Dodge Dakota (R1). Manual - part 559
OPERATION
Voltage to operate the electric pump is supplied
through the fuel pump relay.
Fuel is drawn in through a filter at the bottom of
the module and pushed through the electric motor
gearset to the pump outlet.
Check Valve Operation: The pump outlet con-
tains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel flow back
into the tank and to maintain fuel supply line pres-
sure (engine warm) when pump is not operational. It
is also used to keep the fuel supply line full of gaso-
line when pump is not operational. After the vehicle
has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop to 0 psi
(cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline will remain
in fuel supply line between the check valve and fuel
injectors. Fuel pressure that has dropped to 0
psi on a cooled down vehicle (engine off) is a
normal condition. Refer to the Fuel Pressure Leak
Down Test for more information.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PUMP
PRESSURE TEST
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pump
Capacity Test, Fuel Pressure Leak Down Test and
Fuel Pump Amperage Test found elsewhere in this
group.
Check Valve Operation: The electric fuel pump
outlet contains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel
flow back into the tank and to maintain fuel supply
line pressure (engine warm) when pump is not oper-
ational. It is also used to keep the fuel supply line
full of gasoline when pump is not operational. After
the vehicle has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop
to 0 psi (cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline will
remain in fuel supply line between the check valve
and
fuel
injectors.
Fuel
pressure
that
has
dropped to 0 psi on a cooled down vehicle
(engine off) is a normal condition. When the elec-
tric fuel pump is activated, fuel pressure should
immediately (1–2 seconds) rise to specification.
All fuel systems are equipped with a fuel tank
module mounted, combination fuel filter/fuel pressure
regulator. The fuel pressure regulator is not con-
trolled by engine vacuum.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER CON-
STANT FUEL PRESSURE EVEN WITH THE ENGINE
OFF. BEFORE DISCONNECTING FUEL LINE AT
FUEL RAIL, THIS PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED.
REFER
TO
THE
FUEL
SYSTEM
PRESSURE
RELEASE PROCEDURE.
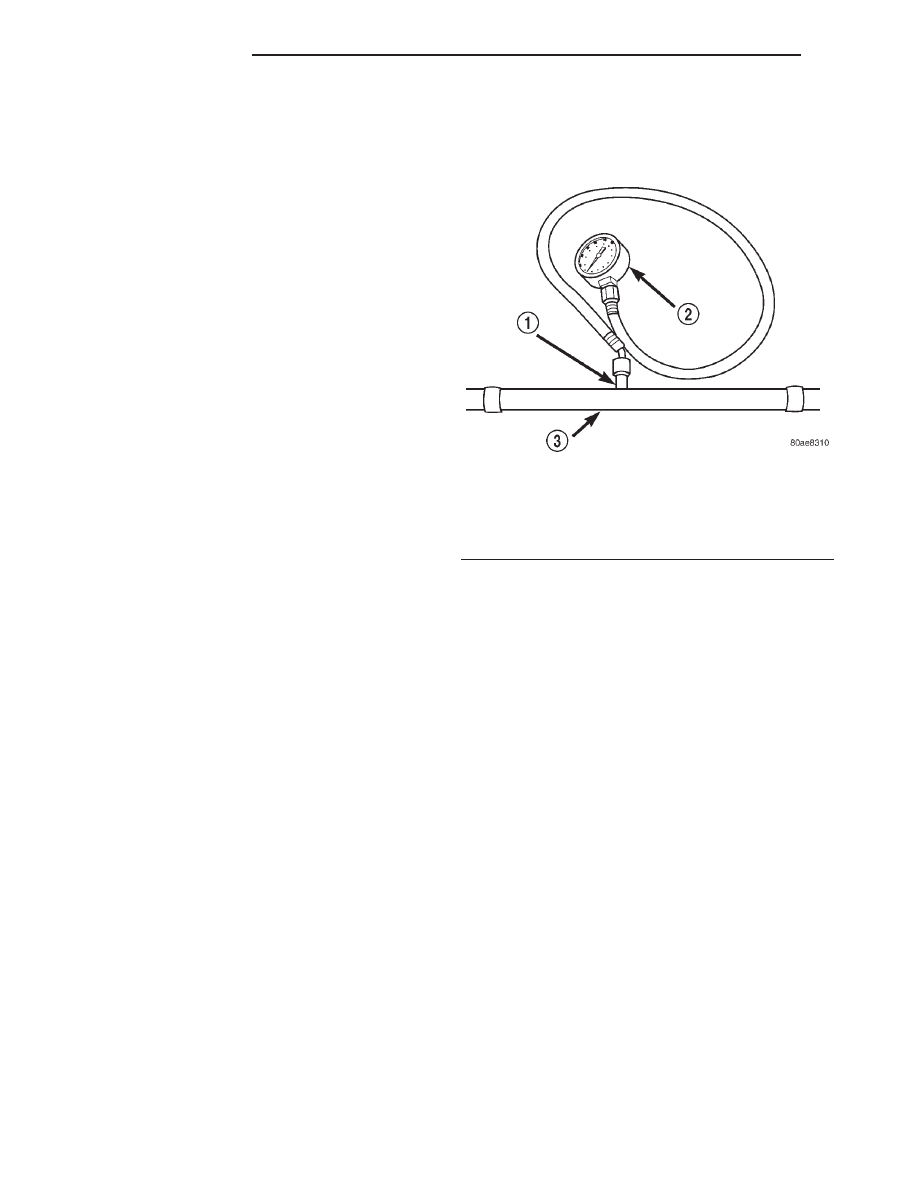
(1) Remove protective cap at fuel rail test port.
Connect the 0–414 kPa (0-60 psi) fuel pressure gauge
(from gauge set 5069) to test port pressure fitting on
fuel rail (Fig. 7). The DRB
t III Scan Tool along
with the PEP module, the 500 psi pressure
transducer,
and
the
transducer-to-test
port
adapter may also be used in place of the fuel
pressure gauge.
(2) Start and warm engine and note pressure
gauge reading. Fuel pressure should be 339 kPa ± 34
kPa (49.2 psi ± 5 psi) at idle.
(3) If engine runs, but pressure is below 44.2 psi,
check for a kinked fuel supply line somewhere
between fuel rail and fuel pump module. If line is not
kinked, but specifications for either the Fuel Pump
Capacity, Fuel Pump Amperage or Fuel Pressure
Leak Down Tests were not met, replace fuel pump
module
assembly.
Refer
to
Fuel
Pump
Module
Removal/Installation.
(4) If operating pressure is above 54.2 psi, electric
fuel pump is OK, but fuel pressure regulator is defec-
tive. Replace fuel filter/fuel pressure regulator. Refer
to Fuel Filter/Fuel Pressure Regulator Removal/In-
stallation for more information.
(5) Install protective cap to fuel rail test port.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PUMP
CAPACITY TEST
Before performing this test, verify fuel pump
pressure. Refer to Fuel Pump Pressure Test.
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pres-
sure Leak Down Test.
(1) Release fuel system pressure. Refer to Fuel
Pressure Release Procedure.
(2) Disconnect fuel supply line at fuel rail. Refer to
Quick-Connect Fittings. Some engines may require
air cleaner housing removal before line disconnection.
Fig. 7 Fuel Pressure Test Gauge (Typical Gauge
Installation at Test Port)
1 - SERVICE (TEST) PORT
2 - FUEL PRESSURE TEST GAUGE
3 - FUEL RAIL
14 - 8
FUEL DELIVERY
AN
FUEL PUMP (Continued)