Mazda Training manual - part 244
4 – VALVE TRAIN
61
Piston Engine Fundamentals
TC010-05-01S
Gear-Driven Camshaft with Friction Gear
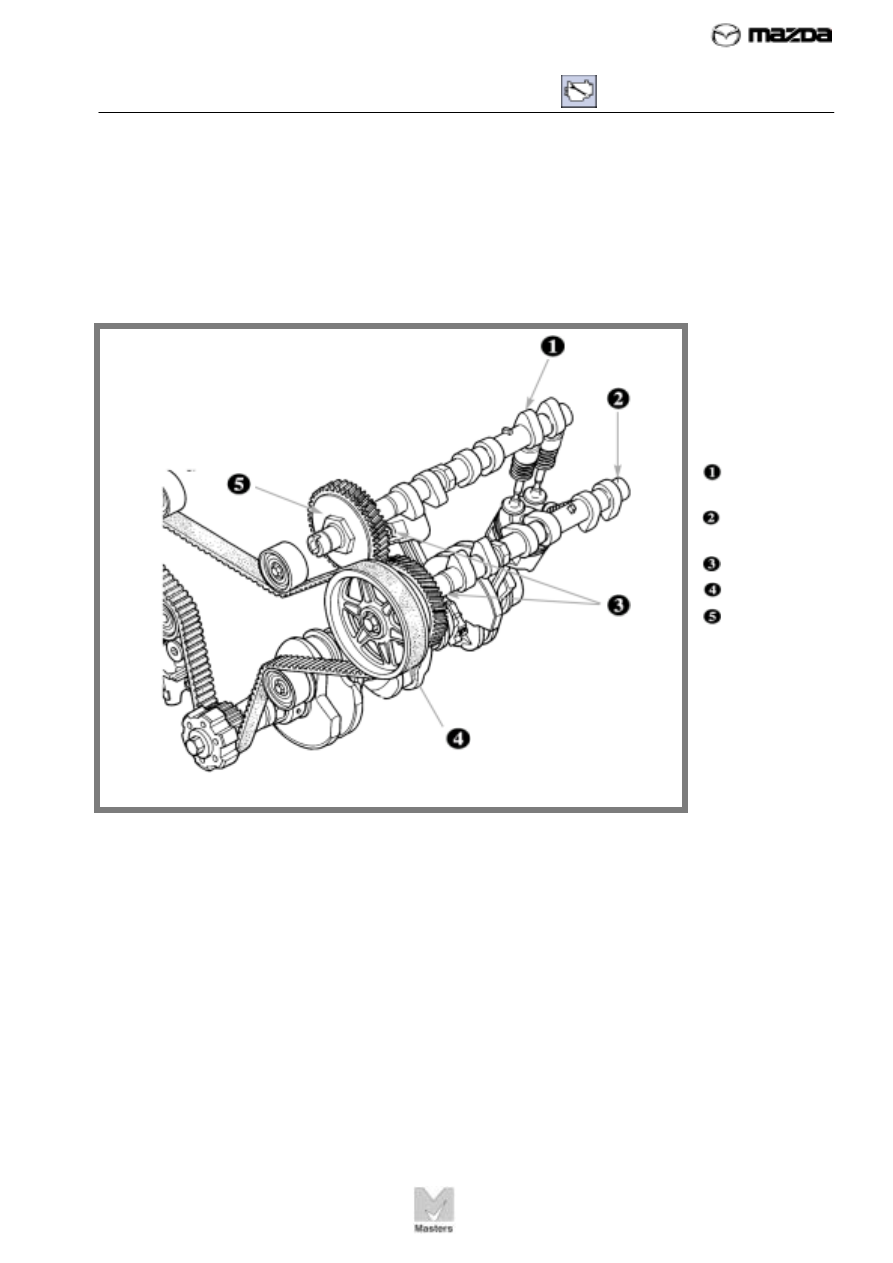
Mazda also uses another type of cam drive that features a gear-driven
camshaft with a friction gear. In this design, shown in Figure 44, the timing
belt drives one camshaft on each head. The other camshaft is driven by
helical gears. The helical gears turn the driven-side camshaft
counter-clockwise. This design creates a more compact valve train, which
allows a lower hood line on the vehicle.
The arrangement of the cam lobes on the two cams causes a clicking
noise as the cams turn. To eliminate this noise, the driven gear is
equipped with a friction gear.
The friction gear has one more tooth than the helical gear. The friction gear
causes a slight bind between the drive and the driven cam gears,
eliminating any clicking noise resulting from backlash/freeplay between the
gears.
FIGURE 44 The
drive camshaft is
driven by the
timing belt. The
driven camshaft is
driven by helical
and friction gears.
Driven
camshaft
Drive
camshaft
Helical gears
Timing belt
Friction gear