Chrysler Town & Country/Voyager, Dodge Caravan, Plymouth Voyager. Manual - part 191
• BOSCH STARTERS: Replace the solenoid
• NIPPONDENSO STARTERS: Replace the starter
assembly
ALTERNATOR TEST PROCEDURES ON VEHICLE
INDEX
page
page
Current Output Test
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Output Wire Resistance Test
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
OUTPUT WIRE RESISTANCE TEST
The alternator output wire resistance test shows the
amount of voltage drop across the alternator output
wire between the alternator B+ terminal and the
positive battery post.
PREPARATION
Before starting test, make sure the vehicle has a fully
charged battery. Tests and procedures to check for a
fully charged battery are shown in the Battery section
of this Group.
(1) Turn the ignition switch OFF.
(2) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(3) Disconnect the alternator B+ output wire from
the alternator output battery terminal (Fig. 1).
(4) Connect a 0-150 ampere scale (DC) ammeter in
series between B+ terminal and output wire (Fig. 1 and
2). Connect positive lead to B+ terminal, and negative
lead to output wire.
(5) Using 0-18 volt scale voltmeter, connect the posi-
tive lead to the disconnected (B+) output wire. Connect
the negative lead to positive battery cable at positive
post.
(6) Remove fresh air hose between Engine Control-
ler and air cleaner if necessary.
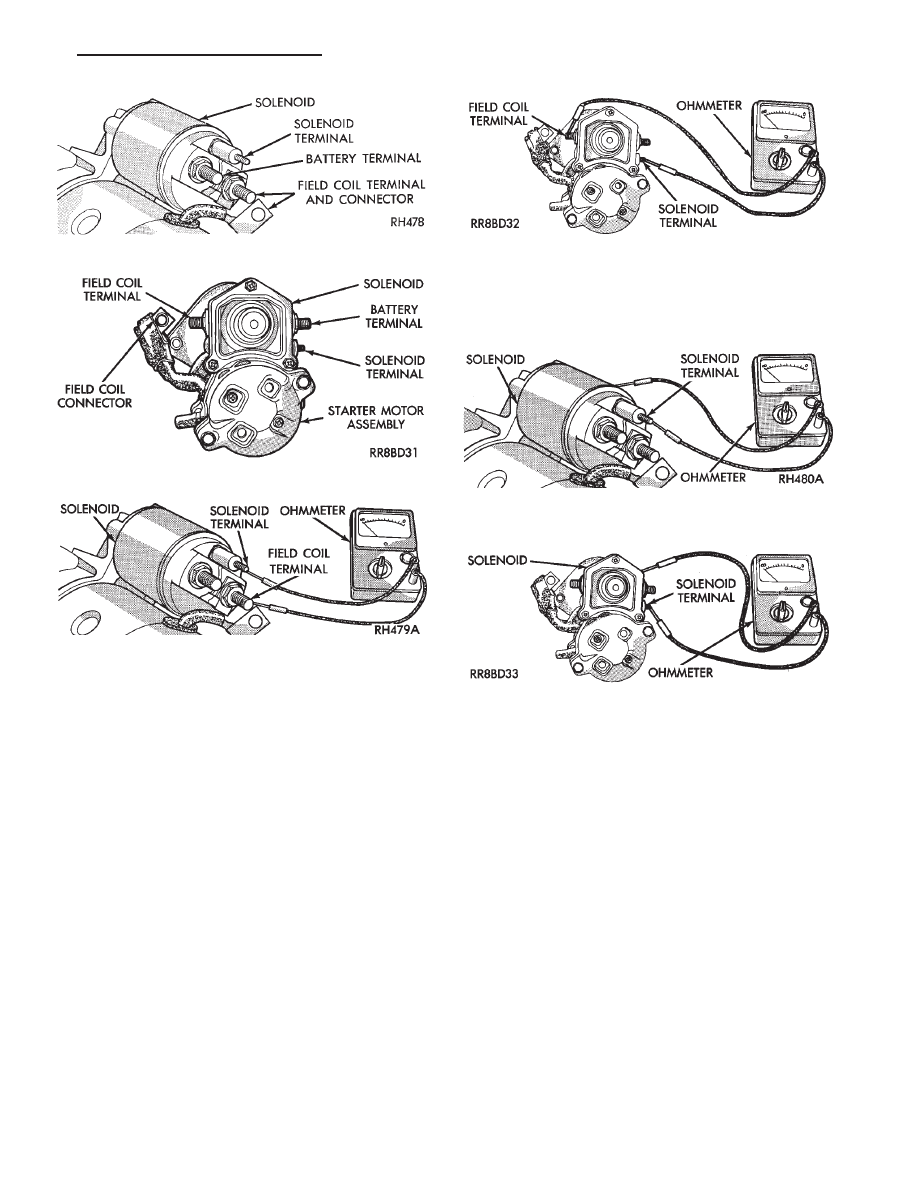
Fig. 15 Field Coil Wire Terminal—Bosch
Fig. 16 Field Coil Wire Terminal—Nippondenso
Fig. 17 Continuity Test Between Solenoid Terminal
and Field Coil Terminal—Bosch
Fig. 18 Continuity Test Between Solenoid Terminal
and Field Coil Terminal—Nippondenso
Fig. 19 Continuity Test Between Solenoid Terminal
and Solenoid Case —Bosch
Fig. 20 Continuity Test Between Solenoid Terminal
and Solenoid Case —Nippondenso
.
BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS
8A - 15