Almera Tino V10 (2003 year). Manual - part 202
CYLINDER BLOCK
EM-81
[QG]
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
A
EM
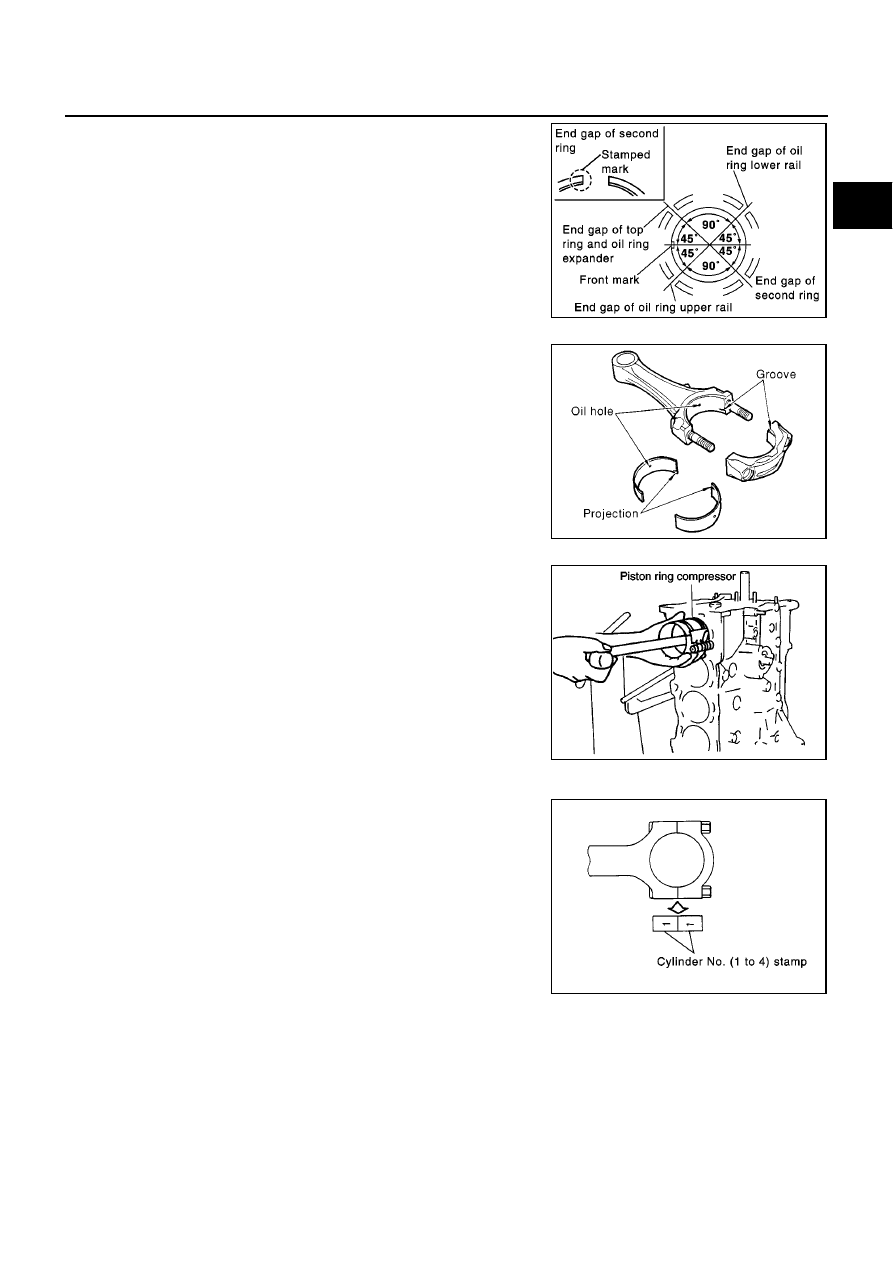
10. Install piston rings with piston ring expander (commercial ser-
vice tool).
CAUTION:
●
Be careful not to damage piston.
●
When installing top ring, be careful not to break end gap
step.
●
Position end gaps of each piston ring to piston front mark as
shown in figure, then install rings.
●
Install top ring with stamp mark side facing upward.
11. Install the connecting rod bearings to the connecting rod and the
connecting rod cap.
●
When installing the connecting rod bearings, apply engine oil
to the bearing surface (inside). Do not apply oil to the back
surface, but thoroughly clean it.
●
When installing, align the connecting rod bearing stopper pro-
trusion with the notch of the connecting rod to install.
●
Check the oil holes on the connecting rod and those on the
corresponding bearing are aligned.
12. Install the piston and connecting rod assembly to the crankshaft.
●
Position the crankshaft pin corresponding to the connecting
rod to be installed onto the bottom dead center.
●
Apply engine oil sufficiently to the cylinder bore, piston and
crankshaft pin.
●
Match the cylinder position with the cylinder No. on the con-
necting rod to install.
●
Using a piston ring compressor, install the piston with the front
mark on the piston crown facing the front of the engine.
CAUTION:
Be careful not to damage the crankshaft pin, resulting from
an interference of the connecting rod big end.
13. Install the connecting rod cap.
●
Match the stamped cylinder number marks on the connecting
rod with those on the cap to install.
PBIC0977E
PBIC0482E
PBIC0267E
PBIC0593E