DAF LF45, LF55 Series. Manual - part 501
7
LF45/55 series
General
STEERING BOX
2-1
2. GENERAL
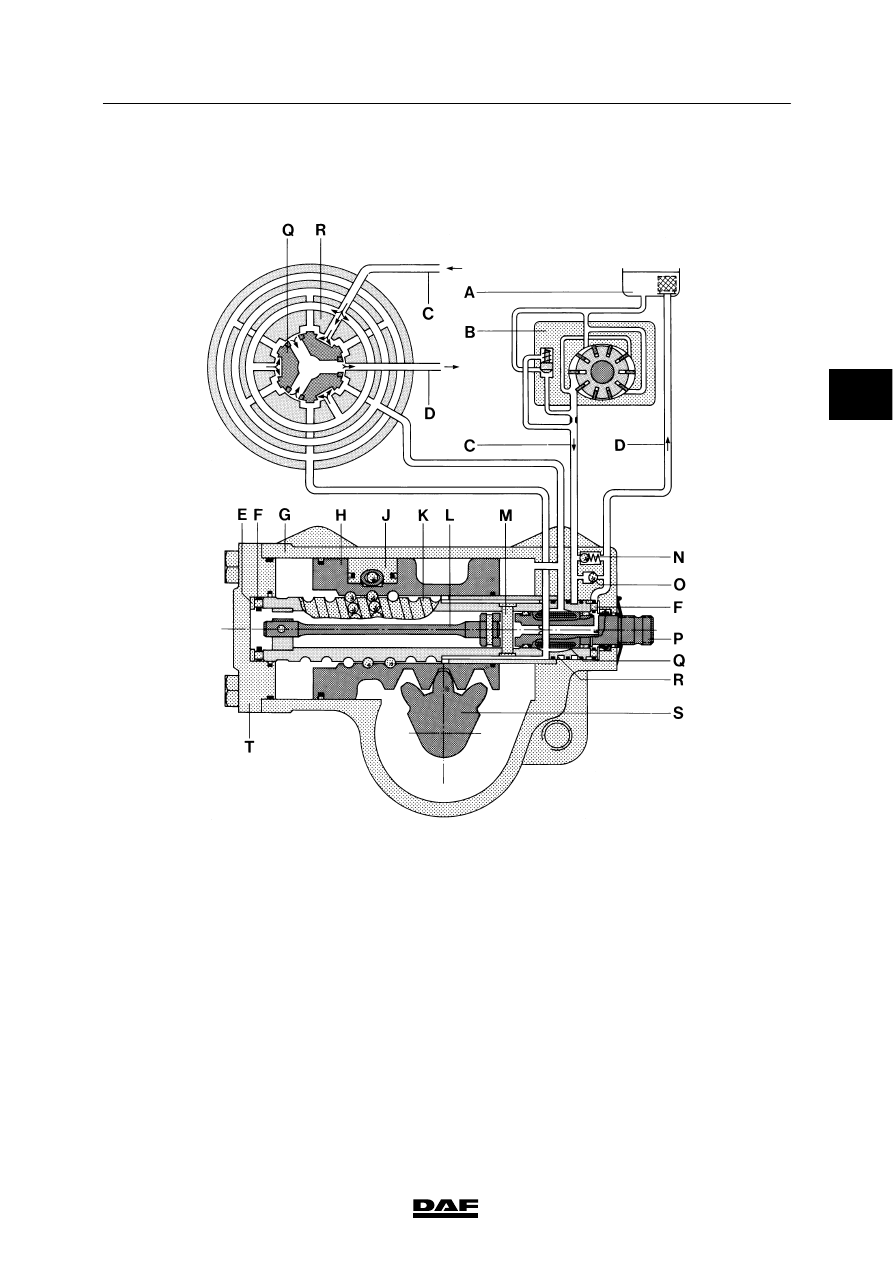
2.1 OVERVIEW DRAWING OF STEERING BOX
S7 00 265
A.
Reservoir
B.
Steering pump
C.
Delivery pipe
D.
Return pipe
E.
Shim
F.
Pivot bearing
G.
Box
H.
Piston
J.
Ball nut
K.
Worm shaft
L.
Torsion bar
M.
Pin (with internal end stop)
N.
Pressure-limiting valve
O.
Make-up valve (by-pass valve)
P.
Input shaft
Q.
Control valve core
R.
Control valve casing
S.
Sector shaft
T.
Cover
ᓻ 200322
3