SsangYong Korando III (2010 year). Manual - part 368
15-17
0000-00
(3) Accelerometer Control
a. Resetting the pilot injection
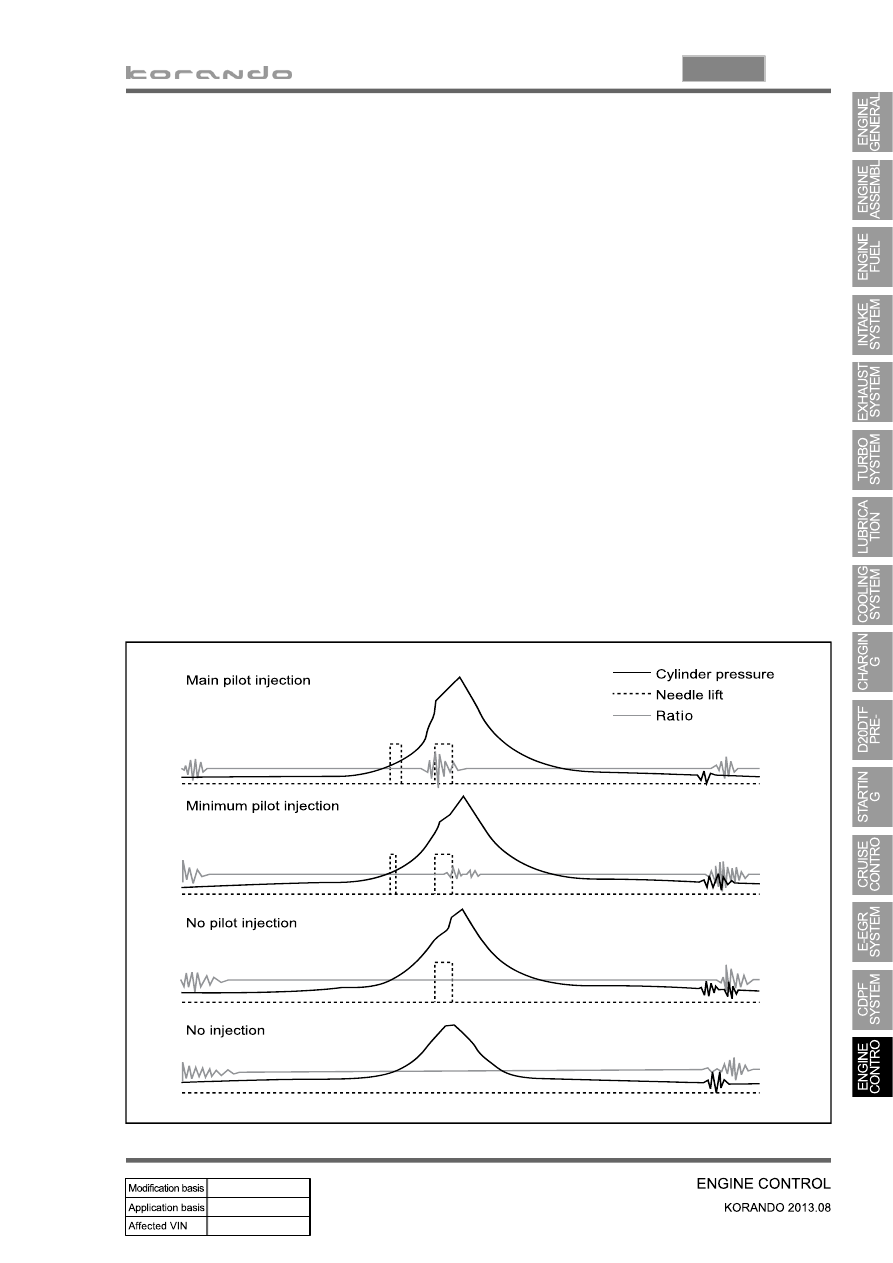
The accelerometer is used to reset the pilot injection flow in closed loop for each injector. This method
allows the correction of any injector deviations over a period of time. The principle of use of the
accelerometer is based on the detection of the combustion noises.
The sensor is positioned in such a way as to receive the maximum signal for all the cylinders. The raw
signals from the accelerometer are processed to obtain a variable which quantifies the intensity of the
combustion. This variable, known as the ratio, consists of the ratio between the intensity of the
background noise and the combustion noise.
A first window is used to establish the background noise level of the accelerometer signal for each
cylinder. This window must therefore be positioned at a moment when there cannot be any
combustion.
The second window is used to measure the intensity of the pilot combustion. Its position is such that
only the combustion noises produced by the pilot injection are measured . It is therefore placed just
before the main injection.
1.
2.
The accelerometer does not allow any evaluation of the quantity injected. However, the pulse value will
be measured when the injector starts injection and this pulse value is called the MDP (Minimum Drive
Pulse). On the basis of this information, it is possible to efficiently correct the pilot flows. The pilot
injection resetting principle therefore consists of determining the MDP, in other words the pulse
corresponding to the start of the increase in value of the ratio (increase of vibration due to fuel
combustion).