Acura CSX. Manual - part 401
03
02
ABS Features
Anti-lock control
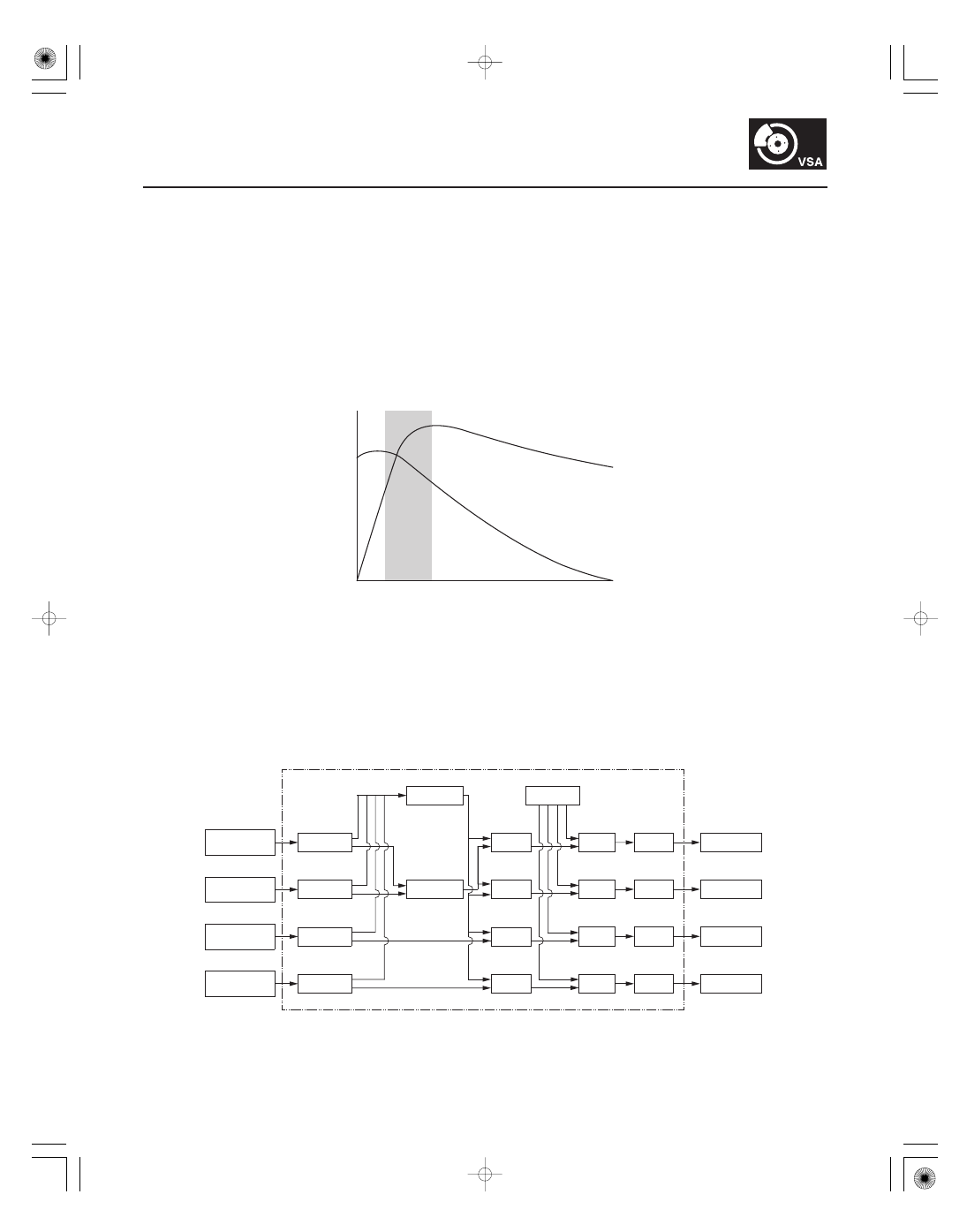
Grip force of tire and road surface
Main Control
19-109
COEFFICIENT OF
FRICTION
TARGET SLIP RATE
ROTATIONAL
DIRECTION
RADIAL
DIRECTION
OF THE
ROTATIONAL
DIRECTION
SLIP RATE
LEFT-REAR
WHEEL SPEED
SENSOR
RIGHT-REAR
WHEEL SPEED
SENSOR
LEFT-FRONT
WHEEL SPEED
SENSOR
RIGHT-FRONT
WHEEL SPEED
SENSOR
Select Low
Speed Wheel
Detect
Vehicle Speed
Drive
Solenoid
RIGHT-REAR
SOLENOID
LEFT-REAR
SOLENOID
RIGHT-FRONT
SOLENOID
LEFT-FRONT
SOLENOID
CONTROL UNIT
ABS
Control
Reference
Slip Rate
Drive
Solenoid
ABS
Control
Drive
Solenoid
ABS
Control
Drive
Solenoid
ABS
Control
RIGHT-FRONT
LEFT-FRONT
Detect
Wheel Speed
Detect
Slip Rate
RIGHT-REAR
LEFT-REAR
Detect
Slip Rate
Detect
Slip Rate
Detect
Slip Rate
Detect
Wheel Speed
Detect
Wheel Speed
Detect
Wheel Speed
Without ABS, when the brake pedal is pressed while driving, the wheels sometimes lock before the vehicle comes to a
stop. In such an event, the maneuverability of the vehicle is reduced if the front wheels are locked, and the stability of
the vehicle is reduced if the rear wheels are locked, creating an extremely unstable condition. With ABS, the system
precisely controls the slip rate of the wheels to ensure maximum grip force from the tires, and it thereby ensures
maneuverability and stability of the vehicle. The ABS calculates the slip rate of the wheels based on the four wheel
speeds, and then it controls the brake fluid pressure to reach the target slip rate.
The control unit detects the wheel speed based on the wheel speed sensor signals it receives, then it calculates the
vehicle speed based on the detected wheel speed. The control unit detects the vehicle speed during deceleration
based on the wheel speeds.
The control unit calculates the slip rate of each wheel, and transmits the control signal to the modulator unit solenoid
valve when the slip rate is high.
The hydraulic control has three modes: Pressure intensifying, pressure reducing, and pressure retaining.
08/08/21 15:04:53 61SNR030_190_0109