Isuzu KB P190. Manual - part 914
Battery
Page 6D1-3–16
N O T E
Charging a battery at higher current rates can
significantly reduce the life of the battery.
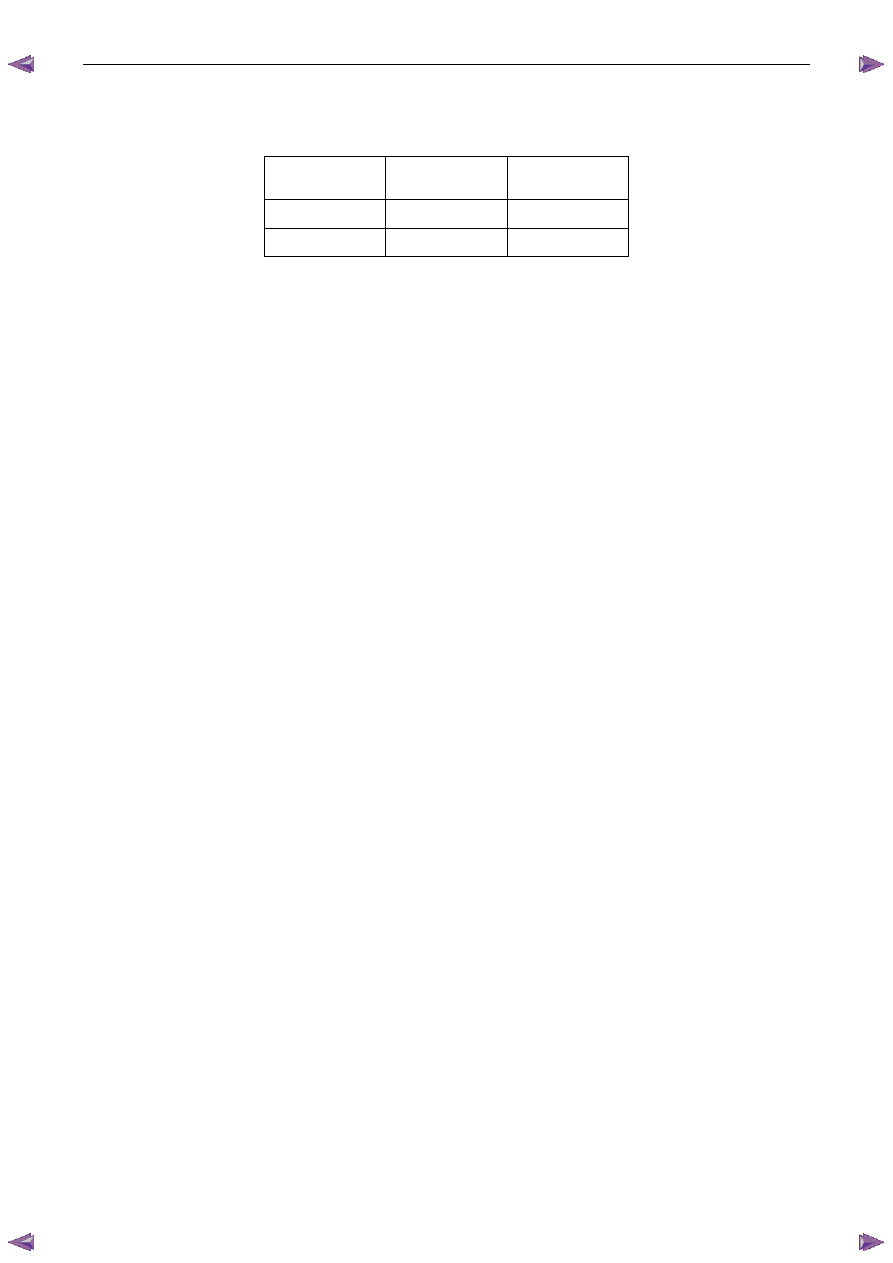
Charge Rate
Initial Current
Maximum Time
Required
Slow charge
4 A
24 hours
Fast charge
35 A
2 hours
6
After a few minutes, check the colour and specific gravity of the electrolyte. Refer to 3.3
Hydrometer Test.
7
Monitor the electrolyte temperature while the battery is charging. If the electrolyte temperature reaches 55
°C:
a
switch the charging current off,
b
allow the battery to cool,
c
reduce the charging current, and
d
restart charging the battery.
N O T E
For the best results, charge the battery with the
electrolyte and plates at room temperature. An
extremely cold battery may not appear to accept
current for several hours after starting the battery
charger. If the battery does not appear to accept
charge after several hours replace the battery.
8
For slow charging check the voltage and specific gravity each hour or more regularly for fast charging. Stop the
charging when there is no change in voltage or electrolyte specific gravity over three checks.
9
If the battery was fast charged connect the battery to a slow-charger for a few hours to bring the battery to the fully
charged condition. Ensure the last few hours of charge do not exceed 1 A.
10
Tighten the filler caps. Ensure they are secure.
11
Install the battery in the vehicle. Refer to 4.1
Battery.
4.3
Emergency Jump Starting Procedure
Safety Precautions
•
Read and obey the general safety precautions for working with batteries, refer to 2 Safety Precautions.
•
Do not allow the vehicles to touch each other during the jump starting procedure.
•
Ensure the assisting vehicle battery has the same voltage rating and connects negative to ground. If this is not the
case, serious injury and damage to electrical equipment can result.
•
Do not push or tow the vehicle to start it. Damage can result when unburnt fuel reaches the catalytic converter and
ignites.
•
Do not start the vehicle using a fast charger.
•
When using jumper leads, treat both the booster battery and the discharged battery with care.
•
Do not allow sparks, flame or smoking near the battery.
•
Ensure that metal tools or jumper cables do not simultaneously contact the battery positive terminal and any other
metal part of the vehicle.
Jump Starting Procedure
1
Position the assisting vehicle so the batteries of both vehicles are close together, refer to Figure 6D1-3 – 10.
2
Apply the park brake on both vehicles.
3
Ensure that P (park) is selected for automatic transmission and N (neutral) is selected for manual transmissions.