Hyundai Excavator R210LC-7. Service and repair manual - page 8
2-64
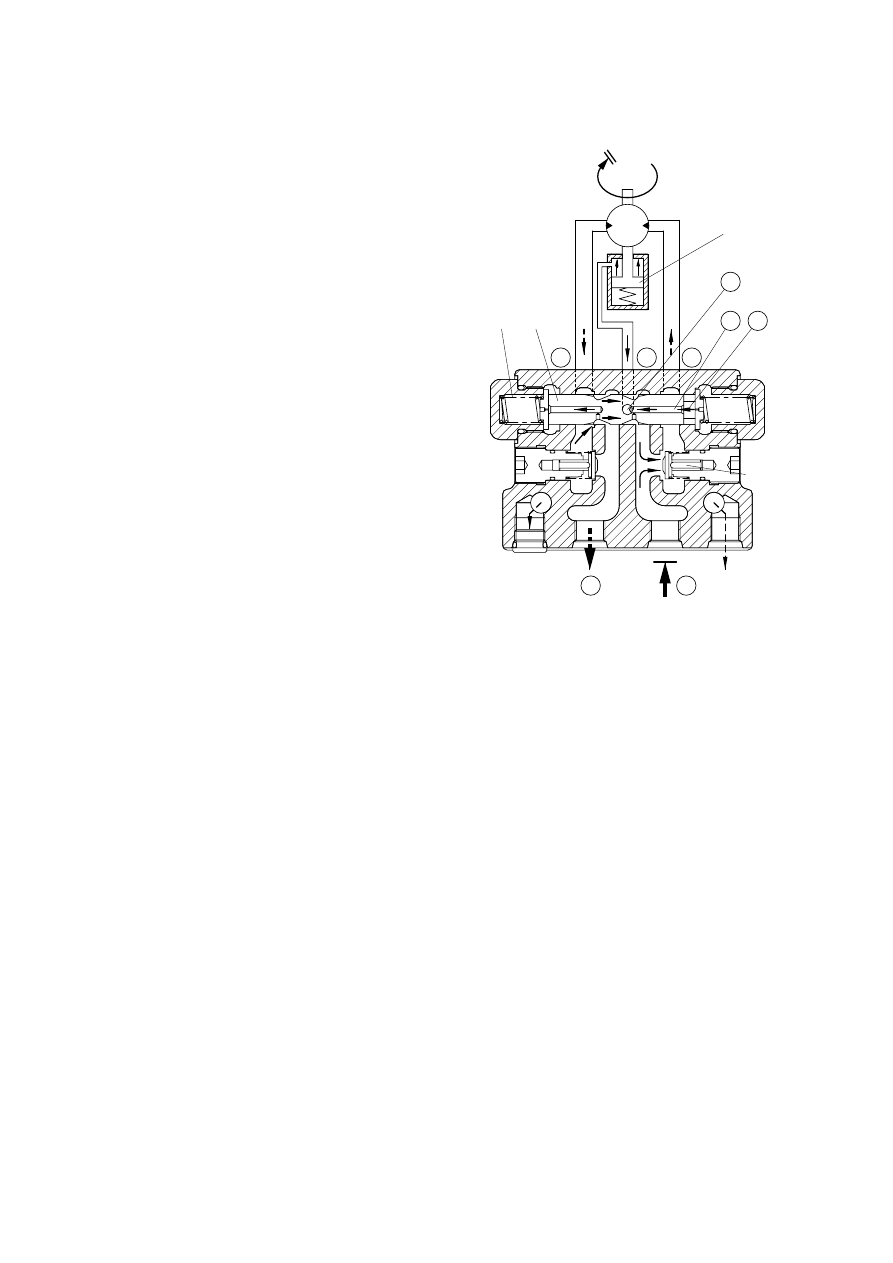
Braking effect on downhill travel
If the machine traveling downhill with a
relatively small supply of high pressure oil
to its travel motors should start coasting,
the same braking effect as the one
described above would automatically
occur.
In the coasting condition, the motor is
driven, instead of driving the track, from
the ground and sucks high pressure oil
in.
In other words, the motor tends to draw
more high pressure oil than is being
supplied.
Under this condition, port A goes
negative to pull oil out of chamber
through oil way
, moving back the
spool(323) rather rapidly.
The clearance on the left then becomes
smaller to throttle the outgoing oil more
than before, thereby obstructing the
pumping action of the motor.
As in stopping the machine, pressure will
build up in port D to make it harder to
drive the motor from the ground: This is
the braking action.
C
E
323
328
D
a
b
327
B
A
Drain
P
112