Dodge Dakota (R1). Manual - part 814
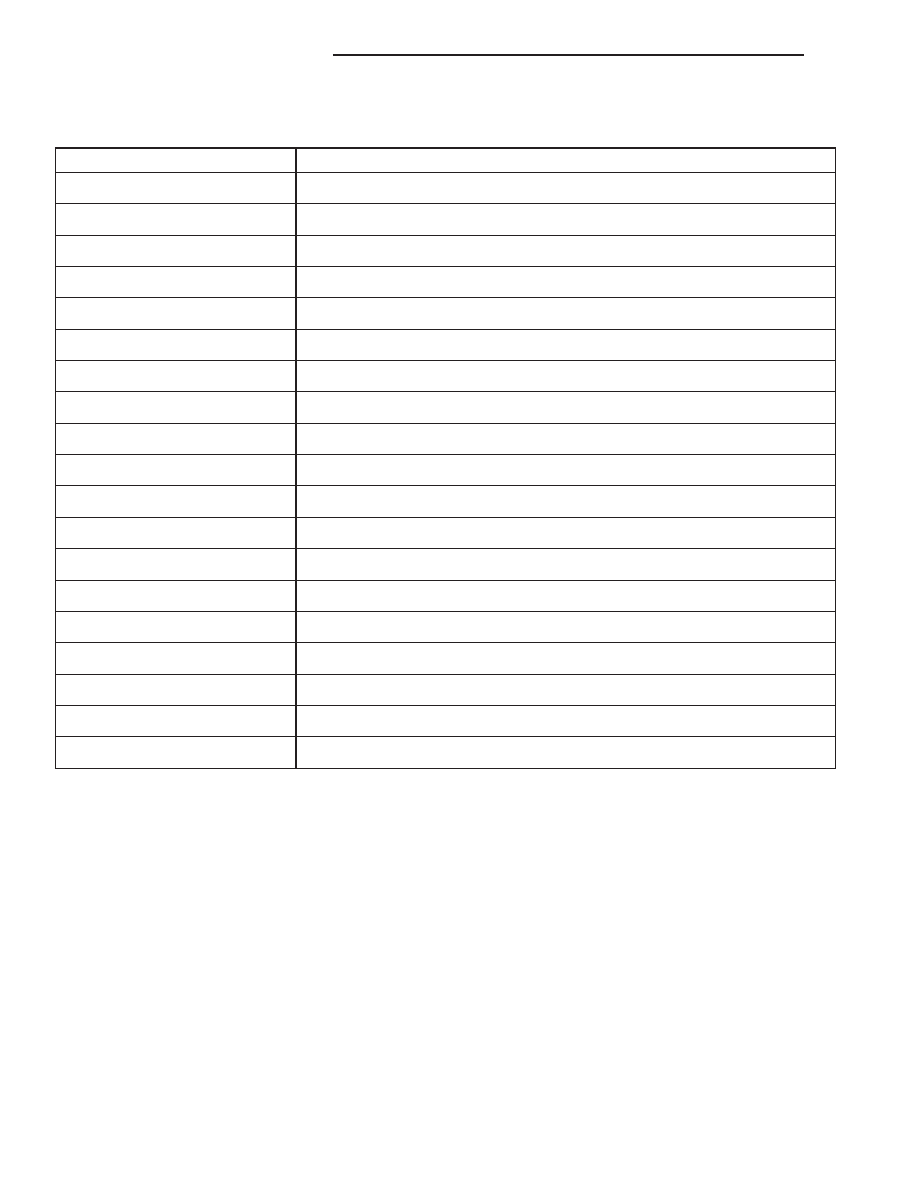
PCM DRBIII
T CODES
Generic Scan Tool Code
DRBIII
T
Scan Tool Display
P0117
Engine Coolant Volts Low
P0118
Engine Coolant Volts High
P0462
Fuel Level Sending Unit volts Too Low
P0463
Fuel Level Sending Unit volts Too High
P0500
Vehicle Speed Signal
P0522
Oil Pressure Sense Low
P0523
Oil Pressure Sense High
P0601
Internal Controller Failure
P0622
Generator Field Not Switching Properly
P1296
5 VDC Output
P1391
Loss of Cam or Crank
P1492
Ambient/Batt temp Sen Volts Too High
P1493
Ambient/Batt temp Sen Volts Too Low
P1594
Charging System Voltage Too High
P1682
Charge Output Low
P1685
SKIM Invalid Key
P1686
No SKIM Bus Message Recieved
P1687
No MIC Bus Message
P1696
PCM Failure EEPROM Write Denied
25a - 6
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS
R1
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS (Continued)