SsangYong Korando III (2010 year). Manual - part 94
02-28
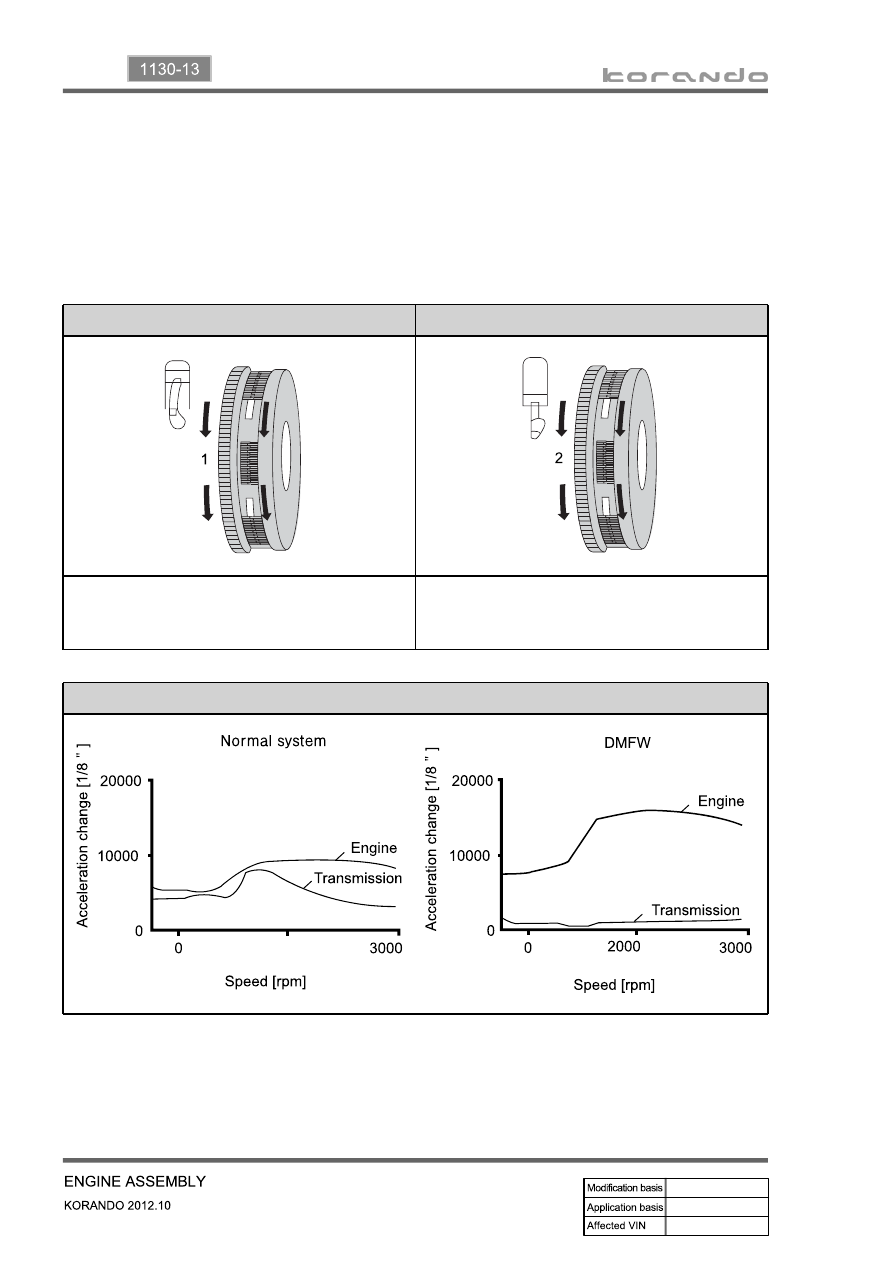
2) Operation of DMF
Compensating the irregular operation of engine: The secondary flywheel operates almost evenly so
does not cause gear noises
The mass of the primary flywheel is less than conventional flywheel so the engine irregularity
increases more (less pulsation absorbing effect).
Transaxle protection function: Reduces the torsional vibration to powertrain (transaxle) by reducing
the irregularity of engine.
-
-
-
Compression stroke
Combustion stroke
Small changes from engine (k):
Damper increases the torque changes to clutch
Large changes from engine (j):
Damper decreases the torque changes to
transaxle by absorbing the impact
Torque change curve of engine and drive shaft