Mitsubishi Eclipse. Technical Information Manual (1994) - part 67
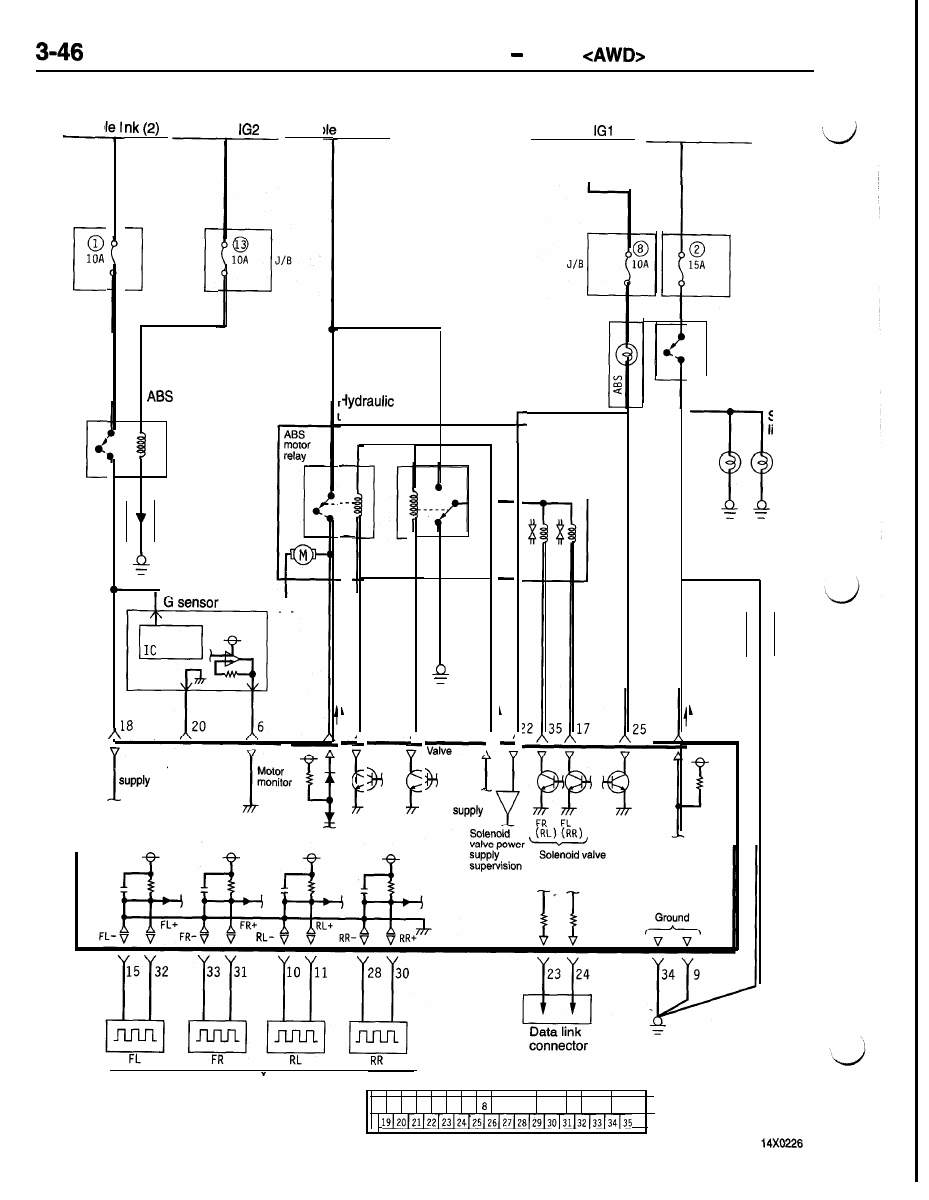
DRIVE-CONTROL COMPONENTS ABS
ABS ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
Ignition
switch
Ignition
F u s i b l e l i n k ( 2 )
switch ,
Fusib i
Fusit
link (9)
Dedicated
fuse
Dedicated
fuse
Combination
meter
Stop light
switch
power
relay
Diode
rnit (HU)
5
7
ABS
valve
relay
2 6
7
Motor
relay
relay
Motor
7
power
stop
light
I
1
Solenoid
valve
ABS-ECU
r
ECU power
2
4
Resistor
29
Wheel speed sensor
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
ABS-ECU Connector Pin Configuration