Hyundai Excavator R210LC-7. Service and repair manual - page 7
2-57
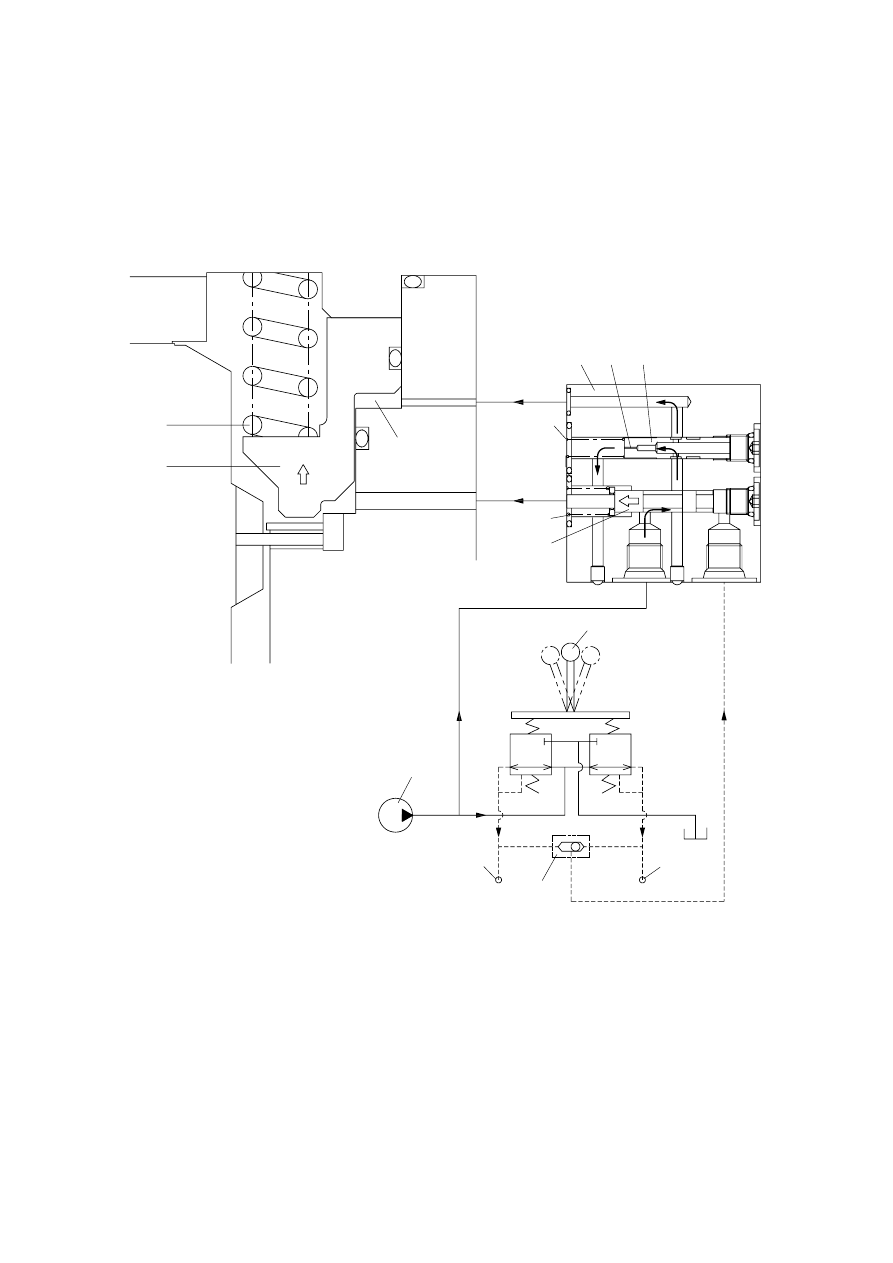
When the swing control(1) lever is set the neutral position, the spool(5) returns right in the time
delay valve(3).
Then, the piston(6) is moved lower by spring force and the return oil from the chamber G flows
back to D-port through orifice(10) of the poppet(7).
At this time, the poppet(7) works to make a time lag for 5 seconds.
1
Swing control lever
2
Swing control valve(MCV)
3
Time delay valve
4
Shuttle valve
5
Spool
6
Piston
7
Poppet
8
Spring
9
Spring
10
Orifice
11
Spring
12
Pilot pump
9
6
G
3
10
7
P
g
11
D
8
5
S
h
1
12
P
3
2
4
2
c.