Infiniti Q45 (FY33). Manual - part 387
SEL462W
6.
Touch “OK”.
7.
Carry out the next system setting or contact Communicator
Response Center and inform them that data has been updated
or IVCS unit has been replaced. For details, refer to EL-536.
NOTE: Whenever the phone number is updated or the IVCS
unit is replaced, the INFINITI Communicator system
automatically contacts the Communicator Response
Center the first time the vehicle is stared.
SEL466W
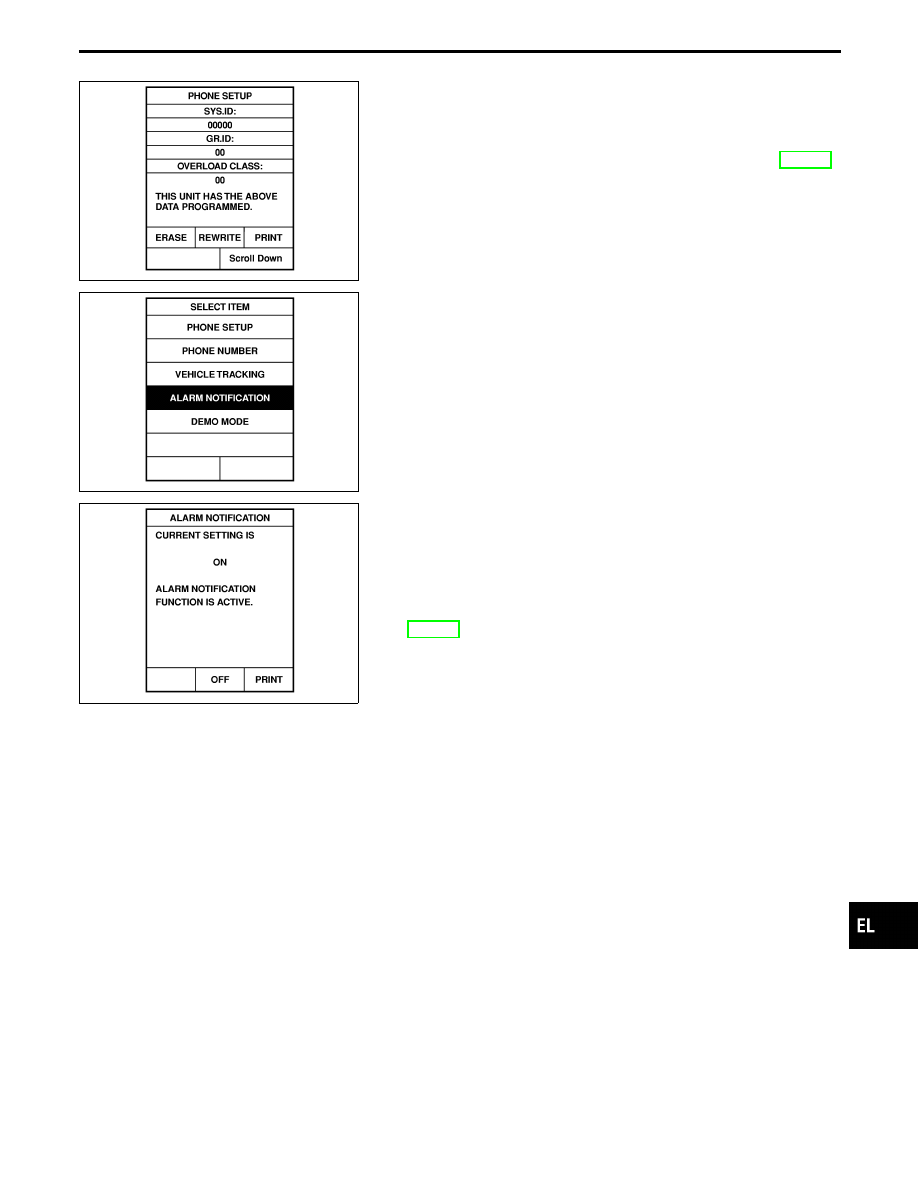
STOLEN VEHICLE TRACKING/ALARM NOTIFICATION
SETTING CHECK
1.
Touch “CONFIGURATION”.
2.
Touch “VEHICLE TRACKING” or “ALARM NOTIFICATION”.
SEL467W
3.
This function should always be “ON” (function activate.)
NOTE:
I
If either setting is “OFF”, contact the Communicator
Response Center at 1-888-427-4812 to verify the system
setting.
I
Whenever dialing the above number, information about
the vehicle is required by the operator. For details, refer to
EL-506.
GI
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
AT
PD
FA
RA
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
IDX
INFINITI COMMUNICATOR (IVCS)
System Setting (When IVCS unit is replaced)
(Cont’d)
EL-539