with a thorough visual inspection of the
engine, particularly at the area of the suspected leak.
If an oil leak source is not readily identifiable, the
following steps should be followed:
(1) Do not clean or degrease the engine at this
time because some solvents may cause rubber to
swell, temporarily stopping the leak.
(2) Add an oil soluble dye (use as recommended by
manufacturer). Start the engine and let idle for
approximately 15 minutes. Check the oil dipstick to
make sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated
with a bright yellow color under a black light.
(3) Using a black light, inspect the entire engine
for fluorescent dye, particularly at the suspected area
of oil leak. If the oil leak is found and identified,
repair per service manual instructions.
(4) If dye is not observed, drive the vehicle at var-
ious speeds for approximately 24km (15 miles), and
repeat inspection.
(4)
If the oil leak source is not positively
identified at this time, proceed with the air leak
detection test method.
Air Leak Detection Test Method
(1) Disconnect the breather cap to air cleaner hose
at the breather cap end. Cap or plug breather cap
nipple.
(2) Remove the PCV valve from the cylinder head
cover. Cap or plug the PCV valve grommet.
(3) Attach an air hose with pressure gauge and
regulator to the dipstick tube.
CAUTION: Do not subject the engine assembly to
more than 20.6 kpa (3 PSI) of test pressure.
9 - 14
4.0L ENGINE
WJ
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)