Dodge Dakota (R1). Manual - part 565
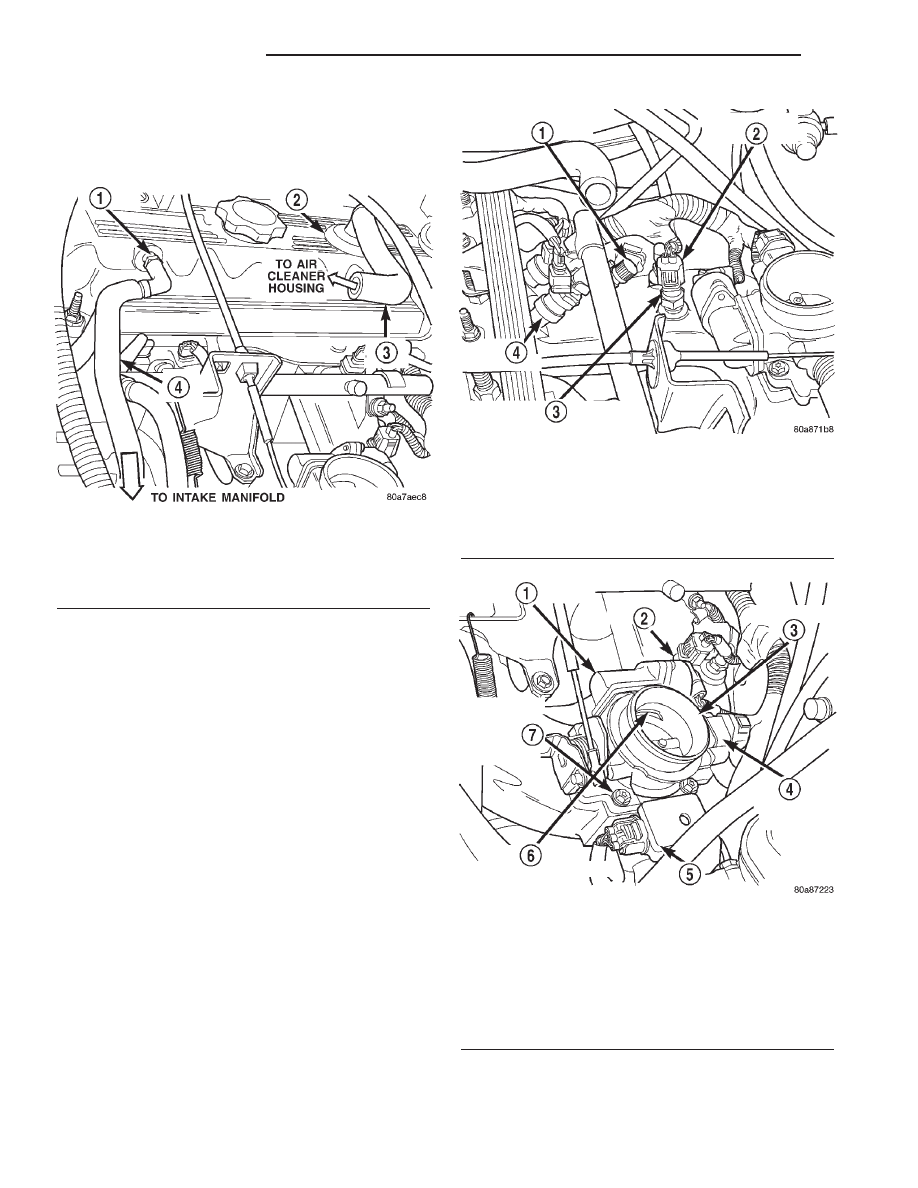
(8) Verify Crankcase Ventilation (CCV) system
operation. Verify CCV system hoses and fixed orifice
fitting are firmly connected (Fig. 16). Refer to 25,
Emission Control System for additional information.
(9) Inspect fuel tube quick-connect fitting-to-fuel
rail connections.
(10) Verify hose connections to all ports of vacuum
fittings on intake manifold are tight and not leaking.
(11) Inspect accelerator cable and throttle cable.
Check their connections to throttle arm of throttle
body for any binding or restrictions.
(12) If equipped with vacuum brake booster, verify
vacuum booster hose is firmly connected to fitting on
intake manifold. Also check connection to brake vac-
uum booster.
(13) Inspect air cleaner inlet and air cleaner ele-
ment for dirt or restrictions.
(14) Inspect radiator grille area, radiator fins and
air conditioning condenser for restrictions.
(15) Verify intake manifold air temperature sensor
wire connector is firmly connected to harness connec-
tor (Fig. 17).
(16) Verify MAP sensor electrical connector is
firmly connected to MAP sensor (Fig. 18). Also verify
rubber L-shaped fitting from MAP sensor to throttle
body is firmly connected.
(17) Verify fuel injector wire harness connectors
are firmly connected to injectors in the correct order.
Each harness connector is numerically tagged with
injector number (INJ 1, INJ 2 etc.) of its correspond-
ing fuel injector and cylinder number.
(18) Verify harness connectors are firmly con-
nected to idle air control (IAC) motor, throttle posi-
Fig. 16 CCV System—2.5L Engine
1 - FIXED ORIFICE FITTING
2 - AIR INLET FITTING
3 - CCV TUBE
4 - CCV TUBE
Fig. 17 Intake Manifold Air Temperature Sensor—
2.5L Engine
1 - FUEL PRESSURE TEST PORT
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
3 - INTAKE MANIFOLD AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
4 - FUEL INJECTOR
Fig. 18 Sensor Location—2.5L Engine
1 - IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR
2 - IAT SENSOR
3 - THROTTLE BODY
4 - THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
5 - MAP SENSOR
6 - IDLE AIR CONTROL PASSAGE INLET
7 - THROTTLE BODY MOUNTING BOLTS (4)
14 - 32
FUEL INJECTION
AN
FUEL INJECTION (Continued)