SsangYong Korando III (2010 year). Manual - part 555
12-19
0000-00
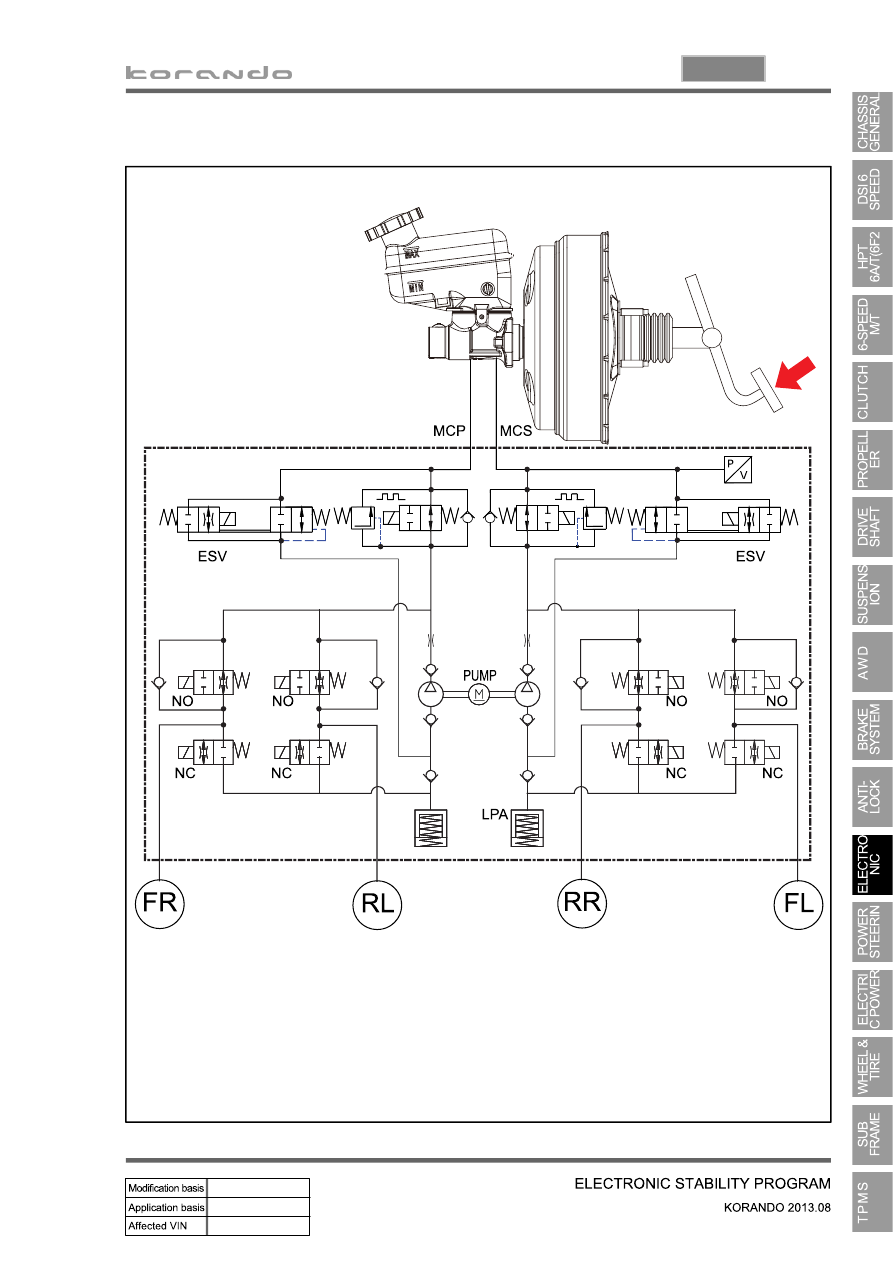
6. HYDRAULIC CIRCUIT OF ESP
MCP: Master Cylinder Primary
MSP: Master Cylinder Secondary
ESV: Electric Shuttle Valve
NO: Normal Open
NC: Normal Close
LPA: Low Pressure Accumulator
|
|
|

12-19 0000-00 6. HYDRAULIC CIRCUIT OF ESP MCP: Master Cylinder Primary MSP: Master Cylinder Secondary ESV: Electric Shuttle Valve NO: Normal Open NC: Normal Close LPA: Low Pressure Accumulator |