Mitsubishi 380. Manual - part 292
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM
35A-2
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
M1351000100440
The brake system has been designed to give greater
reliability and durability and to provide excellent brak-
ing performance.
FEATURES
.
Improved braking performance
1. An 8+9 inch tandem brake booster provides suffi-
cient braking force in sudden braking range.
2. 296mm front ventilated disc brakes provide sta-
ble braking force and improved braking feel.
3. 303mm rear ventillated disc brakes are used.
.
Improved stability
1. A 4-wheel anti-lock braking system (4ABS) pre-
vents slipping caused by the vehicle wheels lock-
ing up, in order to maintain a stable vehicle
posture and steering performance.
2. An electronic brake-force distribution (EBD)
makes it possible to maintain the maximum
amount of braking force even when the vehicle's
load is unevenly distributed.
3. Front- and rear-wheel X-type brake line layout
are used.
4. Ventilated discs brakes improve anti-fading per-
formance.
.
Improved serviceability
1. A diagnosis function for the ABS system makes
inspection easier.
2. An outer disc separated hub and rotor make
removal and installation easier.
3. The master cylinder reservoir is utilised for both
brake and clutch fluid on manual transmission
vehicles.
4. The master cylinder filter is coloured black for
improved viewing.
5. The ABS-ECU and hydraulic unit are integrated
to make them more compact and light weight.
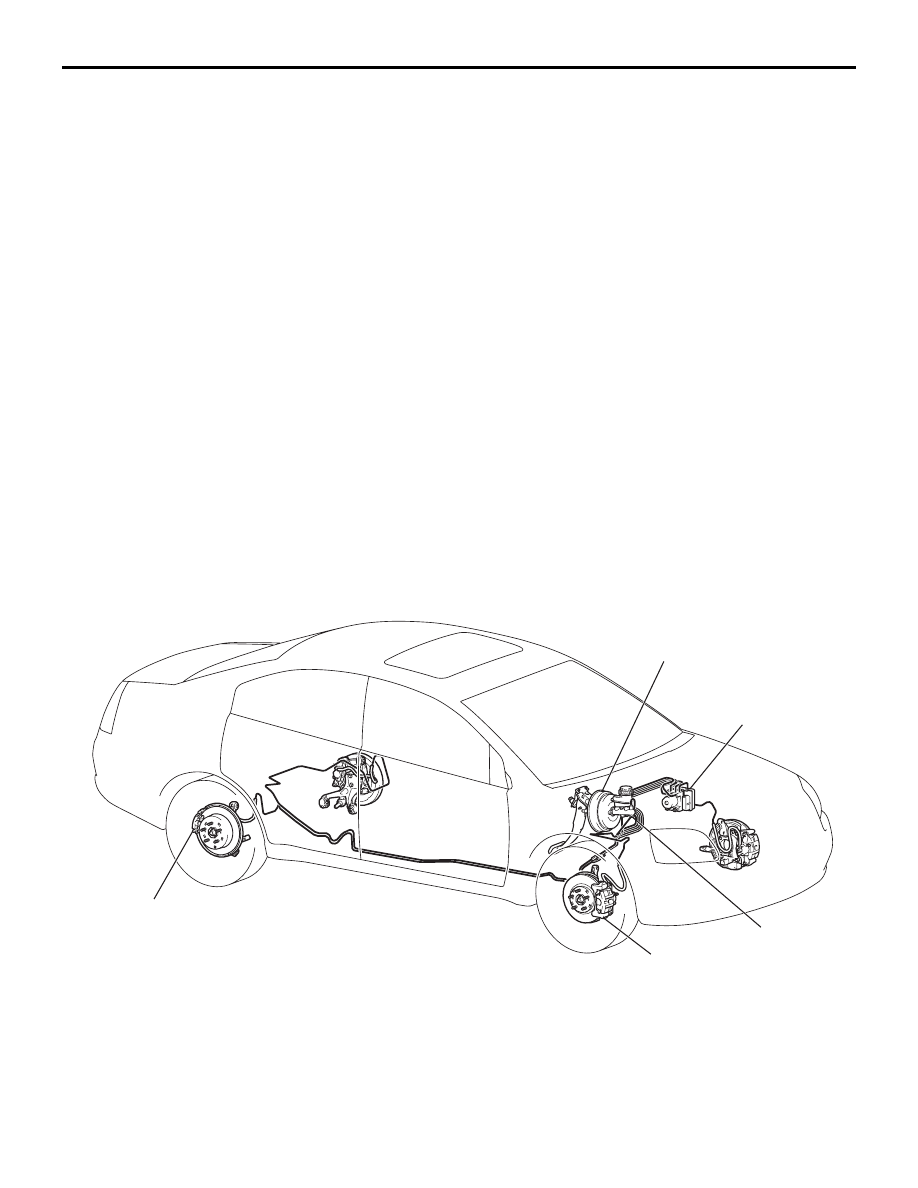
CONSTRUCTION DIAGRAM
BRAKE BOOSTER
HYDRAULIC UNIT
(INTEGRATED WITH
THE ABS-ECU)
MASTER CYLINDER
FRONT DISC BRAKE
REAR DISC BRAKE
<VEHICLE WITH ABS>