Mazda Training manual - part 242
4 – VALVE TRAIN
53
Piston Engine Fundamentals
TC010-05-01S
OVERHEAD CAM VALVE TRAIN
The overhead cam (OHC) design provides more direct control over valves
than the OHV design. This advantage may explain why overhead cams are
the most commonly used design. The overhead cam design includes
engines with a single overhead cam (OHC or SOHC), as well as engines
with dual overhead cams (DOHC).
Overhead Cam (OHC or SOHC)
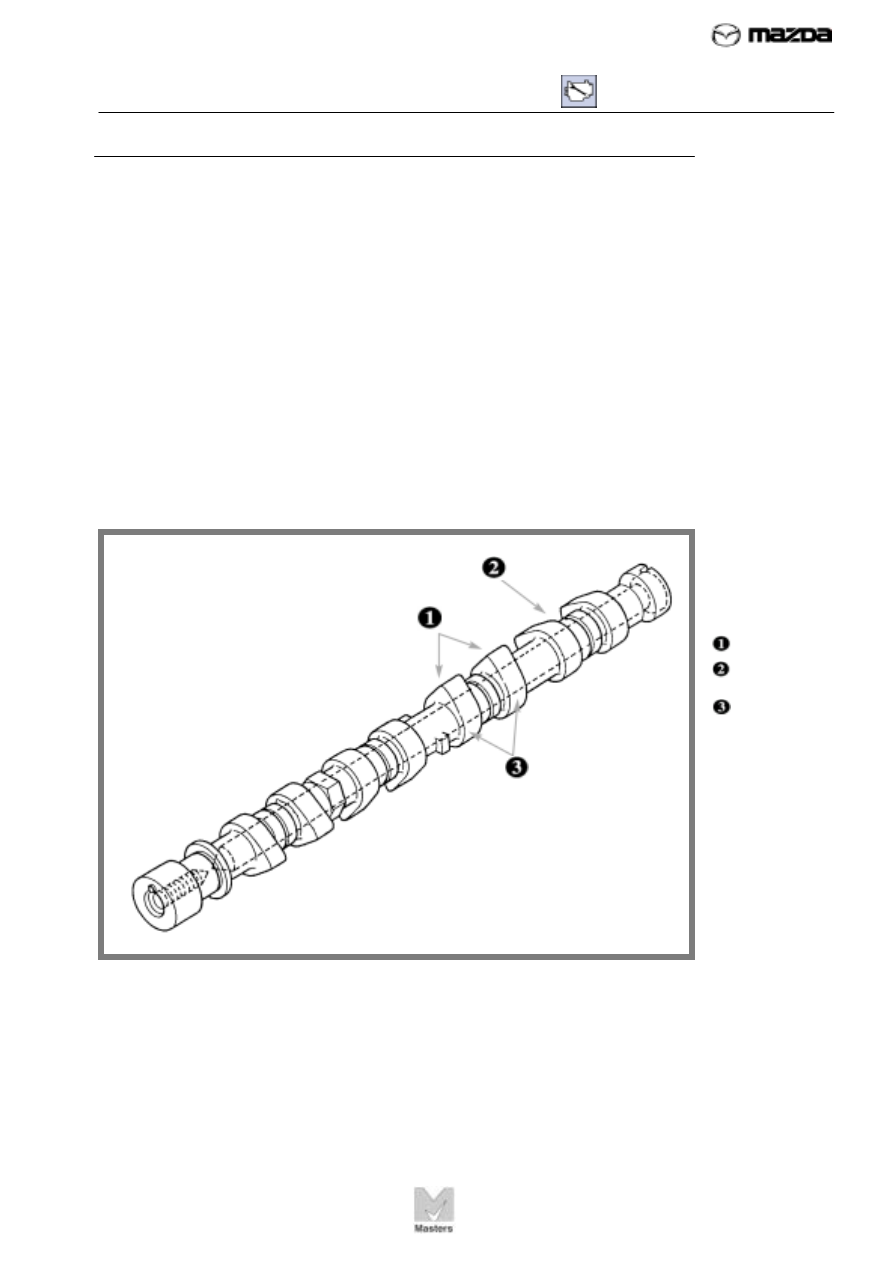
In an overhead cam engine, the camshaft is installed in the cylinder head
above the valves. The camshaft, shown in Figure 36, is a solid or hollow
cast iron shaft with several cams on it. Each cam has an off-center bulge
on one side called a cam lobe. On most Mazda OHC engines, the
camshaft runs directly on the cylinder head journal surface without insert
bearings.
FIGURE 36. The
camshaft rides
directly on the
cylinder head
journal surface.
Cam lobes
Camshaft
journal
Cams