Subaru Legacy IV (2008 year). Manual - part 194
GD(H4SO)-78
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Detecting Criteria
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
AS:DTC P0223 THROTTLE/PEDAL POSITION SENSOR/SWITCH “B” CIRCUIT
HIGH
1. OUTLINE OF DIAGNOSIS
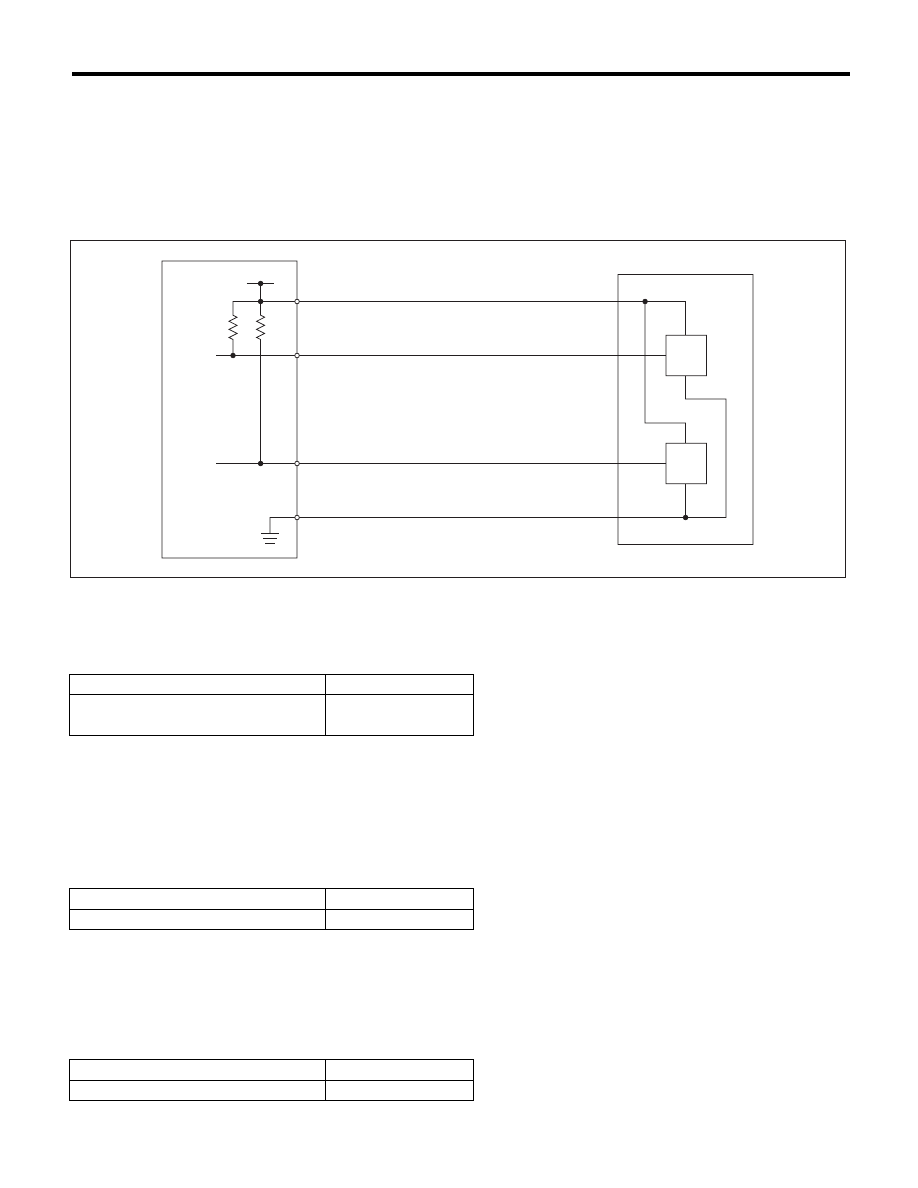
Detect the open or short circuit of throttle position sensor 2.
Judge as NG if out of specification.
2. COMPONENT DESCRIPTION
3. ENABLE CONDITION
4. GENERAL DRIVING CYCLE
Always perform the diagnosis continuously.
5. DIAGNOSTIC METHOD
• Abnormality Judgement
If the duration of time while the following conditions are met is longer than the time indicated, judge as NG.
Time Needed for Diagnosis: 24 ms
Malfunction Indicator Light Illumination: Illuminates as soon as a malfunction occurs.
• Normality Judgement
Judge as OK and clear the NG if the continuous time while the following conditions are established is more
than the predetermined time.
Time Needed for Diagnosis: 24 ms
(1)
Throttle position sensor 1 signal
(3)
Throttle position sensor
(4)
Engine control module (ECM)
(2)
Throttle position sensor 2 signal
Secondary Parameters
Enable Conditions
Ignition switch
ON
Battery voltage
t 6 V
Judgement Value
Malfunction Criteria
Threshold Value
Sensor 2 input voltage
t 4.858 V
Judgement Value
Malfunction Criteria
Threshold Value
Sensor 2 input voltage
< 4.858 V
EN-01859
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)