Dodge Dakota (R1). Manual - part 511
(8) Disconnect
accelerator
linkage
and
if
so
equipped, the speed control and transmission kick-
down cables.
(9) Remove distributor cap and wires.
(10) Disconnect the coil wires.
(11) Disconnect heat indicator sending unit wire.
(12) Disconnect heater hoses and bypass hose.
(13) Remove cylinder head covers and gaskets
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLIN-
DER HEAD COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(14) Remove
intake
manifold
(Refer
to
9
-
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE
MANIFOLD
-
REMOVAL) and throttle body as an assembly. Dis-
card the flange side gaskets and the front and rear
cross-over gaskets.
(15) Remove exhaust manifolds (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/EXHAUST
MANIFOLD
-
REMOVAL).
(16) Remove rocker arm assemblies and push rods.
Identify to ensure installation in original locations.
(17) Remove the head bolts from each cylinder
head and remove cylinder heads. Discard the cylin-
der head gasket.
(18) Remove spark plugs.
CLEANING
Clean all surfaces of cylinder block and cylinder
heads.
Clean cylinder block front and rear gasket surfaces
using a suitable solvent.
INSPECTION
Inspect all surfaces with a straightedge if there is
any reason to suspect leakage. If out-of-flatness
exceeds
0.00075mm/mm
(0.0001in./in.)
times
the
span length in any direction, either replace head or
lightly machine the head surface.
FOR EXAMPLE:—A 305 mm (12 in.) span is
0.102 mm (0.004 in.) out-of-flat. The allowable out-of-
flat is 305 x 0.00075 (12 x 0.00075) equals 0.23 mm
(0.009 in.). This amount of out-of-flat is acceptable.
The
cylinder
head
surface
finish
should
be
1.78-3.00 microns (70-125 microinches).
Inspect push rods. Replace worn or bent rods.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean all surfaces of cylinder block and cylin-
der heads.
(2) Clean cylinder block front and rear gasket sur-
faces using a suitable solvent.
(3) Position new cylinder head gaskets onto the
cylinder block.
(4) Position cylinder heads onto head gaskets and
cylinder block.
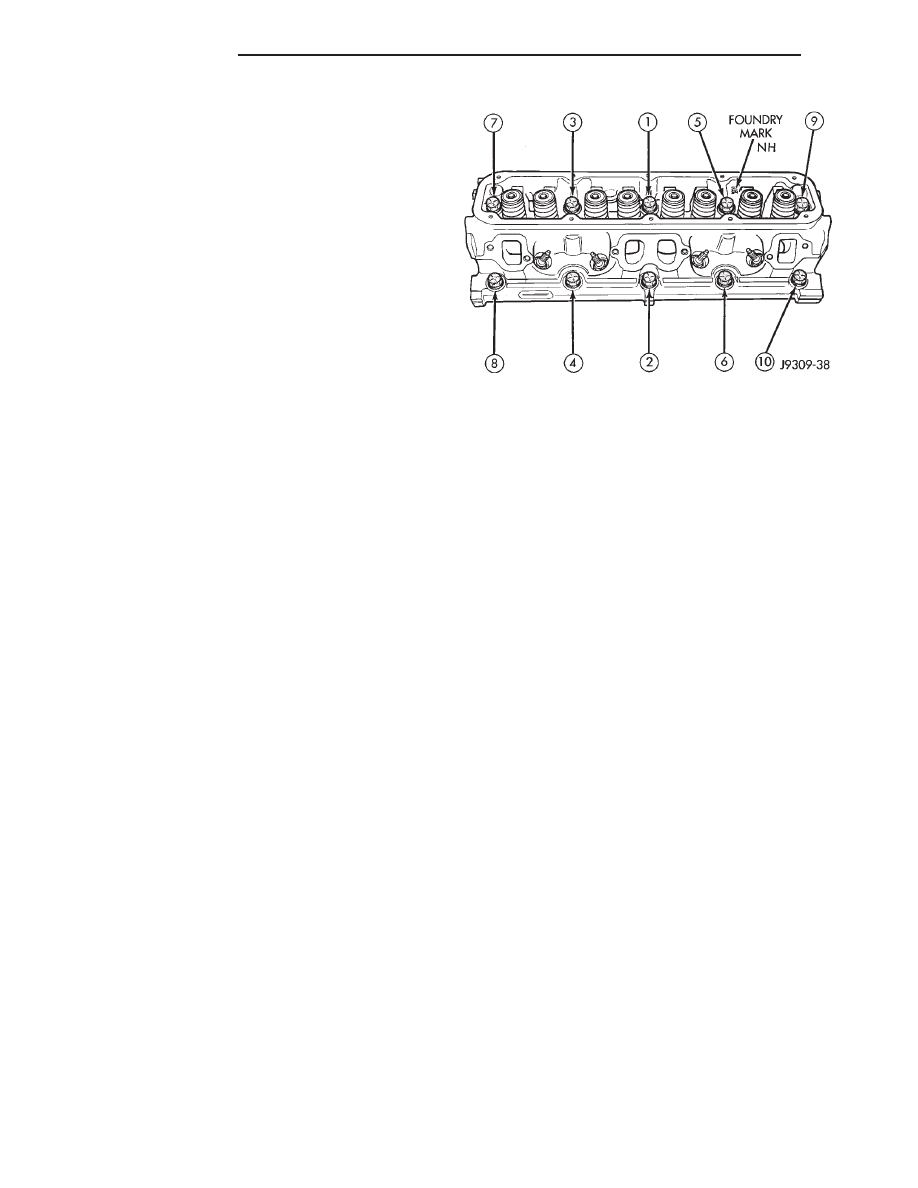
(5) Starting at top center, tighten all cylinder head
bolts, in sequence (Fig. 6).
CAUTION: When tightening the rocker arm bolts,
make sure the piston in that cylinder is NOT at
TDC. Contact between the valves and piston could
occur.
(6) Install push rods and rocker arm assemblies in
their original position. Tighten the bolts to 28 N·m
(21 ft. lbs.) torque.
(7) Install the intake manifold (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE
MANIFOLD
-
INSTALLATION) and throttle body assembly.
(8) Install
exhaust
manifolds
(Refer
to
9
-
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/EXHAUST
MANIFOLD
-
INSTALLATION).
(9) If required, adjust spark plugs to specifications.
Install the plugs and tighten to 41 N·m (30 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(10) Install coil wire.
(11) Connect heat indicator sending unit wire.
(12) Connect the heater hoses and bypass hose.
(13) Install distributor cap and wires.
(14) Connect the accelerator linkage and if so
equipped, the speed control and transmission kick-
down cables.
(15) Install the fuel supply line (Refer to 14 -
FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL
DELIVERY/QUICK
CON-
NECT FITTING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(16) Install the generator and drive belt (Refer to 7
- COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION). Tighten generator mounting bolt
to 41 N·m (30 ft. lbs.) torque. Tighten the adjusting
strap bolt to 23 N·m (200 in. lbs.) torque.
(17) Install
the
intake
manifold-to-generator
bracket support rod. Tighten the bolts.
(18) Place the cylinder head cover gaskets in posi-
tion and install cylinder head covers (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/CYLINDER
HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(19) Install closed crankcase ventilation system.
Fig. 6 Cylinder Head Bolt Tightening Sequence
9 - 232
ENGINE 5.9L
AN
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)