Honda Odyssey 2004. Manual - part 396
01
S0X4A00G10100000000FEAT20
Performance Test
21-60
Heating/Air Conditioning
A/C System Test
A
B
• Compressed air mixed with R-134a forms a
combustible vapor.
• The vapor can burn or explode causing serious
injury.
• Never use compressed air to pressure test
R-134a service equipment or vehicle air
conditioning systems.
• Air conditioning refrigerant or lubricant vapor
can irritate your eyes, nose, or throat.
• Be careful when connecting service equipment.
• Do not breathe refrigerant or vapor.
The performance test will help determine if the air
conditioner system is operating within specifications.
Use only service equipment that is U.L.-listed and is
certified to meet the requirements of SAE J2210 to
remove HFC-134a (R-134a) from the air conditioning
system.
If accidental system discharge occurs, ventilate work
area before resuming service.
R-134a service equipment or vehicle air conditioning
systems should not be pressure tested or leak tested
with compressed air.
Additional health and safety information may be
obtained from the refrigerant and lubricant
manufacturers.
1. Connect a R-134a refrigerant recovery/recycling/
charging station to the high-pressure service port
and the low-pressure service port, as shown,
following the equipment manufacturer’s
instructions.
2. Determine the relative humidity and air
temperature.
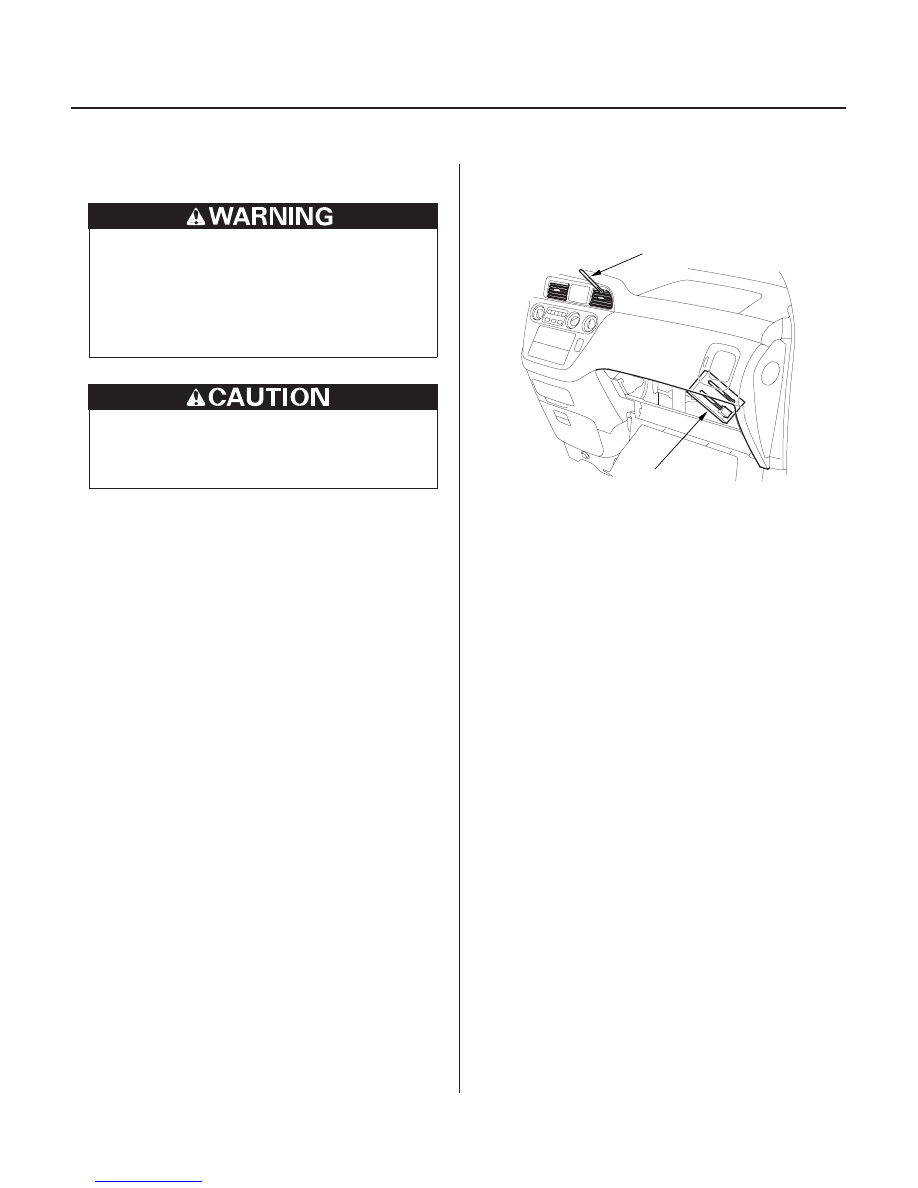
3. Remove the glove box stop, and let the glove box
hang down (see page 20-71).
4. Insert a thermometer (A) in the center vent.
5. Place a thermometer (B) near the blower unit.
6. Test conditions:
• Avoid direct sunlight.
• Open hood.
• Open front doors.
• Set the temperature control dial or button on
Max Cool (60°F or 18°C), the mode control switch
on Vent and the recirculation control switch on
Recirculate.
• Turn the A/C switch on and the fan switch on Max.
• Run the engine at 1,500 rpm.
• No driver or passengers in vehicle.
7. After running the air conditioning for 10 minutes
under the above test conditions, read the delivery
temperature from the thermometer in the center
vent, the intake temperature near the blower unit,
and the high and low system pressure from the A/C
gauges.
03/07/29 10:11:52 61S0X050_210_0061