Dacia Solenza (engine E7J). Manual - part 174
88
WIRING
88 - 25
DISMOUNTING
Disconnect the battery (-) terminal.
Detach from clips the crane handle.
Dsimount the rear door panel (see chapter 72 “ Rear door panel”).
Dismount the rear door deflective panel.
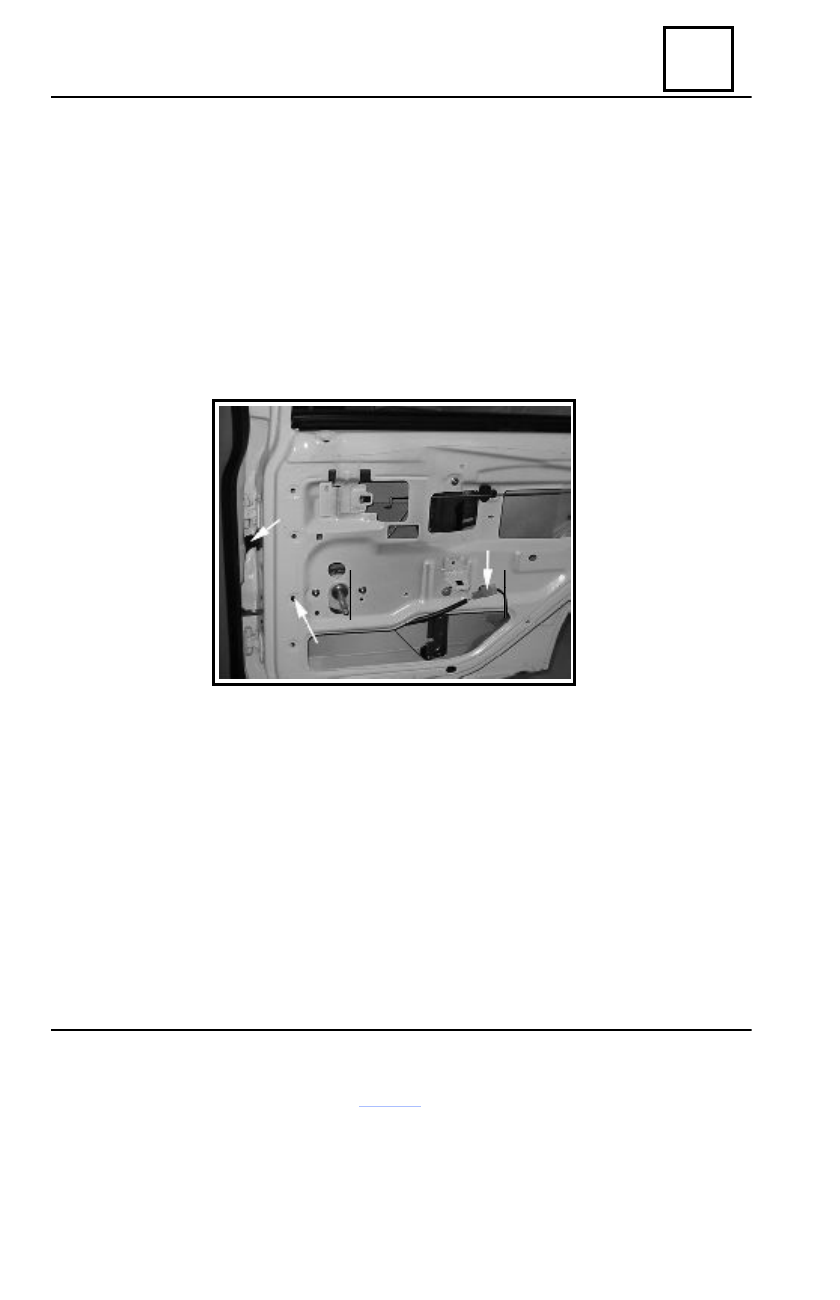
Dismount the attachment clip (1) of the rear wiring.
Disconnect and detach from clips actuator’s connector (2).
Remove the wiring protector (3) from the rear door and middle pillar. Mark the mounting
position of the protector.
Remove the rear wiring from the door. Mark the mounting position of the rear wiring.
Carefully remove protector off the wiring
1
2
3
Rear door wiring protector
REMOUNTING
Perform the dismounting operations in the reverse order, observing the mounting position
previously existent.
Replace the attachment clip (1).
Check the actuator’s operation and windows’ operation.