DAF CF65, CF75, CF85 Series . Manual - part 896
6
CF65/75/85 series
Description of components
OPERATION OF BRAKE COMPONENTS
2-19
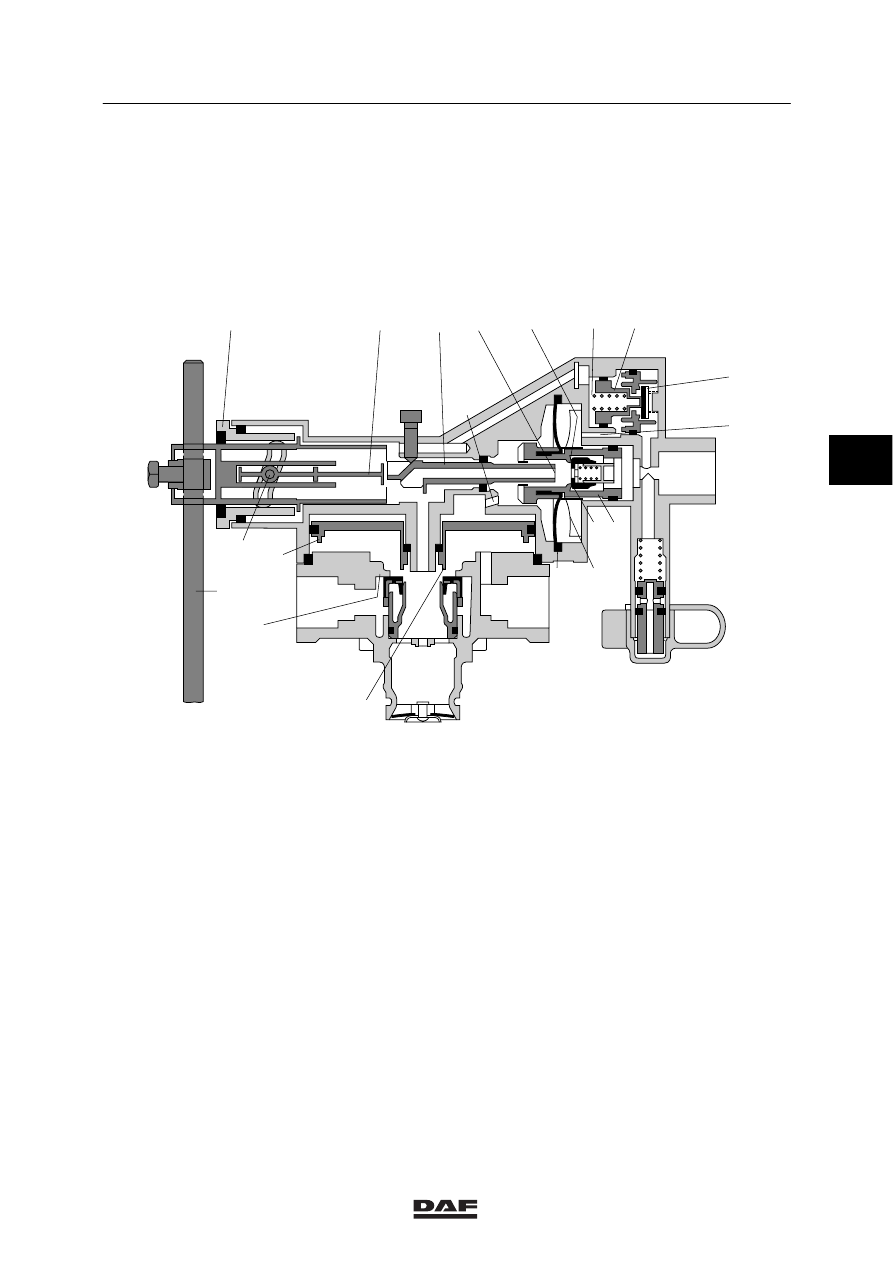
2.10 LOAD SENSING VALVE, LEAF SUSPENSION
Purpose
Automatic control of the brake force depends on
the deflection of the springs and therefore on
the loading condition of the vehicle. Thanks to
the integrated relay valve, the brake cylinders
are aerated and vented quickly.
3
2
1
4
E
C
C
F
D
A
G
B
a
n
o
m
d
g
q
j
i
f
e
l
k
p
h
c b
R600456
Operation
The control valve is attached to the chassis and
connected to the rear axle by means of a rod.
With unloaded vehicles, the distance between
the regulator and the axle is largest and the
lever (j) points fully downwards. When the
vehicle is loaded, this distance decreases and
the lever moves upwards, towards full load
position.
Pin ‘i’ rotates with the lever and moves to the
right via the control groove in bearing cover ‘p’
as a result. Rod ‘q’ brings the tappet (g) in a
position that corresponds with the loading
condition.
4
ᓻ 200324