Dodge Neon / Neon SRT-4. Manual - part 442
EVAP/PURGE SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION (Fig. 2)
OPERATION
All vehicles use a proportional purge solenoid. The
solenoid regulates the rate of vapor flow from the
EVAP canister to the throttle body. The PCM oper-
ates the solenoid.
During the cold start warm-up period and the hot
start time delay, the PCM does not energize the sole-
noid. When de-energized, no vapors are purged.
The proportional purge solenoid operates at a fre-
quency of 200 hz and is controlled by an engine con-
troller circuit that senses the current being applied
to the proportional purge solenoid (Fig. 2) and then
adjusts that current to achieve the desired purge
flow. The proportional purge solenoid controls the
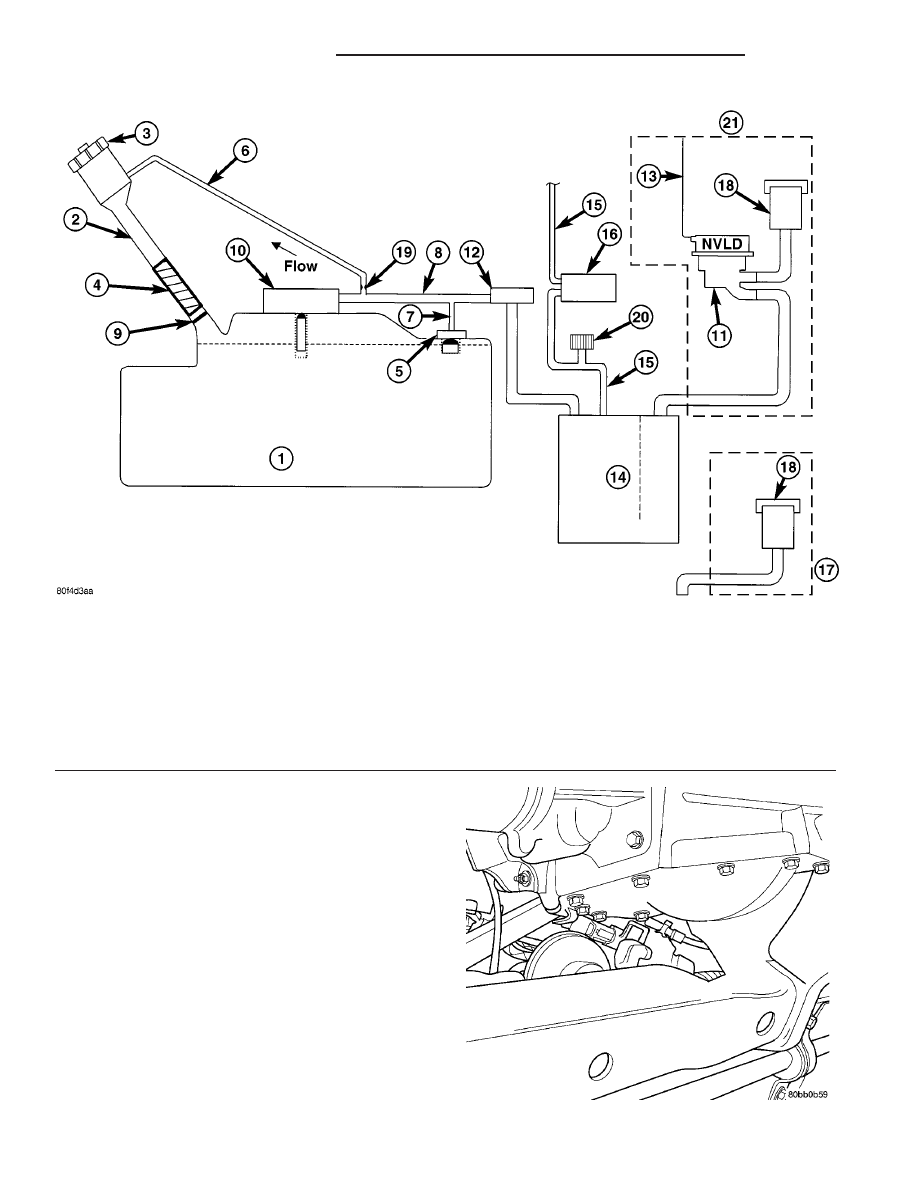
Fig. 1 ORVR System Schematic (PZEV)
1 - FUEL TANK (PLASTIC)
11 - NATURAL VACUUM LEAD DETECTION (NVLD)
2 - FUEL FILLER TUBE
12 - LIQUID SEPARATOR (IF EQUIPPED)
3 - FUEL CAP (PRESSURE/RELIEF)
13 - ENGINE WIRING HARNESS TO NVLD
4 - FILL TUBE TO FUEL TANK CONNECTOR (ELASTOMERIC)
14 - VAPOR CANISTER
5 - TANK VENT/ROLLOVER VALVE(S)
15 - PURGE LINE
6 - VAPOR RECIRCULATION LINE
16 - PURGE DEVICE
7 - TANK VAPOR LINE
17 - WITHOUT NVLD
8 - VAPOR LINE TO CANISTER
18 - BREATHER ELEMENT
9 - CHECK VALVE (N/C)
19 - FLOW CONTROL ORIFICE
10 - CONTROL VALVE
20 - SERVICE PORT
21 - WITH NVLD
Fig. 2 Proportional Purge Solenoid
25 - 12
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS
PL/SRT-4
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS (Continued)