Chrysler 300/300 Touring/300C, Dodge Magnum. Manual - part 791
INTRUSION MODULE - EXPORT
DESCRIPTION
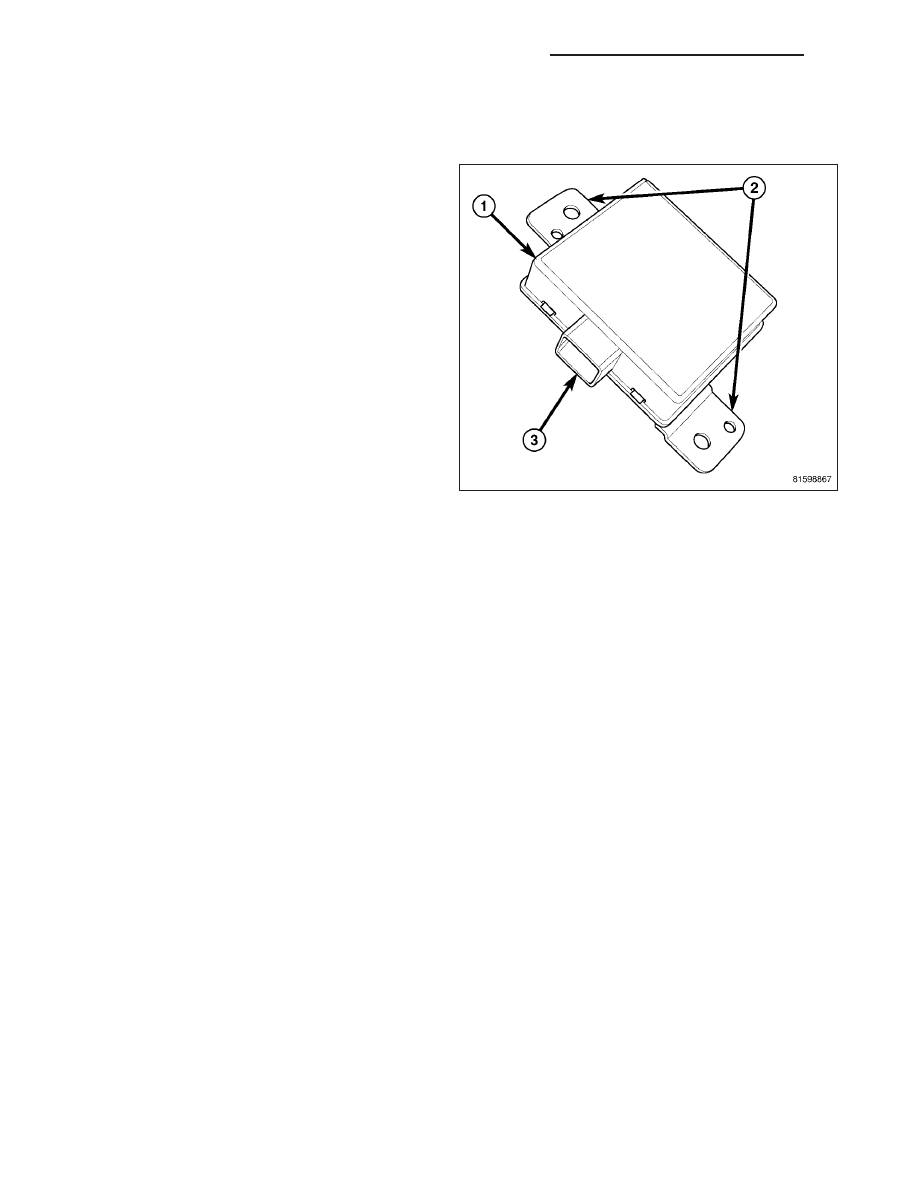
An intrusion module (1) is part of the premium version
of the Vehicle Theft Security System (VTSS). The pre-
mium version of the VTSS is only available in vehicles
built for certain markets, where the additional features
offered by this system are required. The intrusion
module is located in the passenger compartment. This
unit is designed to work in conjunction with the intru-
sion sensor transmitter and intrusion sensor receiver
to provide interior motion detection and serves as the
interface between the Forward Control Module (FCM),
the
ElectroMechanical
Instrument
Cluster
(EMIC),
sometimes referred to as the Cab Compartment Node
(CCN), and the alarm siren.
The intrusion module has two integral mounts (2) that
are secured behind the passenger side instrument
panel, just above the glove box. Concealed within the
molded plastic housing is the circuitry of the module,
which includes a microprocessor. The module is con-
nected to the vehicle electrical system by a connector
of the body wire harness.
The intrusion module unit cannot be adjusted or repaired and, if faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
OPERATION
The microprocessor in the intrusion module contains the motion detection logic circuits and controls all of the fea-
tures of the premium version of the Vehicle Theft Security System (VTSS). The module uses On-Board Diagnostics
(OBD) and can communicate with other modules in the vehicle as well as with a diagnostic scan tool using the
Controller Area Network (CAN) data bus. This method of communication is used by the module to communicate with
the Forward Control Module (FCM) and the ElectroMechanical Instrument Cluster (EMIC), sometimes referred to as
the Cab Compartment Node (CCN). The module also communicates with the alarm siren over a dedicated serial
bus circuit.
The intrusion module microprocessor continuously monitors inputs from the intrusion sensor transmitter and receiver
as well as inputs from the EMIC/CCN and the alarm siren module. The module energizes the intrusion sensor trans-
mitter, which transmits ultrasonic signals into the vehicle cabin through a transmit transducer, then monitors the
current draw of the transmitter to detect problems with the transmitter and transmitter circuits. The module also
energizes the intrusion sensor receiver, which listens to the ultrasonic signals through a receive transducer as they
bounce off of objects in the vehicle interior, then monitors the current draw of the receiver for data signals and to
detect problems with the receiver and receiver circuits. If an object is moving in the interior, a detection circuit in the
module senses this movement through the modulation of the returning data signals from the receiver.
If movement is detected, the intrusion module sends an electronic message to the FCM over the CAN data bus to
flash the exterior lighting and sends another message to the alarm siren module over the dedicated serial bus line
to sound the siren. When the EMIC/CCN or FCM detect a breach in the perimeter protection through a door or hood
ajar switch input, they send an electronic message to the intrusion module and the module sends a message to the
FCM to flash the exterior lighting and a message to the alarm siren module to sound the siren. The module also
monitors message inputs from the alarm siren module for siren battery or siren input/output circuit tamper alerts,
and siren battery condition alerts, then sets active and stored Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC) for any monitored
system faults it detects. An active fault only remains for the current ignition switch cycle, while a stored fault causes
a DTC to be stored in memory by the module. If a fault does not recur for 50 ignition cycles, the module will auto-
matically erase the stored DTC.
The intrusion module receives constant battery voltage (when armed), and is grounded at all times through a hard
wired remote ground point. These connections allow the module to remain operational, regardless of the ignition
switch position. Use a diagnostic scan tool and refer to the appropriate diagnostic information for proper diagnosis
of the system.
8Q - 132
VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY - SERVICE INFORMATION
LX