Great Wall Florid. Manual - part 27
GWFLORID Maintenance Manual
106
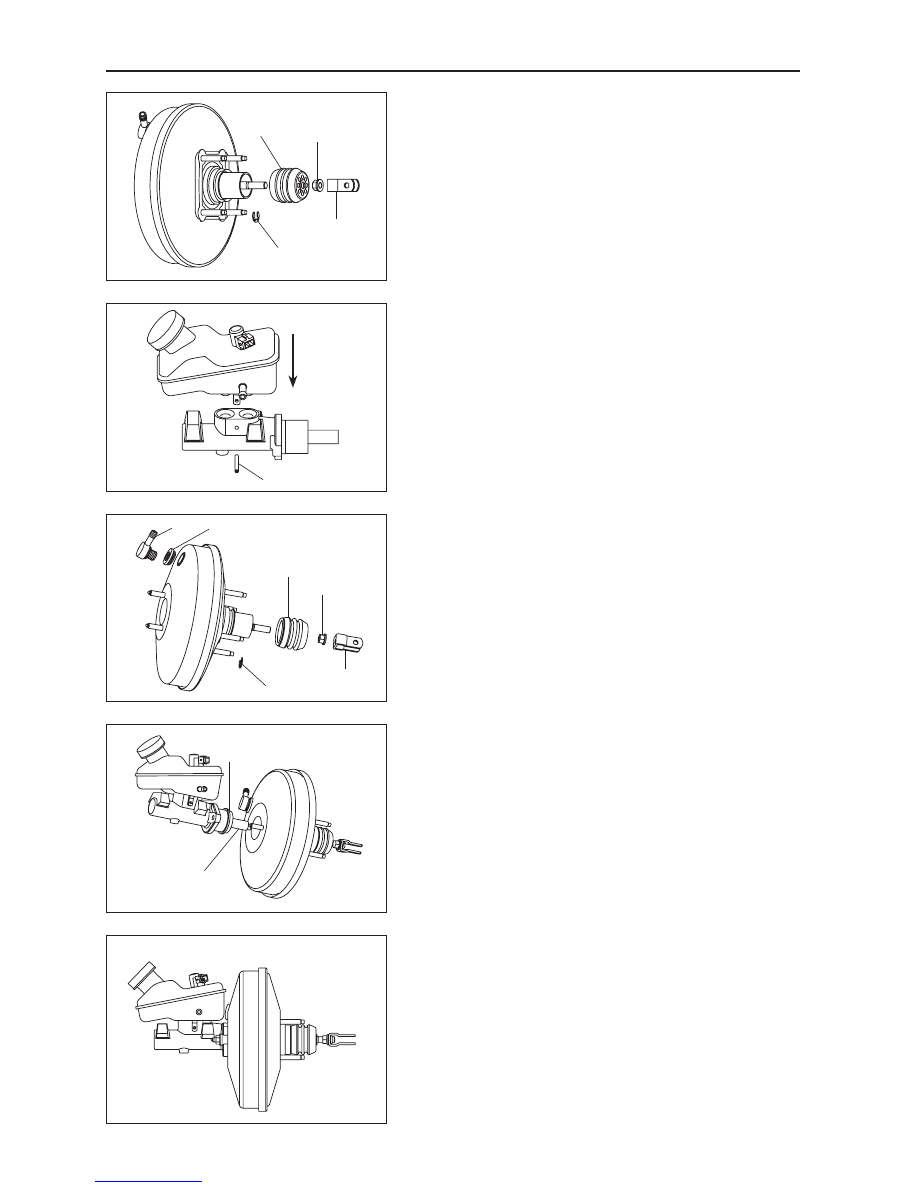
4. Remove the dust cover.
If necessary to replace the dust cover, replace it using the
following steps.
(a) Twist off the rod clevis.
(b) Screw off the nut.
(c) Pull out the split ring.
(d) Pull out the dust cover.
Removal of the vacuum booster with brake cylinder
assembly is now complete.
Vacuum booster with brake cylinder assem-
bly installation
1. Install the brake cylinder assembly.
Tighten the cover of the brake reservoir, place the outlet
port of the brake reservoir against the master cylinder inlet,
push the brake reservoir assembly into the master cylinder
assembly, and then insert the cylindrical pin to complete the
installation.
Caution: Check and ensure the cleanliness of the
reservoir outlet port and master cylinder inlet. Do not
lose the sealing ring inside the master cylinder inlet.
2. Installation of the vacuum booster assembly.
Install each part of booster using the following steps.
(a) Install the check valve seat.
(b) Install the check valve.
(c) Install the dust cover.
(d) Install the split ring.
(e) Install the lock nut.
(f) Install the rod clevis.
3. Installaion of the vacuum booster assembly and brake
cylinder assembly.
(a) Install the rectangular sealing ring, and then place the
brake pump assembly into the front case’s housing. Pay
attention when pushing the booster's push rod head into
the first piston hole.
(b) Put the two holes of the cylinder body’s flange surface
into the front case bolts of the vacuum booster, and
then tighten the nuts with a torque wrench.
Tightening torque: 20-26 N·m
4. The installation of the vacuum booster with brake
cylinder assembly is the reversed procedure of its
removal. Hence no more elaboration will be provided
here.
Tightening torque of the four lock bolts on the brake
pedal: 23±3 N·m
Tightening torque of master cylinder outlet port rigid
pipe: 15 N·m
Rod clevis
Nut
Split ring
Dust cover
Elastic cylindrical pin
Check valve Check valve seat
Lock nut
Rod clevis
Split ring
Dust cover
Rectangular sealing ring
First piston