Nissan Terrano r20e. Manual - part 96
Normal control
Input/output signal chart
Sensor
Input Signal to ECM
ECM Function
Actuator
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC)
Engine speed
Fuel injection con-
trol (Normal con-
trol)
Electronic control fuel injec-
tion pump
Accelerator position sensor
Accelerator position
Vehicle speed sensor
Vehicle speed
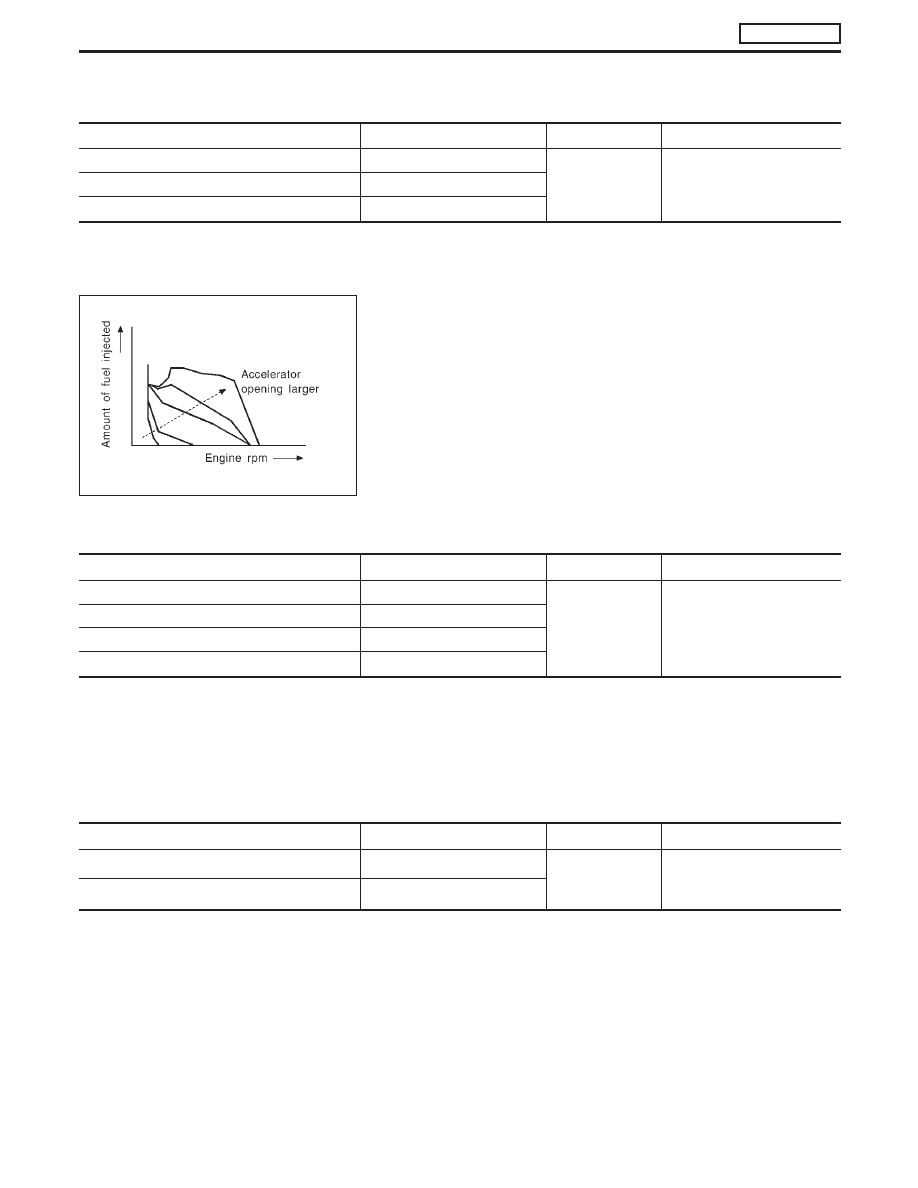
The amount of fuel injected under normal driving conditions is
determined according to sensor signals. The crankshaft position
sensor (TDC) detects engine speed and the accelerator position
sensor detects accelerator position. These sensors send signals to
the ECM.
The fuel injection data, predetermined by correlation between vari-
ous engine speeds and accelerator positions, are stored in the
ECM memory, forming a map. The ECM determines the optimal
amount of fuel to be injected using the sensor signals in compari-
son with the map.
Maximum amount control
Input/output signal chart
Sensor
Input Signal to ECM
ECM Function
Actuator
Mass air flow sensor
Amount of intake air
Fuel injection con-
trol (Maximum
amount control)
Electronic control fuel injec-
tion pump
Engine coolant temperature sensor
Engine coolant temperature
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC)
Engine speed
Accelerator position sensor
Accelerator position
The maximum injection amount is controlled to an optimum by the engine speed, intake air amount, engine
coolant temperature, and accelerator opening in accordance with the driving conditions.
This prevents the oversupply of the injection amount caused by decreased air density at a high altitude or
during a system failure.
Deceleration control
Input/output signal chart
Sensor
Input Signal to ECM
ECM Function
Actuator
Accelerator switch (F/C)
Accelerator position
Fuel injection con-
trol (Deceleration
control)
Electronic control fuel injec-
tion pump
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC)
Engine speed
The ECM sends a fuel cut signal to the electronic control fuel injection pump during deceleration for better
fuel efficiency. The ECM determines the time of deceleration according to signals from the accelerator switch
(F/C) and crankshaft position sensor (TDC).
SEF649S
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
ZD30DDTi
Fuel Injection Control System (Cont’d)
EC-21