SsangYong Rexton. Manual - part 518
SSANGYONG Y200
4E-36 ABS AND TCS
ABS INDICATOR LAMP ILLUMINATED CONTINUOUSLY, NO DTCS
STORED
YAD4E150
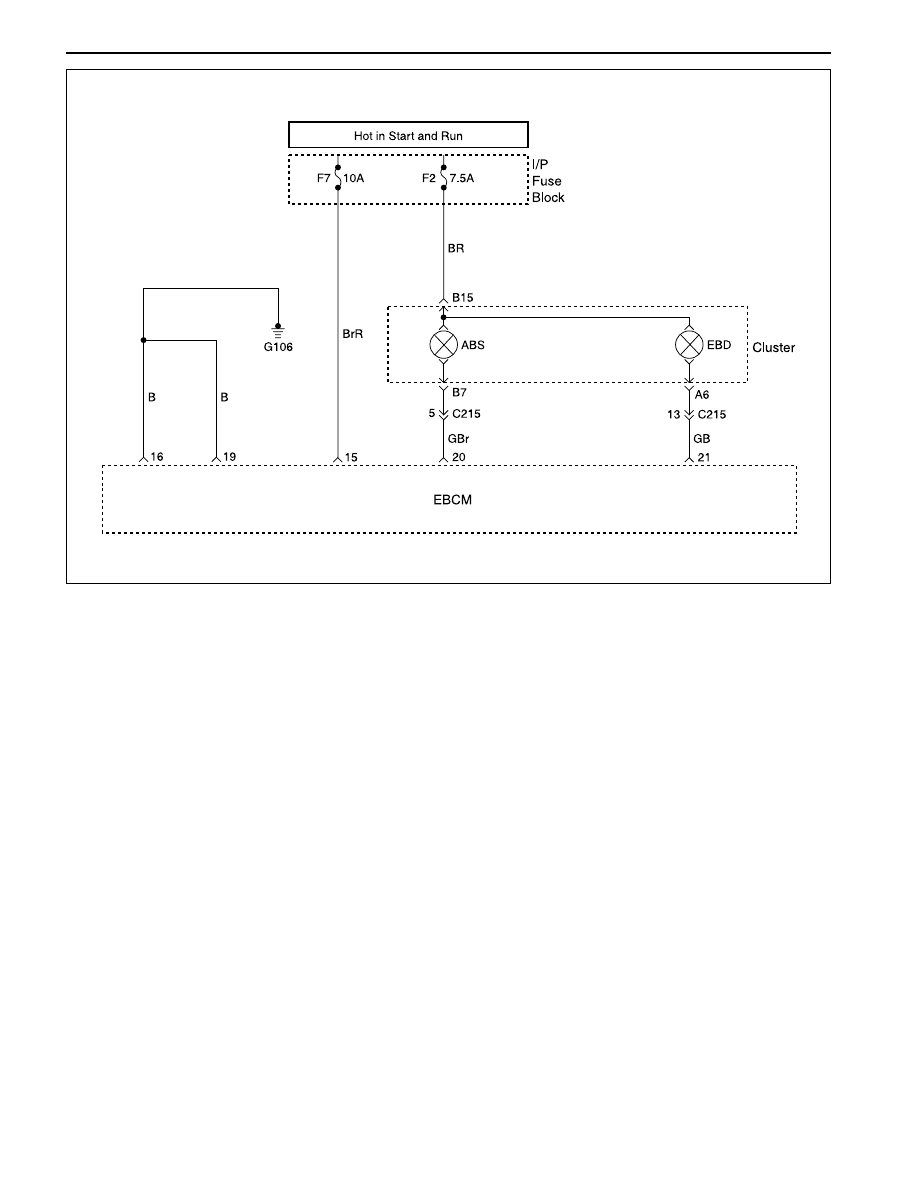
Circuit Description
Battery voltage is supplied to the ABS warning lamp
with the ignition in ON or START. The warning lamp
should be activated only by the ABS control module
internally supplying ground to terminal 20.
Diagnosis
This procedure checks for a short to ground in the
wiring or a defective electronic brake control module
(EBCM).
Cause
•
There is a short to ground in the circuit between the
cluster terminal D7 and the EBCM terminal 31.
•
The EBCM is faulty.