Suzuki Grand Vitara JB419. Manual - part 126
Air Conditioning System: 7B-10
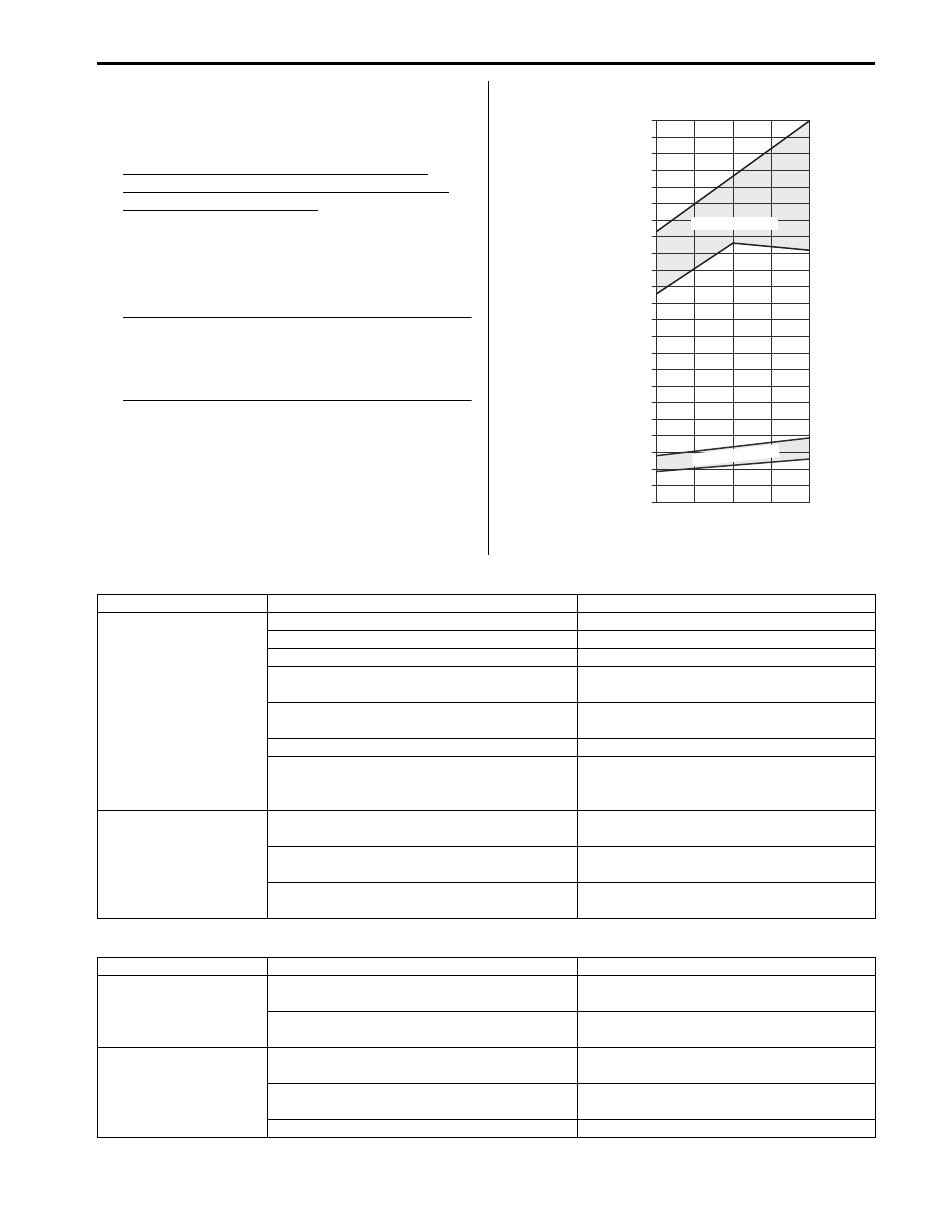
10) Check for each pressure of low side and high side if
it is within shaded range of graph. If each gauge
reading is out of specified pressure, correct defective
part referring to the table.
Low side and high side pressure example,
gauges should read as follows when ambient
temperature is 30
°C (86 °F)
Pressure on high pressure gauge (HI): 1570 –
1970 kPa (15.7 – 19.7 kg/cm
2
, 223 – 280 psi)
Pressure on high pressure gauge (LO): 230 – 330
kPa (2.3 – 3.3 kg/cm
2
, 33 – 47 psi)
NOTE
Pressure registered on gauge varies with
ambient temperature. Therefore, use the
graphs when determining if pressures are
normal or not.
High pressure gauge
Low pressure gauge
14.2
28.4
Pressure of Lo
Pressure Gauge
22
312.9
2200
0
1
23
327.1
2300
2
3
30
70
30
70
%
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
21
298.7
2100
20
42.7
56.9
71.1
85.3
99.5
113.8
128.0
142.2
151.4
170.6
184.9
199.1
213.3
227.5
241.7
256.0
270.2
284.4
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
1000
1100
1200
1300
1400
1500
1600
1700
1800
1900
2000
25
30
35
77
86
95
psi
kPa kg/cm
2
Ambient Temperature
C
F
w
Pressure of High Pressure
Gauge
“A”
“B”
“C”
“D”
Humidity
Acceptab
le range
Acceptable range
I5JB0B720006-03
Condition
Possible Cause
Correction
Pressure is higher than
acceptable range
(“A” area)
Refrigerant overcharged
Recharge.
Expansion valve frozen or clogged
Check expansion valve.
Clogged refrigerant passage of high side
Clean or replace.
Radiator cooling fan malfunction (Insufficient
cooling of condenser)
Check radiator cooling fan.
Dirty or bent condenser fins (Insufficient
cooling of condenser)
Clean or repair.
Compressor malfunction (Insufficient oil etc.) Check compressor.
Engine overheat
Check engine cooling system referring to
“Engine Cooling Symptom Diagnosis in
Section 1F”.
Pressure is lower than
acceptable range
(“B” area)
Insufficient refrigerant (Insufficient charge or
leakage)
Check for leakage, repair if necessary and
recharge.
Expansion valve malfunction (valve opens too
wide)
Check expansion valve.
Compressor malfunction (Insufficient
compression)
Check compressor.
Condition
Possible Cause
Correction
Pressure is higher than
acceptable range
(“C” area)
Expansion valve malfunction (valve opens too
wide)
Check expansion valve.
Compressor malfunction (Insufficient
compression)
Check compressor.
Pressure is lower than
acceptable range
(“D” area)
Insufficient refrigerant (Insufficient charge or
leakage)
Check for leakage, repair if necessary and
recharge.
Expansion valve malfunction (valve opens too
narrow)
Check expansion valve.
Clogged refrigerant passage (crashed pipe)
Repair or replace.