содержание .. 729 730 731 732 ..
Nissan X-Trail 32. Manual - part 731
SYSTEM
EC-53
< SYSTEM DESCRIPTION >
[MR20DD]
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
A
EC
N
P
O
The mixture ratio feedback system provides the best air-fuel mixture ratio for driveability and emission control.
The three way catalyst (manifold) can better reduce CO, HC and NOx emissions. This system uses A/F sen-
sor 1 in the exhaust manifold to monitor whether the engine operation is rich or lean. The ECM adjusts thein-
jection pulse width according to the sensor voltage signal. And the correcting factor to control the pulse width
is displayed as “A/F CORRECTION”, or “S-FUEL TRM-B1 [%]”. For more information about A/F sensor 1,
refer to
EC-38, "Air Fuel Ratio (A/F) Sensor 1"
. This maintains the mixture ratio within the range of stoichio-
metric (ideal air-fuel mixture). This stage is referred to as the closed loop control condition.
Heated oxygen sensor 2 is located downstream of the three way catalyst (manifold). Even if the switching
characteristics of A/F sensor 1 shift, the air-fuel ratio is controlled to stoichiometric by the signal from heated
oxygen sensor 2.
Open Loop Control
The open loop system condition refers to when the ECM detects any of the following conditions. Feedback
control stops (clamp) in order to maintain stabilized fuel combustion.
• Deceleration and acceleration
• High-load, high-speed operation
• Malfunction of A/F sensor 1 or its circuit
• Insufficient activation of A/F sensor 1 at low engine coolant temperature
• High engine coolant temperature
• During warm-up
• After shifting from N to D
• When starting the engine
MIXTURE RATIO SELF-LEARNING CONTROL
The mixture ratio feedback control system monitors the mixture ratio signal transmitted from heated oxygen
sensor 1. This feedback signal is then sent to the ECM. The ECM controls the basic mixture ratio as close to
the theoretical mixture ratio as possible. However, the basic mixture ratio is not necessarily controlled as orig-
inally designed. Both manufacturing differences (i.e., mass air flow sensor hot wire) and characteristic
changes during operation (i.e., fuel injector clogging) directly affect mixture ratio.
Accordingly, the difference between the basic and theoretical mixture ratios is monitored in this system.This is
then computed in terms of “injection pulse duration” to automatically compensate for the difference between
the two ratios.
“Fuel trim” refers to the feedback compensation value compared against the basic injection duration. Fuel trim-
includes short term fuel trim and long term fuel trim.
“Short term fuel trim” is the short-term fuel compensation used to maintain the mixture ratio at its theoretical
value. The signal from heated oxygen sensor 1 indicates whether the mixture ratio is RICH or LEAN compared
to the theoretical value. The signal then triggers a reduction in fuel volume if the mixture ratio is rich, and anin-
crease in fuel volume if it is lean.
“Long term fuel trim” is overall fuel compensation carried out long-term to compensate for continual deviation
of the short term fuel trim from the central value. Such deviation will occur due to individual engine differ-
ences,wear over time and changes in the usage environment.
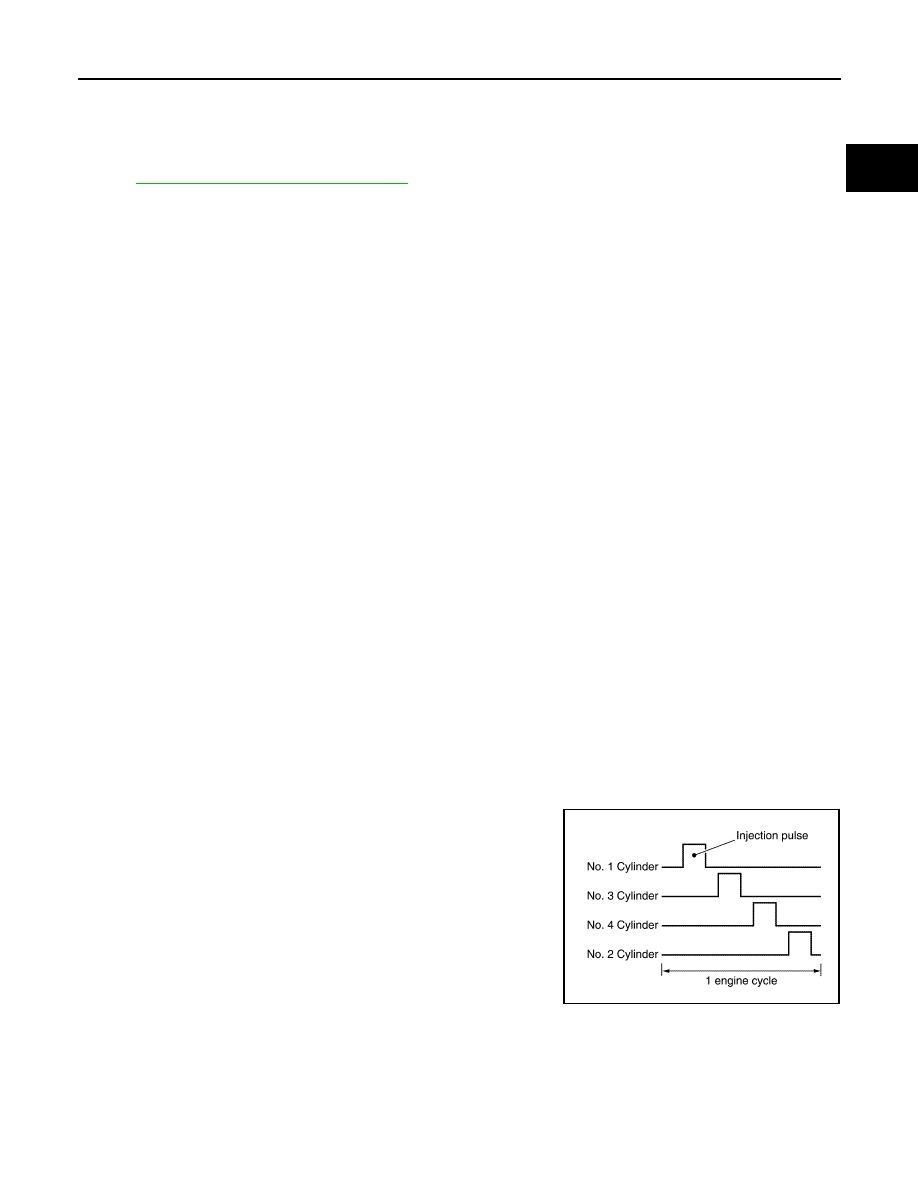
FUEL INJECTION TIMING
Fuel is injected into each cylinder during each engine cycle accord-
ing to the ignition order.
STRATIFIED-CHARGE START CONTROL
The use of the stratified-charge combustion method enables emissions-reduction when starting with the
engine cold.
FUEL SHUT-OFF
Fuel shut-off during deceleration
Fuel to each cylinder is cut off during deceleration for restraint of HC and improvement of fuel efficiency.
JPBIA4704GB