Dodge Dakota (R1). Manual - part 236
(17) Install wheel and tire assembly. (Refer to 22 -
TIRES/WHEELS/WHEELS - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
ADJUSTMENTS - REAR DRUM BRAKE
The rear drum brakes are equipped with a self-ad-
justing mechanism. Under normal circumstances, the
only time adjustment is required is when the shoes
are replaced, removed for access to other parts, or
when one or both drums are replaced.
Adjustment can be made with a standard brake
gauge or with adjusting tool. Adjustment is per-
formed with the complete brake assembly installed
on the backing plate.
ADJUSTMENT WITH BRAKE GAUGE
(1) Be sure parking brakes are fully released.
(2) Raise rear of vehicle and remove wheels and
brake drums.
(3) Verify that left and right automatic adjuster
levers and cables are properly connected.
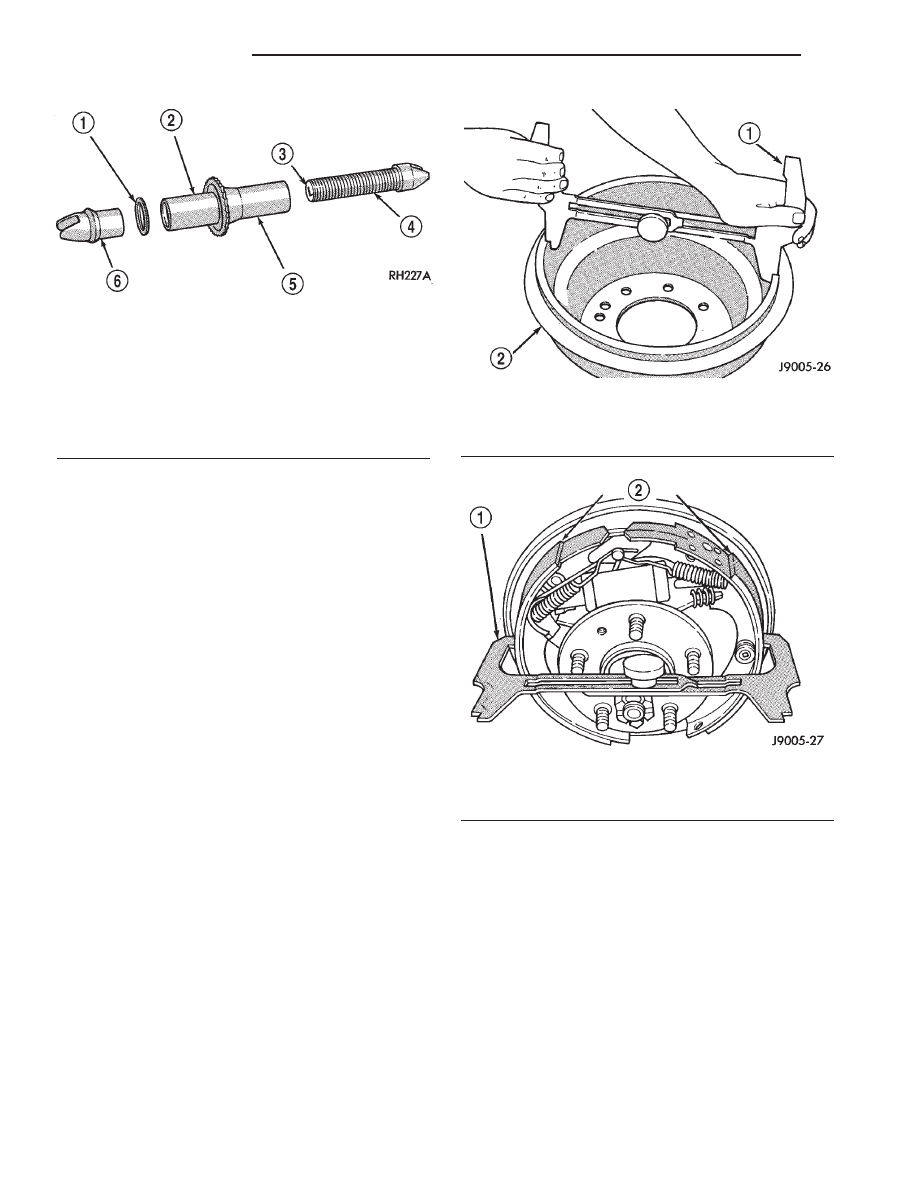
(4) Insert brake gauge in drum. Expand gauge
until gauge inner legs contact drum braking surface.
Then lock gauge in position (Fig. 31).
(5) Reverse gauge and install it on brake shoes.
Position gauge legs at shoe centers as shown (Fig.
32). If gauge does not fit (too loose/too tight), adjust
shoes.
(6) Pull shoe adjuster lever away from adjuster
screw star wheel.
(7) Turn adjuster screw star wheel (by hand) to
expand or retract brake shoes. Continue adjustment
until gauge outside legs are light drag-fit on shoes.
(8) Install brake drums and wheels and lower
vehicle.
(9) Drive vehicle and make one forward stop fol-
lowed by one reverse stop. Repeat procedure 8-10
times to operate automatic adjusters and equalize
adjustment.
NOTE: Bring vehicle to complete standstill at each
stop. Incomplete, rolling stops will not activate
automatic adjusters.
ADJUSTMENT WITH ADJUSTING TOOL
(1) Be sure parking brake lever is fully released.
(2) Raise vehicle so rear wheels can be rotated
freely.
(3) Remove plug from each access hole in brake
support plates.
Fig. 30 Adjuster Screw
1 - WASHER
2 - SOCKET
3 - STAMPED LETTER
L-LEFT BRAKE
R-RIGHT BRAKE
4 - SCREW THREADS
5 - NUT
6 - BUTTON
Fig. 31 Adjusting Gauge On Drum
1 - BRAKE GAUGE
2 - BRAKE DRUM
Fig. 32 Adjusting Gauge On Brake Shoes
1 - BRAKE GAUGE
2 - BRAKE SHOES
5 - 20
BRAKES - BASE
AN
DRUM (Continued)