Dodge Neon / Neon SRT-4. Manual - part 424
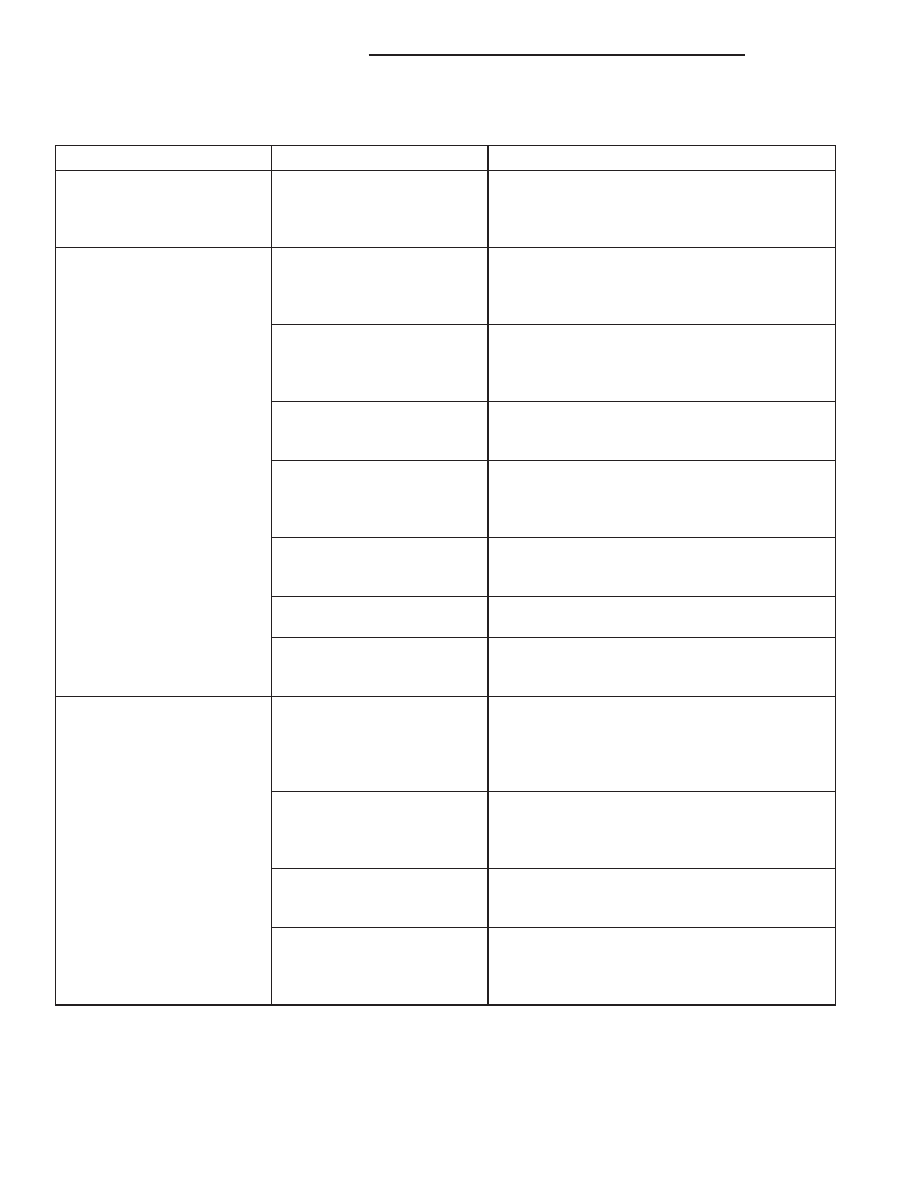
A/C PRESSURE DIAGNOSIS
Condition
Possible Causes
Correction
Rapid A/C compressor clutch
cycling (ten or more cycles
per minute).
1. Low refrigerant system
charge.
1. See Refrigerant System Leaks in this group.
Test the refrigerant system for leaks. Repair,
evacuate and charge the refrigerant system, if
required.
Equal pressures, but the
compressor clutch does not
engage.
1. No refrigerant in the
refrigerant system.
1. See Refrigerant System Leaks in this group.
Test the refrigerant system for leaks. Repair,
evacuate and charge the refrigerant system, if
required.
2. Faulty fuse.
2. Check the fuses in the Integrated Power
Module. Repair the shorted circuit or component
and replace the fuses, if required. Refer to Group
8.
3. Faulty A/C compressor
clutch coil.
3. See A/C Compressor Clutch Coil in this group.
Test the compressor clutch coil and replace, if
required.
4. Faulty A/C compressor
clutch relay.
4. See A/C Compressor Clutch Relay in this
group. Test the compressor clutch relay and relay
circuits. Repair the circuits or replace the relay, if
required.
5. Improperly installed or
faulty A/C low pressure
switch.
5. See A/C Low Pressure Switch in this group.
Test the switch and replace, if required.
6. Faulty A/C high pressure
switch.
6. See A/C High Pressure Switch in this group.
Test the switch and replace, if required.
7. Faulty Powertrain Control
Module (PCM).
7. Refer to the proper Diagnostic Procedures
manual for testing of the PCM. Test the PCM and
replace, if required.
Normal pressures, but A/C
Performance Test air
temperatures at center panel
outlet are too high.
1. Excessive refrigerant oil in
system.
1. See Refrigerant Oil Level in this group.
Recover the refrigerant from the refrigerant
system and inspect the refrigerant oil content.
Restore the refrigerant oil to the proper level, if
required.
2. Temperature control cable
improperly installed or faulty.
2. See Temperature Control Cable this group.
Inspect the cable for proper adjustment and
operation. Adjust or replace the cable as
required.
3. Blend door inoperative or
sealing improperly.
3. See HVAC Housing in this group. Inspect the
blend door for proper operation and sealing.
Repair if required.
4. Blend door not in full cold
position.
4. See Temperature Control Cable this group.
Inspect the cable for proper adjustment and
operation. Adjust or replace the cable as
required.
24 - 4
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING
PL/SRT-4
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)