Content .. 1572 1573 1574 1575 ..
Dodge Durango (HB). Manual - part 1574
4. Start the engine and allow it to idle. After the engine has reached normal operating temperature, allow the pas-
senger compartment to heat up. This will create the need for maximum refrigerant flow into the rear A/C evap-
orator.
5. If the refrigerant charge is sufficient, the discharge (high pressure) gauge should read 827 kPa to 1655 kPa (120
psi to 240 psi). The suction (low pressure) gauge should read 207 kPa to 345 kPa (30 psi to 50 psi). If OK, go
to Step 6. If not OK, replace the faulty rear A/C expansion valve.
WARNING:
Protect the skin and eyes from exposure to liquid CO
2
or personal injury can result.
6. If the suction (low pressure) gauge reads within the specified range, freeze the rear A/C expansion valve for 30
seconds using liquid CO
2
or another suitable super-cold material.Do not spray R-134a or R-12 refrigerant on
the rear A/C expansion valve for this test. The suction (low pressure) gauge reading should drop by 69 kPa
(10 psi). If OK, go to Step 7 If not OK, replace the faulty rear A/C expansion valve.
7. Allow the rear expansion valve control head to thaw. The suction (low pressure) gauge reading should stabilize
at 207 kPa to 345 kPa (30 psi to 50 psi). If not OK, replace the faulty rear A/C expansion valve.
8. When expansion valve testing is complete, test the overall A/C system performance (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C PERFORMANCE TEST).
REMOVAL
WARNING: Refer to the applicable warnings and cautions for this system before performing the following
operation (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - FRONT - WARNINGS) and (Refer to 24
- HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - FRONT - CAUTIONS). Failure to follow the warnings and cau-
tions could result in possible personal injury or death.
1. Recover the refrigerant from the refrigerant system
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - FRONT - STANDARD PROCEDURE
- REFRIGERANT SYSTEM RECOVERY).
2. Remove right rear quarter panel trim (Refer to 23 -
BODY/INTERIOR/QUARTER
PANEL
TRIM
-
REMOVAL).
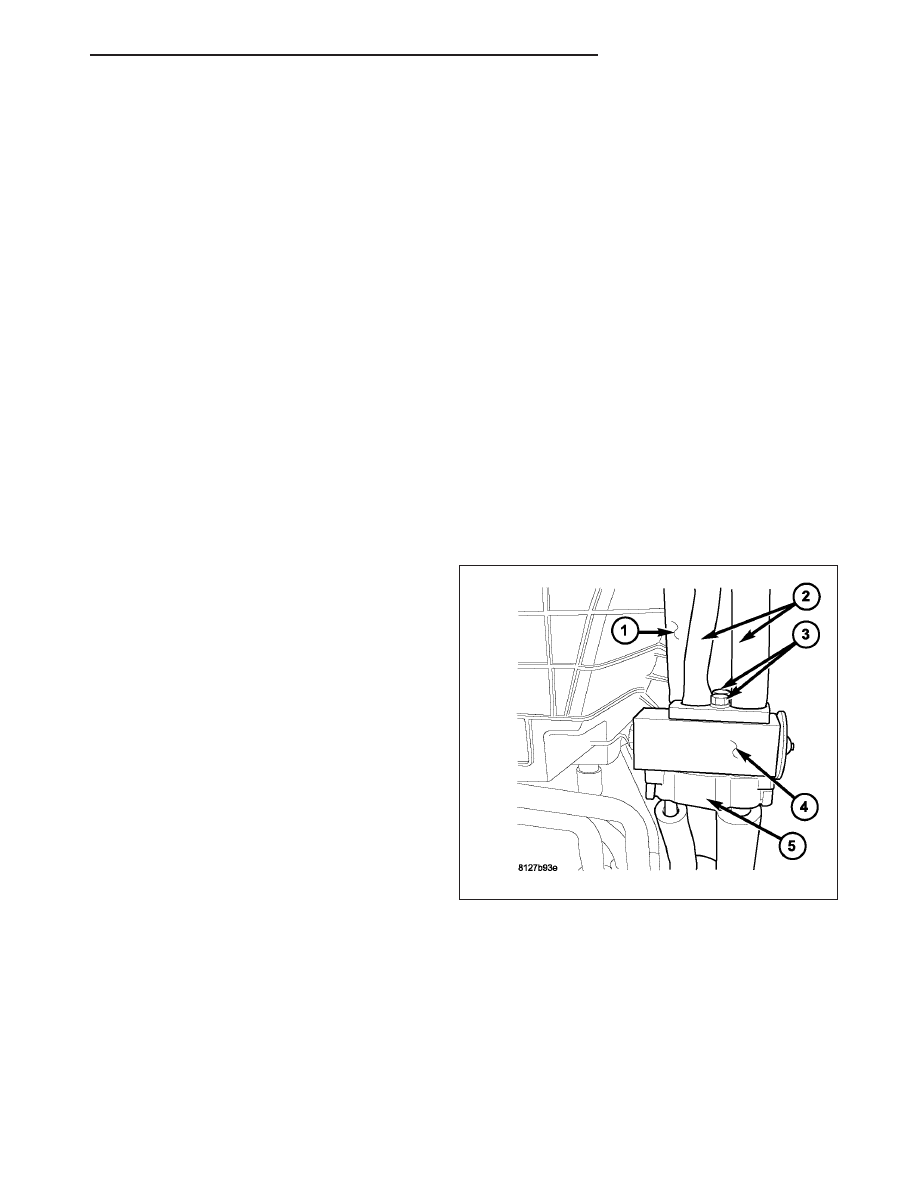
3. Remove the insulator (1) from around the rear A/C
evaporator tubes (2) to gain access the two rear
A/C expansion valve bolts (3).
4. Remove the two bolts that secure the rear A/C
expansion valve (4) between the rear A/C evapora-
tor tubes and the rear evaporator extension tube
tapping block (5).
5. Remove
the
rear A/C
expansion
valve
from
between the rear A/C evaporator tubes and the
rear evaporator extension tube tapping block and
remove and discard the O-ring seals.
6. Install plugs in, or tape over the opened evaporator tubes and extension tube fittings and all rear expansion valve
ports.
HB
PLUMBING - REAR
24 - 489