Nissan Almera Tino V10 (2001 year). Manual - part 156
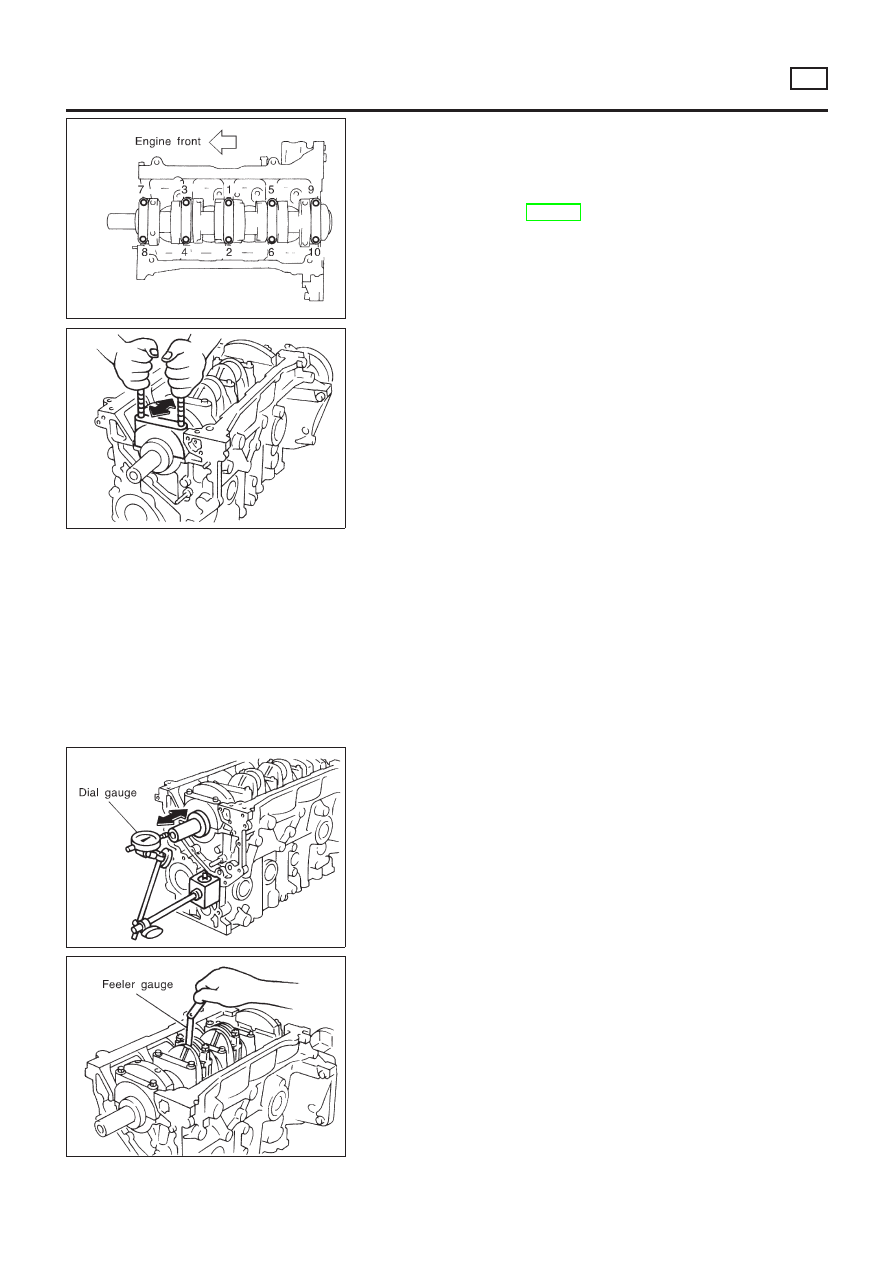
JEM200G
13. Remove main bearing cap bolts.
+
With a TORX socket (size: E-14, Commercial Service Tool),
loosen main bearing cap bolts in several stages in the reverse
order of that shown in the figure and remove them.
+
Before loosening main bearing cap bolts, measure crankshaft
end play. Refer to EM-225, “CRANKSHAFT END PLAY”.
JEM201G
14. Remove main bearing caps.
+
Using main bearing cap bolts, remove by rocking bearing cap
back and forth.
15. Remove crankshaft.
16. Remove main bearings and thrust bearings from cylinder block
and main bearing caps.
+
Check the correct installation locations of removed parts.
Store them so they do not get mixed up.
17. Remove oil jet.
18. Remove oil jet check valve.
JEM202G
Inspection
NLEM0073
CRANKSHAFT END PLAY
NLEM0073S13
+
Measure the moving distance of the crankshaft with the dial
gauge when the crankshaft is moved fully forward or back-
ward.
Standard: 0.10 - 0.25 mm (0.0039 - 0.0098 in)
Limit: 0.30 mm (0.0118 in)
+
If the value exceeds the limit, replace thrust bearings with new
ones and measure again. If the measurement exceeds the limit
again, replace crankshaft with a new one.
JEM203G
CONNECTING ROD SIDE CLEARANCE
NLEM0073S14
+
Measure the side clearance between connecting rod and crank
arm with feeler gauge.
Standard: 0.200 - 0.350 mm (0.0079 - 0.0138 in)
Limit: 0.4 mm (0.0157 in)
+
If the value exceeds the limit, replace connecting rod and mea-
sure again. If the measurement exceeds the limit again,
replace the crankshaft.
CYLINDER BLOCK
YD
Disassembly (Cont’d)
EM-225