Mitsubishi Outlander (2013+). Manual - part 222
GENERAL INFORMATION
LOCAL INTERCONNECT NETWORK (LIN)
54B-2
GENERAL INFORMATION
M2545600100019
LIN refers to "Local Interconnect Network," which is a
serial multiplex communication protocol
*
adminis-
trated by LIN consortium. A communication circuit
employing the LIN protocol connects each ECU, and
switch and sensor data can be shared among ECUs,
which enables more reduction in wiring.
NOTE:
*
: The regulations that have been decided in
detail, from software matters such as the necessary
transmission rate for communication, the system,
data format, and communication timing control
method to hardware matters such as the harness
type and length and the resistance values.
STRUCTURE
M2545600200395
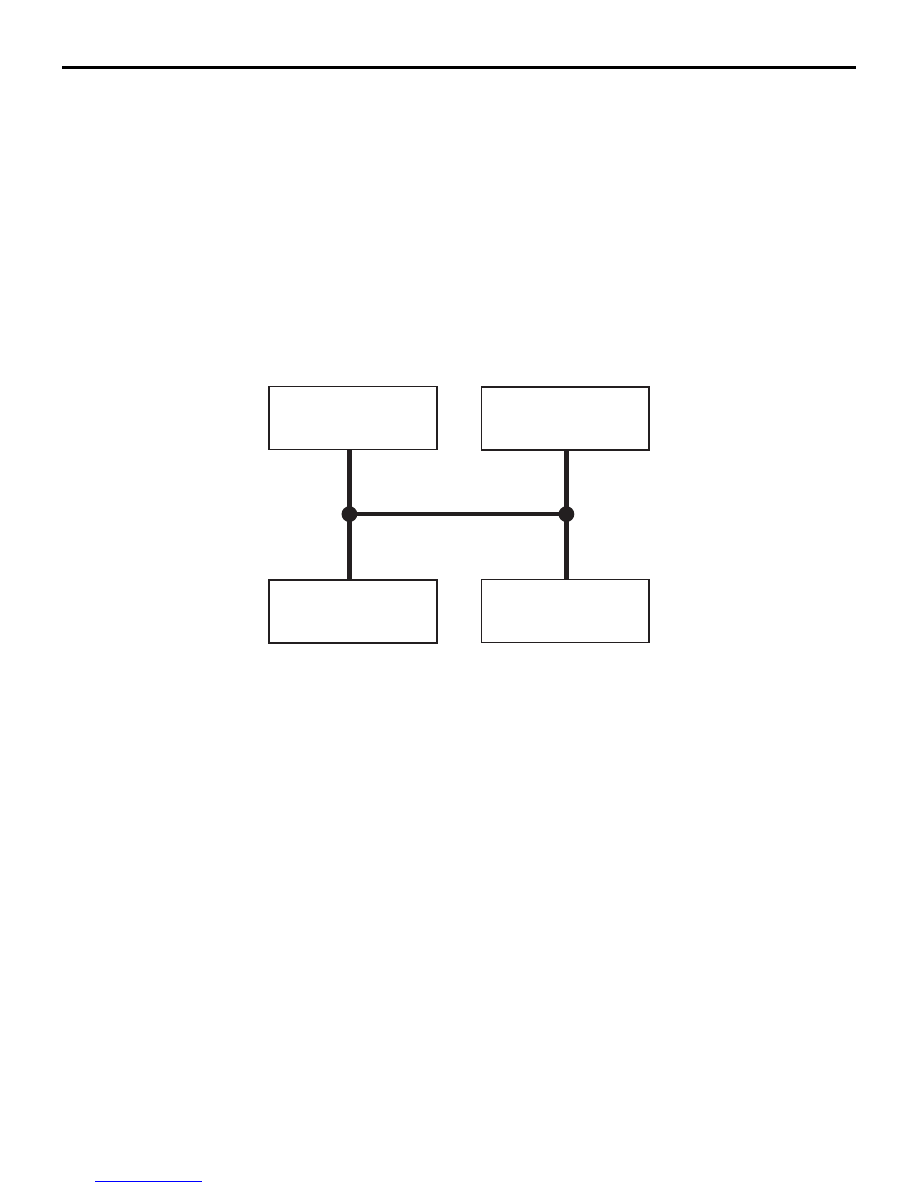
Master and slave ECUs are connected to the LIN
bus lines. The master ECU is the ETACS
*
-ECU, and
the slave ECUs are the column switch (col-
umn-ECU), the sunroof-ECU <vehicles with sunroof>
and the lighting control sensor <vehicles with lighting
control sensor>. The master ECU requests these
slave ECUs to communicate each other via commu-
nication lines.
NOTE:
*
: ETACS (Electronic Time and Alarm Control
System)
AC608956AD
ETACS-ECU
Column switch
(column-ECU)
Sunroof-ECU
<Vehicles with
sunroof>
Slave ECU
Slave ECU
Slave ECU
Master ECU
LIN bus line
Lighting control sensor
<Vehicles with
lighting control sensor>
manuals search engine