Mazda Training manual - part 104
Dynamic Driving Safety Systems
EBA
Overview
•
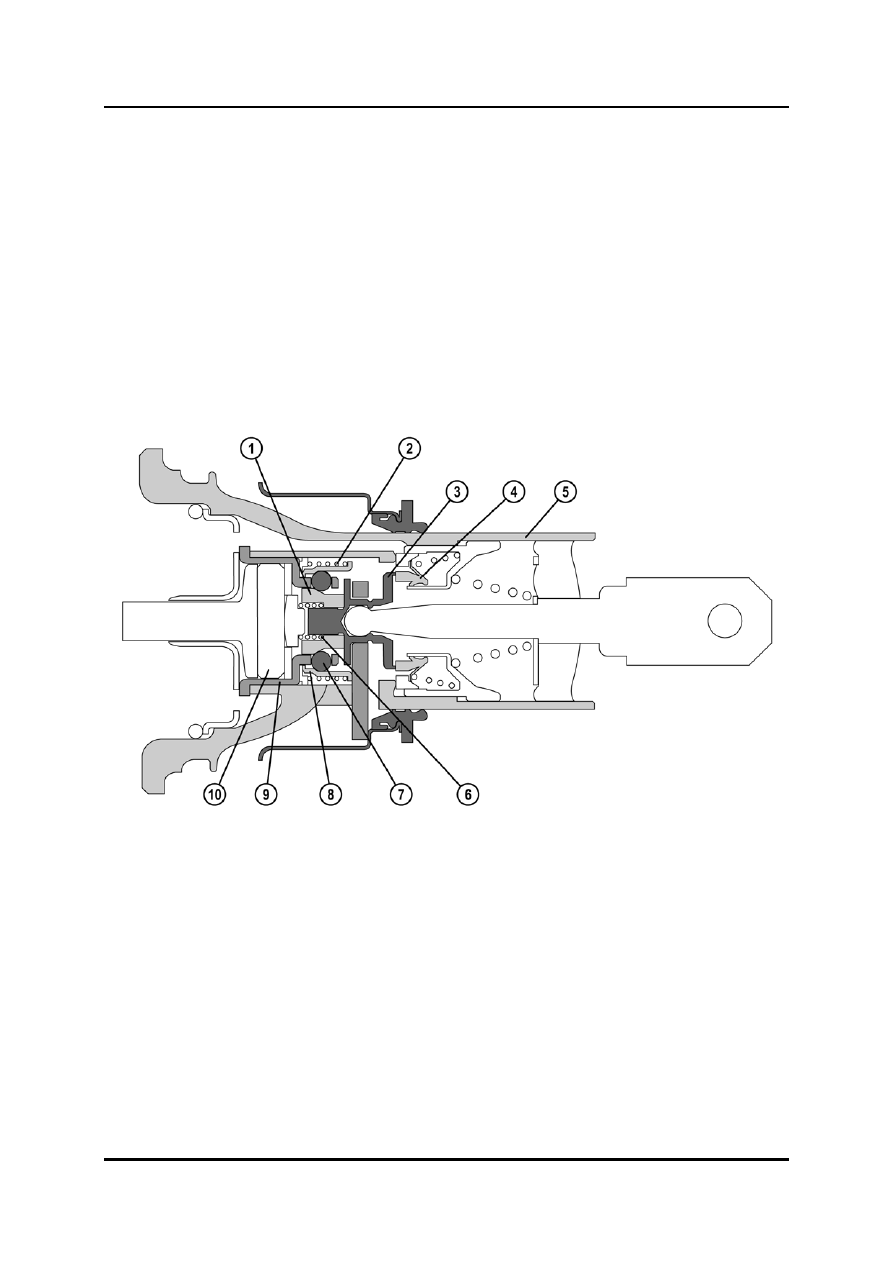
The basic construction of the brake booster with EBA is similar to a conventional type,
except that the following parts have been added:
–
Balls
–
Ball cage
–
Ball sleeve
–
Lock sleeve
–
Spring
–
Centre spring
L2003_02043
1
Ball sleeve
6
Centre spring
2 Spring
7 Ball
3
Valve piston
8
Lock sleeve
4
Disc valve
9
Ball cage
5
Control housing
10
Rubber element
Curriculum Training
02-75