Dodge Dakota (R1). Manual - part 187
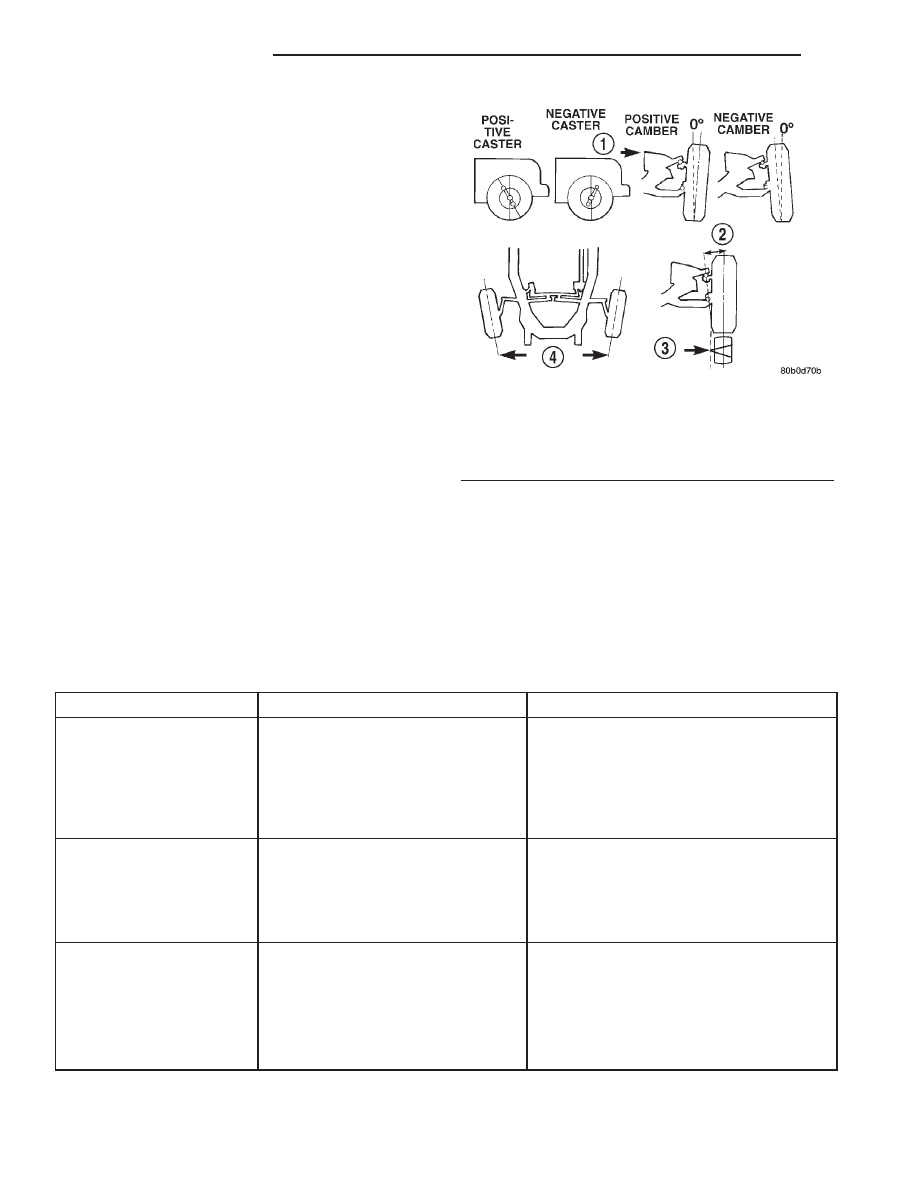
Tilting the top of the wheel outward provides positive
camber. Incorrect camber will cause wear on the
inside or outside edge of the tire (Fig. 2).
• TOE is the difference between the leading inside
edges and trailing inside edges of the front tires.
Wheel toe position out of specification cause’s unsta-
ble steering, uneven tire wear and steering wheel off-
center. The wheel toe position is the final front
wheel alignment adjustment (Fig. 2).
• THRUST ANGLE is the angle of the rear axle
relative to the centerline of the vehicle. Incorrect
thrust angle can cause off-center steering and exces-
sive tire wear. This angle is not adjustable, damaged
component(s) must be replaced to correct the thrust
angle (Fig. 2).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRE-ALIGNMENT
INSPECTION
Before starting wheel alignment, the following
inspection and necessary corrections must be com-
pleted. Refer to Suspension and Steering System
Diagnosis Chart for additional information.
(1) Inspect tires for size, air pressure and tread
wear.
(2) Inspect front wheel bearings for wear.
(3) Inspect front wheels for excessive radial or lat-
eral runout and balance.
(4) Inspect ball studs, linkage pivot points and
steering gear for looseness, roughness or binding.
(5) Inspect suspension components for wear and
noise.
(6) On 4x4 vehicles check suspension height.
(7) Road test the vehicle.
SUSPENSION AND STEERING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION
POSSIBLE CAUSES
CORRECTION
FRONT END NOISE
1. Loose or worn wheel bearing.
1. Replace wheel bearing.
2. Loose or worn steering or
suspension components.
2. Tighten or replace components as
necessary.
3. Lower ball joint (4x4).
3. Gease joint and perform diagnosis and
testing.
EXCESSIVE PLAY IN
STEERING
1. Loose or worn wheel bearing.
1. Replace wheel bearing.
2. Loose or worn steering or
suspension components.
2. Tighten or replace components as
necessary.
3. Loose or worn steering gear.
3. Adjust or replace steering gear.
FRONT WHEELS SHIMMY
1. Loose or worn wheel bearing.
1. Replace wheel bearing.
2. Loose or worn steering or
suspension components.
2. Tighten or replace components as
necessary.
3. Tires worn or out of balance.
3. Replace or balance tires.
4. Alignment.
4. Align vehicle to specifications.
Fig. 2 Wheel Alignment
1 - FRONT OF VEHICLE
2 - STEERING AXIS INCLINATION
3 - PIVOT POINT
4 - TOE-IN
2 - 2
WHEEL ALIGNMENT
AN
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)