Ford Festiva. Instruction - part 60
VACUUM PUMP - DIESEL TROUBLE SHOOTING
VACUUM PUMP (DIESEL) TROUBLE SHOOTING CHART
MANUAL TRANSMISSION
MANUAL TRANSMISSION TROUBLE SHOOTING
MANUAL TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE TROUBLE SHOOTING
Clogged air bleeds
Remove restriction
EGR valve malfunction
Replace EGR valve
Restricted air cleaner filter
Replace air filter
Cracked or broken vacuum hoses
Replace vacuum hoses
Cracked or broken ignition wires
Replace ignition wires
Vacuum advance malfunction
Check unit and replace as
necessary
Defective or fouled spark plugs
Replace spark plugs
Ping or Spark Knock
Incorrect ignition timing
Reset ignition timing see
ENGINE PERFORMANCE
Distributor centrifugal or vacuum advance malfunction
Check operation and replace
as necessary
Carburetor setting too lean
Readjust mixture setting, see
ENGINE PERFORMANCE
Vacuum leak
Eliminate vacuum leak
EGR valve malfunction
Replace EGR valve
Poor Gasoline Mileage
Cracked or broken vacuum
Replace vacuum hoses hoses
Vacuum leaks
Repair vacuum leaks
Defective ignition wires
Replace wires
Incorrect choke setting
Readjust setting, see ENGINE
PERFORMANCE
Defective vacuum advance
Replace vacuum advance
Defective spark plugs
Replace spark plugs
Binding carburetor power piston
Eliminate binding
Dirt in carburetor jets
Clean and/or replace jets
Incorrect float adjustment
Readjust float setting, see
FUEL
Defective power valve
Replace power valve, see
ENGINE PERFORMANCE
Incorrect idle speed
Readjust idle speed
Engine Stalls
Improper float level
Readjust float level
Leaking needle valve and seat
Replace needle valve and seat
Vacuum leaks
Eliminate vacuum leaks
NOTE:
This is GENERAL information. This article is not intended to be specific to any unique situation or
individual vehicle configuration. The purpose of this Trouble Shooting information is to provide a list
of common causes to problem symptoms. For model-specific Trouble Shooting, refer to SUBJECT,
DIAGNOSTIC, or TESTING articles available in the section(s) you are accessing.
NOTE:
Diesel engines mechanical diagnosis is the same as gasoline engines for items such as noisy valves,
bearings, pistons, etc. The following trouble shooting covers only items pertaining to diesel engines.
CONDITION & POSSIBLE CAUSE
CORRECTION
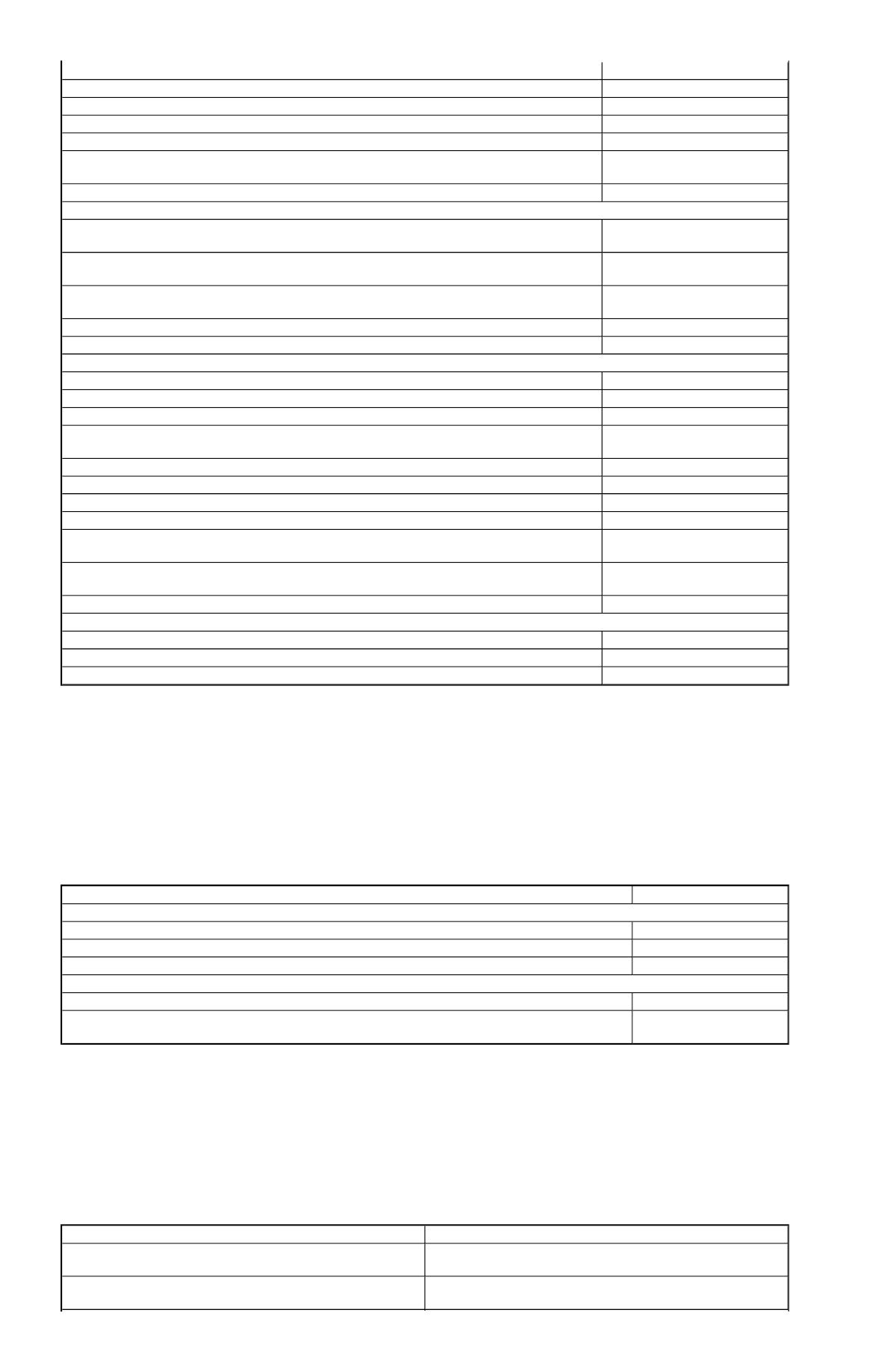
Excessive Noise
Loose pump-to-drive assembly screws
Tighten screws
Loose tube on pump assembly
Tighten tube
Valves not functioning properly
Replace valves
Oil Leakage
Loose end plug
Tighten end plug
Bad seal crimp
Remove and re-crimp
seal
NOTE:
This is GENERAL information. This article is not intended to be specific to any unique situation or
individual vehicle configuration. The purpose of this Trouble Shooting information is to provide a list
of common causes to problem symptoms. For model-specific Trouble Shooting, refer to SUBJECT,
DIAGNOSTIC, or TESTING articles available in the section(s) you are accessing.
Condition
Possible Cause
Noisy In Forward Gears
Low gear oil level, Loose bell housing bolts, Worn bearings or
gears
Clunk On Deceleration (FWD Only)
Loose engine mounts, Worn inboard CV joints, Worn differential
pinion shaft, Side gear hub counterbore in case worn oversize