Nissan March K13. Manual - part 219
SYSTEM
EC-337
< SYSTEM DESCRIPTION >
[HR12DE (TYPE 2)]
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
A
EC
N
P
O
MULTIPORT FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM
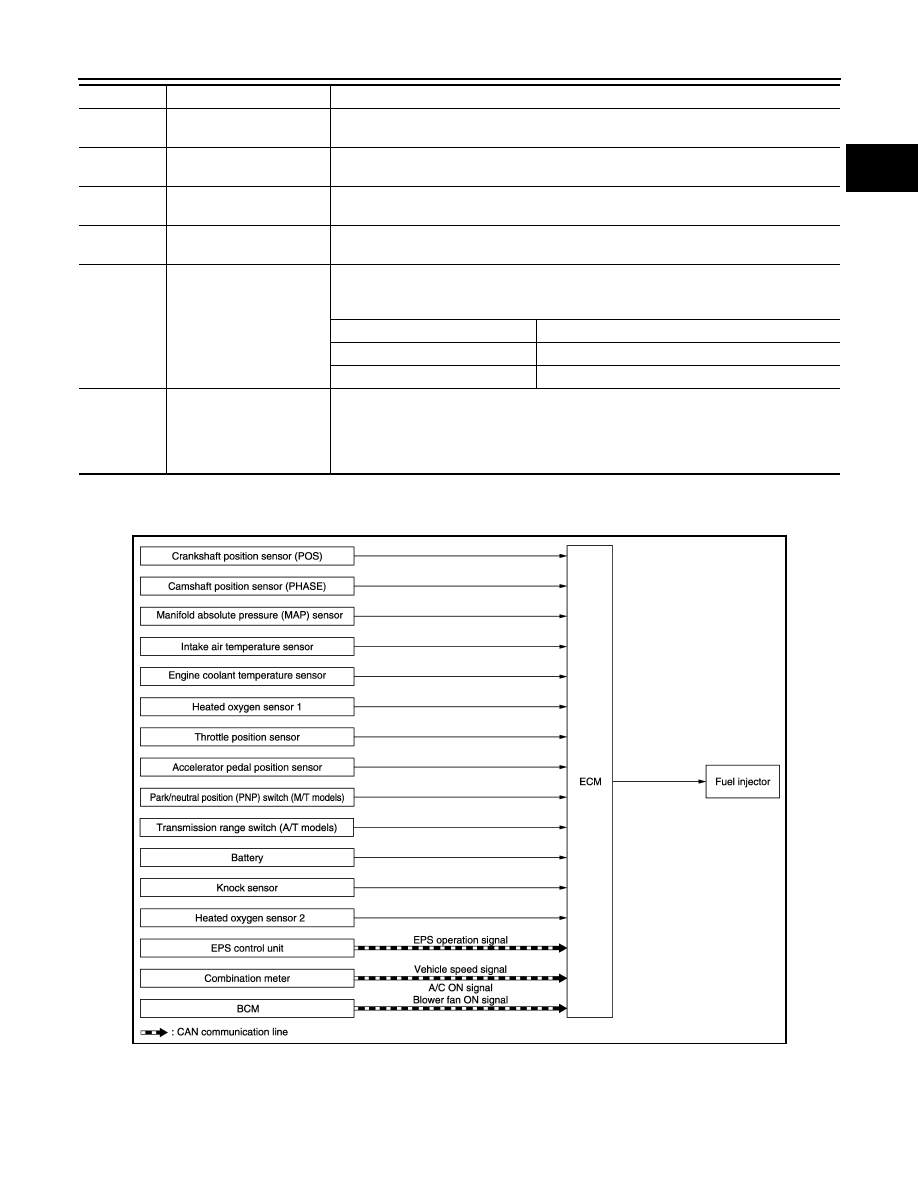
MULTIPORT FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM : System Diagram
INFOID:0000000006036809
MULTIPORT FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM : System Description
INFOID:0000000006036810
INPUT/OUTPUT SIGNAL CHART
P1124
P1126
Throttle control motor relay
ECM stops the electric throttle control actuator control, throttle valve is maintained at a
fixed opening (approx. 5 degrees) by the return spring.
P1128
Throttle control motor
ECM stops the electric throttle control actuator control, throttle valve is maintained at a
fixed opening (approx. 5 degrees) by the return spring.
P1171
Intake air
When accelerator pedal is depressed, engine speed will not rise more than 2,500 rpm due
to fuel cut.
P1229
Sensor power supply
ECM stops the electric throttle control actuator control, throttle valve is maintained at a
fixed opening (approx. 5 degrees) by the return spring.
P1805
Brake switch
ECM controls the electric throttle control actuator by regulating the throttle opening to a
small range.
Therefore, acceleration will be poor.
Vehicle condition
Driving condition
When engine is idling
Normal
When accelerating
Poor acceleration
P2122
P2123
P2127
P2128
P2138
Accelerator pedal position
sensor
The ECM controls the electric throttle control actuator in regulating the throttle opening in
order for the idle position to be within +10 degrees.
The ECM regulates the opening speed of the throttle valve to be slower than the normal
condition.
So, the acceleration will be poor.
DTC No.
Detected items
Engine operating condition in fail safe mode
JSBIA0434GB